Project Management Glossary - Key Terms & Definitions
advertisement

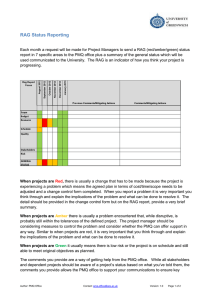
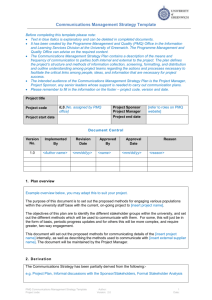
Project Management Glossary Acceptance Criteria A prioritised list of criteria that the final product(s) must meet before the end user will accept them (a measurable definition of what must be done for the final product). Agile methods Principally software development methods that apply the project approach of using short time-boxed iterations where products are incrementally developed. Baseline Reference levels against which an entity is monitored and controlled Benefit The measurable improvement resulting from an outcome perceived as an advantage by one or more stakeholders. Business Analyst (BA) Someone who analyses the existing or ideal organization and design of systems, including businesses, departments, and organisations. Business Case The justification for an organisational activity (project), which typically contains costs, benefits, risks and timescales, and against which viability is tested. Business Process Mapping Refers to the activities involved in defining exactly what a business entity does, who is responsible, to what standard a process should be completed and how the success of a business process can be determined. A business process illustration is produced. Change control The procedure that ensures that all changes that may affect the project’s agreed objectives are identified, assessed and either approved, rejected or deferred. PMQ has a Change Control form which Project Managers can use to issue a change request to the IT Project Board Closure Report Project Manager’s report to the Project Board that confirms the delivery of outputs to the customer and assesses the project against the business case. It also includes reviews on overall project performance and lessons learnt. A template is available from the PMQ Office. Communication Management Strategy A description of the flow of information between the project and its stakeholders. The Communication Management Strategy provides an organised approach to deliver reports on a timely basis to those who need the information for decision making and/or other purposes. A template is available from the PMQ Office. Constraints The restrictions or limitations that the project is bound by. Deliverable An item that the project has to create as part of the requirements. It may be part of the final outcome or an intermediate element on which one or more subsequent deliverables are dependent. Deliverables should be listed in the Project Plan. According to the type of project, another name for a deliverable is ‘product’. Author: PMO Office Contact: pmo-office@greenwich.ac.uk Version: 2.0 Page 1 of 5 Dependency The relationship between products, activities or projects. For example, the development of deliverable C cannot start until deliverable A and B have been completed. Dis-benefit An outcome that is perceived as negative by one or more stakeholders. It is an actual consequence of an activity whereas, by definition, a risk has some uncertainty about whether it will materialise. Governance Effective governance of project management ensures that an organisation’s project portfolio is aligned to the organisation’s objectives, delivered efficiently and is sustainable. Gantt chart A type of bar chart that illustrates a project schedule. It illustrates the start and finish dates of the terminal elements and summary elements of a project. Terminal elements and summary elements comprise the work breakdown structure of the project. The PMQ Office can advise on format/content. Highlight Report A report on the project progress, prepared regularly by the Project Manager for the Project Board. UoG uses a monthly RAG Status Reporting process which ensures that Project Managers are updating the IT Project Board on a regular basis (coordinated by the PMQ Office). Issue A relevant event that has happened, was not planned, and requires management action. It can be any concern, query, request for change, suggestion or off-specification raised during a project. Issue Register A register used to capture and maintain information on all of the issues that are being managed formally. The Issue Register should be monitored by the Project Manager on a regular basis. A template is available from the PMQ Office. Lessons Log An informal collection of good and bad lessons learned about the management and specialist processes and products as the project progresses. At the end of the project, it is formalised and incorporated into a Project Closure Report. The PMQ Office can advise on format/content. Portfolio All the programmes and stand-alone projects being undertaken by the organisation, a group of organisations, or an organisational unit. PRINCE2 PRINCE2 is a project management methodology. The acronym stands for Projects in a Controlled Environment. The PMQ Office at UoG uses elements of the PRINCE2 methodology alongside other established project management processes and tools. Product An input or output, whether tangible or intangible, that can be described in advance, created and tested. A PRINCE2 project creates two kinds of products - Specialist products and Management products. The creation of the specialist products is the reason that the project was started and these are the products that will be given to the users. Management products are documents used solely for the purpose of communication among the project management team and managing the project e.g. Project Plan and Business Case, so the Users are only interested in the Specialist products. Product Description A description of a product’s purpose, composition, derivation and quality criteria. It is produced at planning time, as soon as possible after the need for the product is identified. Author: PMO Office Contact: pmo-office@greenwich.ac.uk Version: 2.0 Page 2 of 5 Programme A temporary flexible organisation structure created to coordinate, direct and oversee the implementation of a set of related projects and activities in order to deliver outcomes and benefits related to the organisation’s strategic objectives. Programme Management and Quality Office (PMQ Office) Established at the UoG in early 2012, to establish standards and templates and provide project support through mentoring and resources, and by delivering strategic, complex projects. Meet the team here. Project A temporary organisation that is created for the purpose of delivering one or more business products according to an agreed business case. Project Assurance The Project Board’s responsibilities to assure itself that the project is being conducted correctly. The Project Board members each have a specific area of focus for Project Assurance, namely user assurance for the Senior User, and supplier assurance for the Senior Supplier. Project Brief (completed for large scale projects at UoG) Statement that describes the purpose, time, cost and performance requirements, and constraints for a project. It is created pre-project during the Starting up a Project process and is used during the Initiating the Project phase. The PMQ Office can advise on format/content. Project lifecycle This term is used to define the period from the start-up of a project to the handover of the finished product to those who will operate and maintain it. Project management The planning, delegating, monitoring and control of all aspects of the project, and the motivation of those involved, to achieve the project objectives within the expected performance targets for time, cost, quality, scope, benefits and risks. Project Management Team The total management structure of the project from top to bottom, from the Project Board to the Project Manager, Team Managers and Project Support roles. Project Manager The person given the authority and responsibility to manage the project on a day-to-day basis to deliver the required products within the constraints agreed with the Sponsor and Project Board. A detailed role description can be found here. Project Mandate Information generated by the authority commissioning the project that forms the trigger for Starting up a Project. Project Plan A formal document used by the Project Manager to guide both project execution and project control. The primary uses of the project plan are to document planning assumptions and decisions, facilitate communication among stakeholders, and document approved scope, cost, and schedule baselines. A project plan may be summary or detailed. A template is available from the PMQ Office. Quality The totality of features and inherent or assigned characteristics of a product, person, process, service and/or system that bears on its ability to show that it meets expectations or satisfies stated needs, requirements or specifications. Quality Management Strategy A plan of action that defines the quality requirements and control methods for all the products in the project. Author: PMO Office Contact: pmo-office@greenwich.ac.uk Version: 2.0 Page 3 of 5 Resources People, equipment, facilities, funding, or anything else required for the completion of a project activity. Risk An event that, if it occurs, may have a positive or negative effect on the project’s objectives. Project Managers have the task of identifying risks that apply and taking appropriate steps (e.g. avoid, reduce or react to threats). Risk Register A record of identified risks relating to an initiative, including their status and history. A template is available from the PMQ Office. Schedule A graphical representation of a plan (for example, a Gantt chart), typically describing a sequence of tasks, together with resource allocations, which collectively deliver the plan. Scope The sum total of all of the project’s products and the extent of their requirements. Scope creep Uncontrolled changes in a project's scope. This phenomenon can occur when the scope of a project is not properly defined, documented, or controlled. It is generally considered a negative occurrence that is to be avoided. Senior Supplier The Project Board role that provides knowledge and experience of the main discipline(s) involved in the production of the project’s deliverable(s). The Senior Supplier represents the interests of those who are going to deliver the desired products. Senior User The Project Board role accountable for ensuring that the user needs are specified correctly and that the solution meets those needs. Sponsor The person ultimately responsible for the project. The Sponsor's role is to ensure that the project is focused throughout its life cycle on achieving its objectives and delivering a product that will achieve the forecasted benefits. A detailed role description can be found here. Stakeholder Any individual, group or organisation that can affect, by affected by, or perceive itself to be affected by, an initiative (programme, project, activity, risk). Team Manager The person responsible for the production of those products allocated by the Project Manager (as defined in a Work Package) to an appropriate quality, timescale and at a cost acceptable to the Project Board. A detailed role description can be found here. Timeline A graphical representation of a chronological sequence of events chronology. It can also mean a schedule of activities, such as a timetable. Tolerance The permissible deviation above and below a plan’s target for time and cost without escalating the deviation to the next level of management. There may also be tolerance levels for quality, scope, benefit and risk. An information sheet on Project Tolerance can be found here. Author: PMO Office Contact: pmo-office@greenwich.ac.uk Version: 2.0 Page 4 of 5 Work Package The set of information relevant to the creation of one or more products. It will contain a description of the work, the Product Description(s), details of any constraints on production, and confirmation of the agreement between the Project Manager and the person or Team Manager who is to implement the work Package that the work can be done within the constraints. A template is available from the PMQ Office. Author: PMO Office Contact: pmo-office@greenwich.ac.uk Version: 2.0 Page 5 of 5