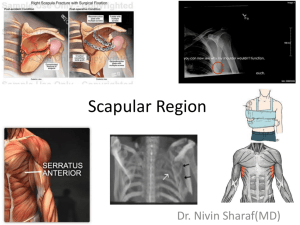
Glenohumeral Joint
advertisement

Glenohumeral Joint Jessica Vila & Carrie A. Hoch Ligaments Anterior view http://www.mlcmarlins.com.au/content/training/coaching_clinic/shoulders/shoulders.htm Bursae subacromial bursa subdeltoid bursa subcoracoid bursa subscapular bursa http://www.aidmybursa.com/shoulder-bursitis.php Cartilage and Articular Capsule glenoid labruim synovial membrane articular cartilage glenoid labruim synovial membrane fibrous layer Anterior/sliced view http://home.comcast.net/~pegglestoncbsd/skeletal.htm Humerus anatomical neck greater tubercle lesser tubercle head anatomical neck surgical neck intertubercular sulcus surgical neck deltoid tuberosity http://www.medicalook.com/human_anatomy/organs/Brachium.html Scapula ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ superior angle ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ subscapular fossa ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ Anterior view ✗ inferior angle Posterior view http://thesebonesofmine.wordpress.com/category/scapula/ Clavicle ⏎ ⏎ http://legacy.owensboro.kctcs.edu/gcaplan/anat/Notes/API%20Notes%20H%20Skeletal%20Arm.htm Rotator Cuff Muscles supraspinatus Rotator cuff teres minor subscapularis infraspinatus http://www.rci.rutgers.edu/~uzwiak/AnatPhys/Blood_Vessels.html Clinical Issues Common rotator cuff injuries: • Tendinitis = tendons are inflamed due to overuse or overload • Bursitis = bursa become irritated or inflamed • Strain or tear = can result from tendinitis or stress http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/rotator-cuff-injury/DS00192 Rotator Cuff Cont. Common causes: • Normal wear & tear - leads to breakdown of collagen in tendons and muscles • Poor posture - muscle or tendons can become pinched under clavicle • Falling - breaking fall w/ arm or falling onto arm can bruise or tear tendon or muscles Common Causes Cont. • Lifting or pulling – can strain or tear tendons or muscles • Repetitive stress – repetitive overhead movement can result in inflammation and tearing in tendons or muscles Risk Factors • Age - most common in people > 40 • Athletes - pitchers, tennis players • Construction trades – painters, carpenters • Weak shoulder muscles Surface Anatomy Essential Clinical Anatomy p. 428 acromial part of deltoid spinal part of deltoid triangle of auscultation middle part of trapezius ascending part of trapezius descending part of trapezius clavipectoral triangle clavicular part of deltoid clavicle clavicular head of pectoralis major manubrium sternocostal head pectoralis major posterior axillary fold anterior axillary fold Accessory Nerve XI, Cervical & Brachial Plexus Cervical plexus C1-C4 ⏎ ⏎ http://www.netteranatomy.com/ImageLibrary/ Nerves ✪ ✪ ✪ ✪ ✪ Brachial Plexus C5-T1 ✪ ✪ ✪ ✪ ✪ ✪ http://www.nerveblocks.net/tutorium/?lang=en_EN&main=1&sub=1&section=content Brachial Plexus ✪ ✪ http://www.netteranatomy.com/ImageLibrary/ Arteries ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ circumflex scapular a. ✓ Deep Scapular artery???? http://www6.ufrgs.br/favet/imunovet/molecular_immunology/circulation.html Veins http://www.rci.rutgers.edu/~uzwiak/AnatPhys/Blood_Vessels.html Anterior Deltoid Origin: Lateral third of clavicle Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity Action: Shoulder flexion, Medial Rotation, Horizontal ADDuction Innervation: Axillary Nerve Vascular supply: Posterior Circumflex artery Middle Deltoid Origin: Acromion process Insertion: Deltoid Tuberosity Action: Shoulder ABDuction Innervation: Axillary nerve Vascular supply: Posterior circumflex artery Posterior Deltoid Origin: Spine of Scapula Insertion: Deltoid Tuberosity Action: Shoulder extension, hyperextension, lateral rotation and horizontal ABDuction Innervation: Axillary Nerve Vascular Supply: Posterior Circumflex artery Pectoralis Major (clavicular and sternal portions) Origin: Medial third of clavicle, sternum, costal cartilages of the first six ribs Insertion: Lateral lip of bicipital groove of humerus Action: Shoulder ADDuction, medial rotation and horizontal ADDuction Innervation: Lateral and medial pectoral nerve Vascular Supply: Lateral thoracic artery 1.)Teres Minor Origin: Axillary border of scapula Insertion: Greater tubercle of Humerus Action: Shoulder Lateral rotation horizontal and horizontal ABDuction Innervation: Axillary nerve Vascular supply: Circumflex scapular artery 2.) Teres Major Origin: Axillary border of scapula (near the inferior angle) 1 Insertion: Crest below lesser tubercle next to the latissimus dorsi muscle attachment Action: Shoulder extension, ADDuction and medial rotation Innervation: Subscapular nerve Vascular supply: Circumflex scapular artery 2 Latissimus Dorsi Origin: Lower three ribs, Spinous processes of T7 through L5( via dorsolumbar fascia), posterior surface of sacrum and iliac crest. Insertion: Medial lip of bicipital groove of humerus Action: Shoulder extension, ADDuction, medial rotation and hyperextension Innervation: Thorocodorsal nerve Vascular supply: DEEP scapular nerve 1.) Subscapularis Origin: Subscapular fossa of the scapula 2 Insertion: Lesser tubercle of the humerus Action: Shoulder medial rotation Innervation: Subscapular nerve 1 3 Vascular supply: Subscapular artery http://thewinger.com/2009/subscapularis 2.)Supraspinatus Origin: Supraspinous fossa of the scapula 2 Action: Shoulder ABDuction 1 3.)Infraspinatus Origin: Infraspinous fossa of scapula Action: Shoulder Lateral rotation horizontal and ABDduction The Supraspinatus and Infraspinaus have the same: Insertion : Greater tubercle of the Humerus Innervation : Suprascapular nerve Vascular Subscapular artery 3 Trapezius Upper Trapezius Origin: Occipital bone, nuchal ligament Insertion: Outer third of clavicle, acromion process 1 Action: Scapular elevation and upward rotation Middle Trapezius 2 Origin: Spinous process of C7 through T3 Insertion: Scapular Spine Action: Scapular depression Lower Trapezius Origin: Spinous processes of middle and lower thoracic vertebrae Insertion: Base of scapular spine Action: Scapular depression and upward rotation Innervation of all Three: Spinal accessory (cranial nerve XI) Vascular supply of all Three: Transverse cervical artery 3 Levator Scapulae Origin: Transverse process of first four cervical vertbrae Insertion: Vertebral border of scapula between the superior angle and spine Action: Scapular elevation and downward rotation Innervation: Third and fourth cervical nerve Vascular supply: Dorsal scapular artery Pectoralis minor Origin: Anterior Surface, third through fifth ribs Insertion: Coracoid process of the scapula Action: With ribs fixed: draws the scapula forward(ABDucts) and rotates scapula downward against the thoracic wall With scapula fixed: elevated the rib cage Innervation: Medial pectoral nerve Vascular supply: Axillary artery Serratus Anterior Origin: Lateral surface of the upper eight ribs Insertion: The anterior surface of vertebral border of the scapula Action: Scapular protraction and upward rotation Innervation: Long thoracic nerve Vascular supply: Lateral thoracic artery The RHOMBOIDES!!! 1.) Rhomboideus minor Origin: Spinous processes of C7 through T1 Insertion: Vertebral border of scapula at the spine process 1 2.) Rhomboideus MAJOR: Origin: Spinous processes of T2 through T5 Insertion: Vertebral border of scapula between the spine and inferior angle The Rhomboideus major and the Rhomboideus major have the same: Action: Scapular retraction and downward rotation Innervation: Dorsal scapular nerve Vascular supply: Dorsal scapular artery 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: Coracoid process Insertion: Medial aspect of humerus Action: Weakly ADDucts shoulder joint Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerves, C6 and C7 Vascular Supply: Brachial Artery Study Reference http://www.rocmd.com/conditions-treated/shoulder Study Reference http://www.netteranatomy.com/ImageLibrary / ! Who is this handsome man?