Product Life Cycle PowerPoint - Engineering Technology Pathways
advertisement

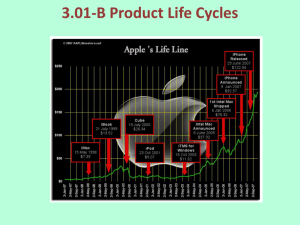
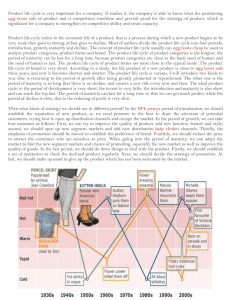
Engineering for Design Product Life Cycle 2006 Greg Heitkamp This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 0402616.) Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the view of the National Science Foundation (NSF). 4 Stages of a Product Life Cycle Product life cycles are based on the biological life cycle an example: • Introduction Seed is planted • Growth It sprouts • Maturity Plant puts down roots and grow leaves • Decline After period as an adult plant it dies Graphic Representation of a Product Life Cycle • http://www.marketingteacher.com /Lessons/lesson_plc.htm Introduction Companies seek to develop product awareness and a market for the product through: • Product Branding and Quality Level – intellectual property protection, patents, and trademarks • Pricing – is very competitive to establish a market product • Distribution – Selective until a demand or want is established for product • Promotion – aimed ant innovators and early adopters. Marketing is aimed to educate consumers and build product awareness. http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/product/l ifecycle/ Growth Stage In the Growth Stage Companies try to build brand preference and build market share for their product. • Product quality is maintained • Pricing is maintained as the demand increases with little competition. Profits rise • Distribution channels are added to increase product delivery to market. • Promotion is directed at a wider buying market. http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/pr oduct/lifecycle/ Maturity Stage In the maturity stage sales growth for the product begins to slow. Competitive products begin to appear. Primary objective is to defend market share. • Product features are added to keep the product different from the competition • Pricing is lower because of new competition. Demand starts to ease toward end of this stage. • Distribution is intense and has incentives are offered to maintain market share. • Promotion stresses difference from other products http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/product/ lifecycle/ Decline Stage A the sales of the product continue to decline the company has three options • Maintain the product by adding features to attempt to revive sales. • Harvest the product –reduce the cost and try to maintain product for a niche market of loyal customers. • Discontinue the product, liquidating remaining inventory, or sell to another company that may maintain or continue the product. http://www.quickmba.com/marketing/ product/lifecycle/ Examples of Different Stages of the Product life Cycle Introduction Growth Maturity Decline Third generation Mobile Phones Portable DVD Players Personal Computers Typewriters E-Conferencing E-Mail Faxes Hand Written Letters All-in-one Racing Skin Suits Breathable Synthetic Fabrics Cotton T Shirts Shell Suits Iris-Based Personal Identity Cards Smart Cards Credit Cards Check Books http://www.tutor2u.net/business/marketing/products_lifecycle.asp Standards Addressed • Standard 1: Students will develop an understanding of the characteristics and scope of technology L: Inventions and innovations are the results of specific goal-directed research. Most developments of technologies these days is driven by the profit motive and the market. Standards Addressed Continued • Standard 4: Students will develop an understanding of the cultural, social, economic, and political effects of technology. I: Making decisions about the use of technology involves the weighing the trade-offs between positive and negative effects. J: Ethical considerations are important in the development , selection and use of technologies. Standards Addressed Continued • Standard 6: Students will develop an understanding of the role of society in the development and use of technology. I: The decision to develop a technology is influenced by societal opinions and demands, in addition to corporate cultures. J: a number of different factors such as advertising, the strength of the economy, the goals of the company, and the latest fads contribute to the shaping of the design of and demand for various technologies. Standards Addressed Continued • Standard 13: Students will develop the abilities to assess the impact of products and systems. J: Collect information and evaluate data. K: Synthesize data, analyze trends, and draw conclusions regarding the effect of technology on the individual, society and the environment.