Empire and Expansion
advertisement
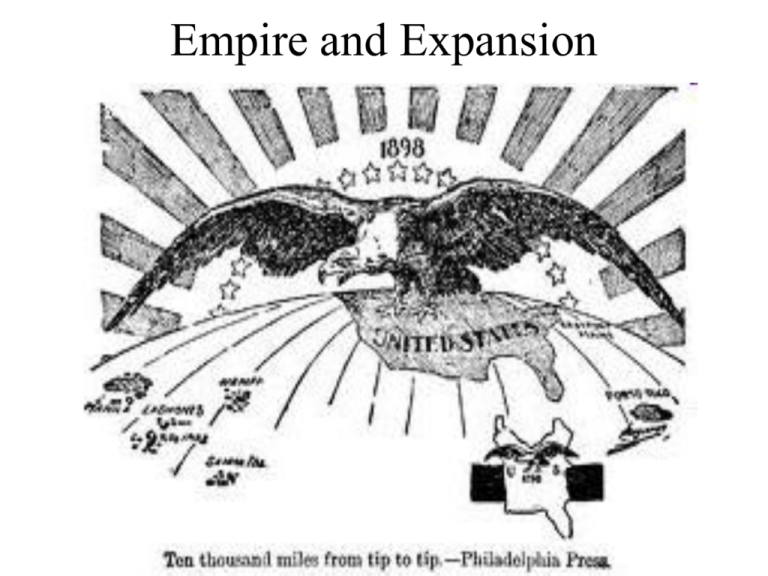
Empire and Expansion America Turns Outward • Between end of Civil War and 1890 US very isolationist. • In the late 19th Century the US became more outward looking. Reasons? – American’s felt a new sense of power – Many people thought the US needed colonies to compete with Europe. – Hearst and Pulitzer “yellow Press” whetted appetites for foreign adventure. – Missionaries saw new opportunities overseas – Overseas seen as the new “frontier.” – Some felt we needed our “share” of Asia and Africa as colonies. – Darwin and Manifest Destiny. America Turns Outward • Alfred Thayer Mahan. – The Influence of Sea Power upon History • Caused all countries to start focusing on their naval resources, including the US. • Led to US to desire naval bases around the world and an isthmian canal America Turns Outward • America’s near wars – 1889 Germany (Samoan Islands) – 1891-Italy – 1892- Chile – 1893 Canada America Turns Outward • Boundary dispute between Venezuela and British Guiana. • Cleveland urged arbitration and invokes the Monroe Doctrine. – First real attempt by US to enforce the doctrine. • South Americans are pleased with US help. • Monroe Doctrine is upheld and takes on new validity • Great Rapprochement- the beginning of friendly relationship between the US and Britain Spurning the Hawaiian Pear • In the 1820s New England missionaries had come to Hawaii • Descendents become the economic leaders. • Important trade crossroads Spurning the Hawaiian Pear • US considers it owns Hawaii, 1840’s warns others to stay away • Contact with whites = declining Native Hawaii population • McKinley Tariff- raised barriers against Hawaiian sugar • White economic leaders now urge annexation Spurning the Hawaiian Pear • Queen Liliuokalani rejects this • 1893- whites revolt against her (with help of US forces) • Grover Cleveland takes office before treaty is signed, study shows Hawaiians wanted self rule Cubans Rise in Revolt • McKinley Tariff cripples economy • Cubans begin rebelling against the Spanish, scorched earth policy worries American interest in area • US 50 mill invested, 100 million in trade Cubans Rise in Revolt • Valeriano “the butcher” Weyler- starts putting Cuban rebels in concentration camps • Yellow Journalism – Hearst- American women getting searched at customs – Published De-Lome letter Cubans Rise in Revolt • US sends SS Maine battleship for friendly visit to Cuba • 1898 Maine explodes – Spanish say internal combustion – US- Spanish mine blew it up • Yellow Journalism hypes war rhetoric- “Remember the Maine, to Hell with Spain! Cubans Rise in Revolt • Spain promises to stop camps, and peace with rebels- but US is in war fever • McKinley doesn’t want war – War vet – Could make affect economy • April 1898- Declares war on Spain • Teller Amendment- when US overthrows Spanish rule, it will give Cubans their freedom Dewey’s May Day Victory at Manila • Teddy Roosevelt (Ass’t Sec. of Navy). • Cabled Commodore George Dewey to attack Spain’s navy in the Philippines in the event of war. • May 1, 1898 Dewey attacks. – Sinks 10 Spanish ships without a single US casualty. – Dewey is a huge hero and immediately promoted to admiral Dewey’s May Day Victory at Manila • Dewey must wait for reinforcements before invading land • Manila captured in August 1898- helped by Emilio Aguinaldo • War in Philippines brings attention to Hawaii • July 1898- US annexes Hawaii Confused Invasion of Cuba • Spain sends old worn down Navy to Cuba, US’s stronger military blockades them • US troops invade Cuba- ill prepared for tropical war • More US troops died of disease (5000) than of battle-inflicted injuries (400). Confused Invasion of Cuba • Rough Riders; Teddy Roosevelt. • Made up of western cowboys, miners and friends from Harvard. • Short on discipline but long on dash and daring. • Colonel Leonard Wood. Confused Invasion of Cuba • Mid-June US forces land near Santiago. Little opposition. • Key battles El Caney and San Juan Hill. • Rough riders charge up San Juan Hill. Treaty Of Paris 1898 • War only last 4 months • Cuba freed from Spanish (US does not claim sovereignty as pledged at the beginning of the war). – America reserves the right to intervene if country goes off track. Also gets naval bases. • US gets Guam, seized at the start of the war (Pacific Island) • US gets Puerto Rico, the last remnant of Spain’s New World Empire. • US purchases Philippines for 20 Mill. The Philippines Question • Problems – Philippines is large island – Diverse population – Can’t give them back to Spain – If we don’t annex them, Germany or Japan can get them • Reasons to go – Missionary movements – Philippines social welfare Anti-Imperialists • Anti-Imperialist League. – Twain, Carnegie, Gompers. • Arguments: – Filipinos wanted freedom and to annex them would be contrary to spirit of Dec. of Indep. – Despotism abroad would breed it at home – Annexation would suck US into politics of the far east Imperialist Arguments • Patriotism. We fought and died for it, giving it back would dishonor US soldiers. • Trade profits in Far East and use of natural resources of the Islands. • Filipinos not yet able to govern themselves. – US would help out its little brown brothers and teach them how to be an independent democratic state until ready to govern themselves. Perplexities in Puerto Rico • Foraker Act – PR gets limited degree of popular government (and no cockfighting) • Insular Cases- PR and Philo, while they are subject to American rule, they do not get American Rights (aka no protection by the Constitution Perplexities in Cuba • US Military Gov. – Huge improvements in finace, ed. Ag. Gov. and public health • Honors Teller Amendment…but • Cuban Constitution and Platt Amendment – Not allowed to make treaties with others that will restrict its sovereignty. – Not allowed to go into debt beyond their means. – US allowed to intervene in Cuba to restore order. – Cubans agree to provide bases to US. “Splendid little war” • Helps US pride. • Brings north and south closer together; • Americans believe that American power is stronger than it is. • Mahan is vindicated; more resources poured into Navy. • US stuck with Philippines and far-east entanglement Little Brown Brothers” In The Philippines • The Filipinos wanted a deal similar to Cubans • 1899 the Filipino’s revolt • War of atrocities on both sides. • US loses more soldiers and spends more money fighting against Filipinos than it had in the SA war. “Little Brown Brothers” In The Philippines • Filipino army is quickly defeated • Turns into guerrilla jungle warfare, • vicious and difficult for Americans to fight. • Anti-imperialist in US redouble their protests. • War finally ends in 1901 when US captures Aguinaldo, but still sporadic guerilla terrorism. Rebuilding Philippines • McKinley appoints a commission. • William Howard Taft. • Millions of US dollars poured in to Philippines to help build the country. – Roads, sanitation, education, public health • Philippines finally get their freedom in 1946 after WWII . • Thousands of Filipinos emigrate to the US. Hinging the Open Door in China • Japan defeats China in 1895. • China weak but filled with huge markets and lush natural resources, • Imperialist powers in Europe and Japan want to exploit China. • Sec. of State, John Hay announces Open Door Policy China. – Respect certain Chinese rights, but allow fair European competition in its markets Hinging the Open Door in China • Boxer Rebellion • In 1900 super-patriotic group of nationalists known as “boxers” rebelled with the mission to “kill foreign devils.” – Over two hundred missionaries and other whites killed – foreign diplomats were besieged in the capital • A multinational force of 18,000, including 2500 Americans sent to put down the rebellion. • Succeed quickly and relatively easily. – US participation is a marked departure from traditional policy of not becoming entangled in foreign disputes Election of 1900 • Republicans- William McKinley- won the war, safeguard to gold standard, got plenty of new land • Teddy- governor of NY, shutting down political bosses, thus bosses push TR into vice president role Election of 1900 • Democrats- William Jennings Bryan • Republicanism over Imperialism – Abe freed 3.5 Africans, McKinely enslaved 7 million Philippines Election of 1900 • McKinley wins by nearly 1 Mill. votes and 292-155 in the electoral vote. Brandishing the Big Stick • McKinley assassination leads to Teddy Roosevelt becoming youngest president in US history • Speak softly and carry a big stick- big stick diplomacy • Strong believer in a strong president • Roosevelt = reformer, McKinley was conservative Building the Panama Canal • The Spanish-American War showed need for a canal somewhere in Central America. – Acquisition of Pacific territories. – Trade to California and East • Clayton-Bulwer Treaty stand in the way • Hay-Pauncefote TreatyBritain gives US right to build canal and fortify it- Building the Panama Canal • French already failed building a canal once • Panama is province of Columbia • Columbia rejects US’s first offer • Panamanians “revolt” 11/3/1903 • US warship prevents Columbia from responding • TR quickly recognizes new Panamanian gov. and gets treaty for canal Roosevelt Corollary • Latin American deeply in debt to Euro, TR worried about Euro influence • Addition to Monroe Doctrine- preventive intervention, in future financial disputes, the US would intervene, take over the customs-houses, pay off the debts • Uncle Sam is policeman of the Caribbean • “bad neighbor policy” • Latin America hates it, feel US is trying to turn the Caribbean into the Yankee Lake TR on the World Stage • 1904 War between Japan and Russia. • Japan running out of men and money. • Japan secretly approaches TR and asks him to negotiate a peace treaty. • He brings the parties to US and rams through a treaty • TR gets Nobel Peace Prize, but both Japan and Russian grow hostile to the US. • Japan starts to emerge as a rival to US interests in the far east. Japanese Laborers In California • Many Japanese moved to California to farm in the lush valleys.— 70,000 • Californians were nervous about “Yellow Peril.” • SF school board ordinance- segregation of Chinese, Japanese, and Korean students Japanese Laborers In California • Japanese government protested. • TR summoned school board to White House. – TR got Japanese to secretly agree to limit emigration to US – School board rescinded their segregation policy TR back down…yea right • TR sends the entire navy battle fleet (The Great White Fleet) on a tour of foreign ports, including Japan • Root-Takahira agreement of 1908- respect territorial possessions in the Pacific, uphold open door policy in China






