Computer Hardware and Software
advertisement

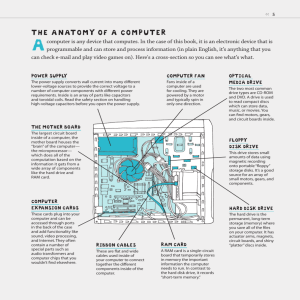
By Mr. Abdalla A. Shaame 1 What is Computer An electronic device that stores, retrieves, and processes data, and can be programmed with instructions. A computer is composed of hardware and software, and can exist in a variety of sizes and configurations. 2 Computer System Computer system consist of four basic hardware components: input, process, output and storage. The term hardware refers to the physical components of your computer such as the sys tem unit, mouse, keyboard, monitor etc. The software is the instructions that makes the computer work. Software is held either in the computers hard disk, CD-ROM, DVD or on a diskette (floppy disk) and is loaded (i.e. copied) from the disk into the computers RAM (Random Access Memory), as and when required. 3 Types of Computers Mini and Mainframe Computers Very powerful, used by large organisations such an banks to control the entire business operation. Very expensive! Personal Computers Cheap and easy to use. Often used as stand-alone computers or in a network. May be connected to large mainframe computers within big companies. Personal computers come in a variety of forms such as desktops, laptops and personal digital assistants (PDA) 4 Hardware Components Input Devices -- "How to tell it what to do“ - A keyboard and mouse are the standard way to interact with the computer. Other devices include joysticks and game pads used primarily for games. Output Devices -- "How it shows you what it is doing" - The monitor (the screen) is how the computer sends information back to you. A printer, speaker are example of output devices. 5 Hardware Components Storage Devices -- "How it saves data and programs“ - Hard disk drives are an internal, higher capacity drive which also stores the operating system which runs when you power on the computer. - "Floppy" disk drives allow you to save work on small disks and take the data with you. Flush disk used as an alternative to floppy disk which is used to store data. It vary in size up to 8GB 6 Identify the following hardware devices 7 Characteristics of Hardware components Speed Capacity Cost 8 Main parts of Computer Memory -- "How the processor stores and uses immediate data“ RAM - Random Access Memory The main 'working' memory used by the computer. When the operating system loads from disk when you first switch on the computer, it is copied into RAM. computer will operate faster if you install more RAM. Data and programs stored in RAM are volatile (i.e. the information is lost when you switch off the computer). 9 Memory ROM – Read Only Memory Read Only Memory (ROM) as the name suggests is a special type of memory chip that holds software that can be read but not written to. A good example is the ROM-BIOS chip, which contains read only software. Often network cards and video cards also contain ROM chips. 10 How Computer Memory Is Measured Bit All computers work on a binary numbering system, i.e. they process data in one's or zero's. This 1 or 0 level of storage is called a bit. Byte A byte consists of eight bits. Kilobyte A kilobyte (KB) consists of 1024 bytes. Megabyte A megabyte (MB) consists of 1024 kilobytes. Gigabyte A gigabyte (GB) consists of 1024 megabytes. 11 Microprocessors "The brain of the computer“ - PCs primarily use microprocessors (sometimes called the chip). The older Intel versions include the 386, 486 and now the Pentium line. The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is normally an Intel Pentium (or equivalent) and it is one of the most important components within your computer. It determines how fast your computer will run and is measured by its MHz speed. Thus a 600 MHz Pentium is much faster than say a 400 MHz Pentium CPU. It is the CPU that performs all the calculations within the computer. 12 Factors that impact the performance of Computer CPU speed RAM size Hard disk speed and capacity 13 Software Components Software refers to any program that tells the computer system what to do. Software are divided into: System Software Application Software System Software: Are those software for system uses. Eg Operating system, and utilities. 14 Operating System Is a software which control all other parts of computer. The operating system is a special type of program that loads automatically when you start your computer. Objectives of Operating system To facilitates communication between the computer system and its users. To facilitates communications among computer system components To facilitates communication between linked computer system. To maximize throughput To optimize the use of computer system resources To keep track of all files in disk storage To provide an envelop of security for the computer system To monitor all system capabilities and alert the user of system failure or potential problems 15 Relationship between the Operating System and Applications Software The operating system coordinates all software activity within a computer system. The interaction of user to Operating system is through the Graphical User Interface (GUI) 16 PC Platforms The most common types of operating system are: Microsoft windows Mac OS UNIX/Linux 17 Window Platforms Early versions of Windows Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows ME are old versions of Windows but still can be used in the home and in business. These old versions of Windows are emerged from MSDOS, a text based operating system. Windows NT was the first operating system to divorce itself from the limitations of MS-DOS Windows 2000 was the successor to Windows NT. 18 Windows Platform Modern PC Operating system Window XP and its successor (ie Windows Vista and Windows 7) is a foundation for Windows family of client operating systems. These Operating System works with Windows 2003 Server, the server side portion of the operating system (which runs on the server computer) to make client/server computing possible. Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows 7 comes in several versions for home, office and taplet PCs. Popular features of modern OS are plug-and-play and home networking 19 Windows Platform Windows CE. NET The Windows CE. NET operating system designed for hand-held, pocket PCs, and other small-footprint devices Windows CE. NET users can share information with other Window based PCs and they can connect to the internet. 20 The Macintosh/Mac OS X Platform The Apple family of microcomputers (including the Power Mac G4, iMac, eMac Desktop and iBook notebook) and its operating system, Mac OS X The Apple line of microcomputers is based on the Motorola family of microprocessors. 21 UNIX/ Linux Created in the 1970s, Unix was the one operating system with the flexibility to be used on almost any computer. UNIX is a multiuser operating system, become very popular in Universities and mostly used for powerful workstation. However the UNIX movement has been slow until recently. Linux is a free and open source software where its source code available free, free to use, to copy and distribute to others. Currently, the Linux is become competitors to Windows system for client and server. 22 UTILITY PROGRAMS A wide variety of system software utility is available to help you with the day-to-day tasks associated with personal computing. It include disk and file maintenance, system recovery, security, backup, virus protection, and so on. The purpose of utility is to keep the system running at peak performance. 23 Application Software Application software are those software designed for users. An application program is the type of program that you use once the operating system has been loaded. Application software divided into: General purpose software: Those software for general uses. Eg, Ms word, Ms Excel, Ms Power point, etc Special purpose software: Those software for special uses. Such as QuickBooks for accounting, Banking software, etc 24 Discussion Why is the selection of a platform such an important decision to an organization. Discus consequence of not performing routine disk maintenance with utility software. 25 Next Lesson Computer impact and applications 26