Unit 1: Anatomy
advertisement

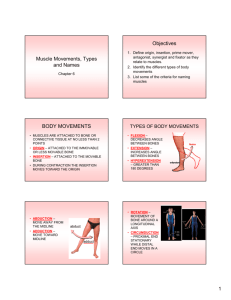
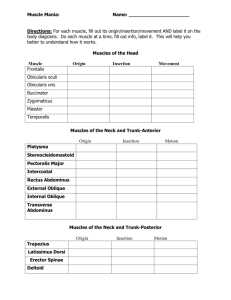
Unit 1: Anatomy Unit 1.2 Key learning intention (KLI) Success criteria Resources Key words ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ The muscular system To understand the structure, function and classification of muscles with focus on the skeletal muscles. Using my knowledge of origins and insertions I can explain which muscles are responsible for the main movements of a sport of my choice. p13-25 Smooth, cardiac, skeletal, epimysium, perimysium, endomysium, actin, myosin, myofibril, muscle fibre, sarcomere, origin, insertion, elasticity, contractility, hypertrophy, atrophy, Frist of all lets discuss what you know already. Look through the rest of unit one and discuss what you already know. Let’s have a little introduction to the muscular system. 1.2.2. Distinguish between the different types of muscle Type of muscle Description Smooth Cardiac skeletal 1.2.3. Annotate the structure of skeletal muscle Example Unit 1: Anatomy component ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Description Epimysium Perimysium Endomysium Muscle fibre Myofibril Sarcomere Actin Myosin In pairs using paper and straws, make a model of the structure of skeletal muscle. Try to include all the components listed in the table above. Unit 1: Anatomy 1.2.4. Define the terms origin and insertion with examples Origin insertion 1.2.5. Identify the location of skeletal muscle in various regions of the body ANTERIOR Muscle: Muscle: Origin Muscle: Origin Insertion Insertion Movements Movements Origin Muscle: Origin Insertion Insertion Movements Movements ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Unit 1: Anatomy Muscle: Muscle: Muscle: Origin Muscle: Origin Insertion Insertion Movements Movements Origin Muscle: Origin Insertion Insertion Movements Movements Origin Muscle: Origin Insertion Insertion Movements Movements ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Unit 1: Anatomy POSTERIOR Muscle: Muscle: Muscle: Origin Muscle: Origin Insertion Insertion Movements Movements Origin Muscle: Origin Insertion Insertion Movements Movements Origin Muscle: Origin Insertion Insertion Movements Movements ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Unit 1: Anatomy Muscle: Muscle: 1.2.1. Origin Muscle: Origin Insertion Insertion Movements Movements Origin Muscle: Origin Insertion Insertion Movements Movements Outline the general characteristics common to muscle tissue Characteristics of muscle tissue ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ Unit 1: Anatomy Unit 1.1 Key learning intention (KLI) Success criteria ‘Progress depends on effort not ability’ The muscular system To understand the structure, function and classification of muscles with focus on the skeletal muscles. Using my knowledge of origins and insertions I can explain which muscles are responsible for the main movements of a sport of my choice. You have finished unit 1.2. You should now be able to achieve the success criteria above. How about some quick revision before you complete the end of unit assessment. Click here Try here too Now go to edmodo and complete the end of unit assessment. If you score more than 90% you can move onto the next unit. Feedback will be given within 24 hours. You will now conduct an experiment on the extensibility of muscle tissue. Collect your DESIGN sheet from Mr Doyle.