Positive Behavior Support in Early
Childhood Settings: Current Issues,
Challenges, and Solutions
Tim Lewis, Susanna Hill, &
Sarah Moore
University of Missouri
Center for SW-PBS
Big Ideas
•
•
•
•
Program-wide vs. school-wide
Primary focus at classroom & individual level
Data collection challenges
Developmentally appropriate / need for direct
instruction of social behavior
• Intensity match intensity of challenges across the
continuum
• Apply basic logic of PBS across
– Data, practices, systems
PD for EC Program-wide
Positive Behavior Support in Missouri
• Networking Summit
– Held annually since 2010 in different parts of the state
(two scheduled for 2013-14)
– Agenda includes presentation of information and
sharing new tools; presentation by exemplar ECC;
round table networking on “hot” topics; tour of local
ECC
– Topics include data collection and analysis, family
engagement, teaching social skills lessons,
developmentally appropriate practices
– 50-75 attendees representing 40 or more centers
across the state
PD for EC Program-wide
Positive Behavior Support in Missouri
• Regional Training, Networking and Technical
Assistance for EC programs
• Early Childhood strand included in Mo SW-PBS
Summer Institute
In the works…
• State-wide email distribution list of all EC
centers, programs, Head Starts, preschools,
etc… implementing Positive Behavior Support
• Quarterly newsletter and/or Blog
• EC specific resources on state PBS website and
made available to regional consultants
• Adaption of current tools, checklist, forms,
etc. to make them more “EC-Friendly”
Kirksville Public Schools
Early Childhood Learning Center
“Whatever it takes, our children are worth it!”
Demographics
•Rural setting in Northeast Missouri
•240 Children
•59% Have IEP’s
•54% Free and Reduced Lunch
•52 Staff Members
•Licensed, Accredited/Project Construct
How They Started (Over)
• Commitment from all staff
• Use of data to create matrix
• Rebuilding of system to meet the
developmental needs of children
• Specific focus on Tier I/Culture of building
• Teams established for each Tier/Meeting times
• New action plans created for each Tier
• Training of all staff, volunteers, interns, etc.
Expectations throughout the building
Teaching Universals
Tier I
Individual Reinforcement System
Tier I
Group Reinforcement System
PBS Challenges
Find ways to give specific praise. It’s harder than it
seems. Try not to use the words “good job”:
• “I like how you are being safe by using your
walking feet.”
•“I like how you are being safe by cleaning up your
area.”
•“That was very kind of you to use such nice
words.”
Keeping Staff Informed
•
•
•
•
Professional Development
Staff Meetings
Monthly Newsletters
PBS Bulletin Board in Staff Room
Staff Newsletter
Staff PBS Board
Tier I
Staff Recognition
Keeping Parents Informed
•
•
•
•
•
Monthly Newsletters
PBS Night
Website
Facebook/Twitter
Positive Post Cards Sent Home
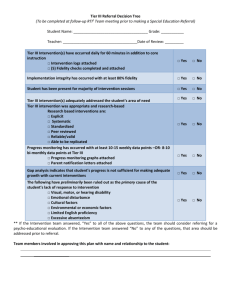
Tier II Meeting Process
Student Identification Process
•Decision Rules
•Staff Referral
•Data Review
•Problem Solving Team Referral
•Screening
•Teacher/team ensures universals, including classroom, are in place. Referral paperwork
is completed.
•Observation is scheduled.
•Student records are reviewed. Problem behavior identified.
•Mini FBA to determine function of behavior if necessary.
•Behavior goal written, including actions, resources and timelines. Tier II Implementation
and Monitoring Form completed.
•Behavior goal evaluated and decision made.
•Review of process.
Data Decision Rules
Data Driven
4 majors in a two
week period
Teacher Nomination
Problem Solving Team
Referral
Screening
Document behaviors
and interventions
6 minors=1 major
Team assists staff in
completing Tier II
Referral Form
Observation
completed
Teacher completes
Tier II Referral Form
Observation
completed
Tier II Team meets
within one week and
makes decision
Tier II Team meets
within one week and
makes decision
Social Skills Group: Tiger Talk
What intervention?
•
The Second Step early learning program is a research-based intervention that promotes:
success across academic, social, and community environments.
Who is it applicable for?
•
A Tier II student who has social skills deficits in the areas of: acquisition, performance, and/or
fluency.
When is it used?
•
A child is recommended by the teacher (teacher nomination form) or has received four major
referrals in a period of two weeks. Six minor referrals equal one major referral.
Who implements it?
•
Social skills small groups will be led by a social worker.
What does it look like?
•
A small group of 4 to 8 children with similarity in age, developmental level, common behavior
problems or issues,
•
Meet weekly for 30 minute
What does success look like?
•
80% accuracy or higher on Social Skills Progress Chart
•
Long-term Success - 80% Accuracy on Social Skills Progress Chart after 10 weeks and decrease
in major and minor referral forms
How do we make sure success continues?
•
Gradually fade intervention and graduate
•
Check in on child after graduation to ensure success
Environmental Interventions
•
•
•
•
•
Change in placement
Additional adult support
Referral for EC Special Ed services
Occupational Therapist intervention
Early Intensive Behavior Intervention
Tools For Program Wide PBS
Program Wide Assessment Tools
EC- SAS - Early Childhood Self Assessment Survey
• Taken by all staff to identify their perception of:
1) School-wide discipline
2) Non-classroom management
3) Classroom management
4)Individual Students engaging in chronic
problem behaviors
Pre-school SAS
Level of Implementation
No
Answer
In
Place
Partially
in Place
Feature
Not in
Place
Available Program Support
In Place
Partially
in Place
Not in
Place
6
5
0
1. Rules for the classroom are clearly
defined.
4
5
2
8
3
0
2. Rules & expected student behaviors
are taught directly in the classroom.
5
6
0
5
1
3
6
0
2
1
5
4
2
4
6
5
4
4
5
4
3
3. Rules and expected student
behaviors are taught for nonclassroom
settings such as the playground.
4
6
1
0
4. Continuum of procedures are in
place to encourage child use of
expected social behaviors.
6
3
1
5
5. Procedures for encouraging
expected behavior are implemented
consistently by all staff.
2
7
2
4
6. A continuum of clear consequences
exists for discouraging/correcting
problem behaviors.
4
5
2
6
7. Procedures for discouraging/
correcting problem behavior are
implemented consistently by all staff.
1
7
3
2
8. Teachers have clear options that
allow classroom instruction to continue
when a student is disruptive.
7
2
2
2
9. Assistance from the pre-school
program is available to manage
difficult student behavior during
emergency or crisis situations.
6
4
1
5
10. Regular opportunities for teacher
assistance for behavioral support in the
classroom (e.g., observations,
instructional strategies, & coaching)
are available from the pre-school
program.
3
3
4
No
Answer
1
EC SET - Early Childhood School-wide Evaluation Tool –
•Adaptation of the School-wide Evaluation Tool (SET) used
in K-12 educational settings which is an external review to
measure critical features of school-wide PBS.
•Some Key Program Wide Features Assessed:
1) Expectations defined
2) Expectations taught
3) Rewarding expectations
4) Responding to behavioral violations
5) Organized and predictable environment
6) Family involvement
7) Additional Supports
TLCLC PRE SET RESULTS
EC BoQ - The Early Childhood Benchmarks of
Quality
• an annual team assessment of Tier I PBIS
implementation.
• The results of the EC BoQ are used to create
an action plan for the continued growth and
support.
The following elements are included in the ECBoQ:
Leadership Team, Staff Buy-In, Family Involvement,
Program-Wide Expectations, Strategies, Teaching
Pyramid, Procedures, Staff Support, and Monitoring.
(TACSEI) at www.challengingbehavior.org
The Teaching Pyramid Observation Tool for
Preschool Classrooms (TPOT)
• Assesses the fidelity of implementation
of the Teaching Pyramid model.
• Can be a pre/post measure
• Supplements other tools
• Meant to be an ongoing tool not a one
time event
(TACSEI) at www.challengingbehavior.org
(Lise Fox, fox@fmhi.usf.edu , Mary Louise Hemmeter,
ML.Hemmeter@Vanderbilt.edu, and Pat Snyder,
patriciasnyder@coe.ufl.edu). Copyright © 2008. All rights reserved.
The Pyramid Infant Toddler
Observation Scale - TPITOS
• Direct observation of adult
behaviors/environmental arrangements
specific to supporting the social emotional
development of infants and toddlers
(TACSEI) at www.challengingbehavior.org
Mary Louise Hemmeter (ml.hemmeter@vanderbilt.edu).
Copyright © 2009. All rights reserved.
Classroom Behavior Log
Teacher:
Date
Time
Student
Behavior
Comments
Behavior Plan
Documenting Minor
Behavior
- Document behavior when
student has to be
removed from instruction
- Take concrete action to
reteach and correct
behavior
- Be patient and consistent
School Wide Information System-SWIS
https://app.swis.org/
https://app.swis.org
Behavior Incident Recording System
for early childhood- BIRS
• Behavior incidents recording system that is
designed for preschools.
• Web site is: www.BehaviorPartnership.com
Early Childhood Data Collection Tool
MO-SWPBS
MO-SWPBS
Last Revised: 8/01/12
TLCLC Lesson Plan
Expectation: Kind
Setting: All School Settings
Skill: Use Kind Words
Matrix Expectations
Matrix Rule and Steps
Context
Identify the locations(s) where
performance of rule is expected.
Tell
Introduce the rule and why it is
important
Be Kind
To use kind words means:
Use words that won’t hurt others feelings
Tone, volume and attitude while we speak are part of using kind words
Use our manners and say Please and Thank You
All School Settings
Teacher gives students some examples of using kind words.
1. Jill is carrying books back to the book shelf. She has too many
to carry by herself. She asks Sally “Could you please help me
carry these books to the shelf?” Sally says “Sure!” Jill says,
“Thank You!”
2. Annie is walking to her cubby. She accidently bumps Tim.
Annie says, “Oops I’m sorry.” Tim says, “that’s ok.”
Show
Teacher demonstrates or models
the rule. Teacher models nonexamples
Discuss how we ask to play with something or when we want something.
We should use our kind words of please and thank you
Discuss why kind words are important. Discuss how it makes you feel
when someone has used kind words with you and how it makes you feel
when someone uses hurtful words with you.
The teacher role plays being a child coloring a picture. Suzy asks if she can
please use her yellow marker. Teacher models kind response of “yes but
can you give it right back when you are finished?” Suzy says “thank you
and yes I will give it right back”.
The teacher asks 2 students to model a situation in the classroom where
they are playing a game. Both of them want to go first. Have them use
kind words about how they can solve the problem. One can ask if they can
please go first then the other student can go first next time. Have the
student thank the other student for letting him go first.
Teacher models the non-example: Teacher role plays being a child
playing a game with Sam. Sam accidently hits the board and the pieces
move. The teacher then responds with a non-example of kind words and
says “Look what you! Why did you do that?”
Teacher then asks class do you see the differences. What are they? How
did Suzy feel? How did Sam feel?
Practice
Give students opportunities to
role play the rule across all
relevant settings
Generate a list of kind words.
Have children sit in a circle and the teacher will direct one child to ask for
the ball using kind words: “Jack, please pass the ball to me”. Then Tom
will say “thank you” when the ball is passed to him. Continue to play the
game until every child has a turn.
Precorrect/Remind “Before we go out to recess let’s discuss what it means to use kind words. Be
Anticipate and give
students a reminder to
perform behavior
kind when you are asking to play with a toy by saying please and thank you.
Remember how it feels when someone uses kind words with you and what it feels
like when someone uses hurtful words with you.”
Supervise
Move, scan and interact with students in various settings (playground, gym,
classroom) to give them feedback about how they are doing using kind words with
others. Correct as needed.
Move, scan and interact
with students
Feedback
Observe student
performance & give
positive, specific feedback
to students
Correction
Observe student
performance & give
specific feedback when
correcting behavior
Reteach
Practice throughout the day
“You used kind words when saying please, Jill! That was so nice of you!”
“Lisa thank you for using a kind words and saying that’s ok when Tammy
accidently bumped into you. That was nice friend!”
“Carl, Lucy asked if you could help her and you said no dummy, was that
using kind words? What is a kind way of answering her?”
Have students share a time when they used kind words with others.
Teaching Universals
Standardized Screening Tools
• ESP (Early Screening Project; 3 tiered; -proactively screens
and identifies three- to five-year-olds who are experiencing
pre-school adjustment problems both internalizing or
externalizing.
(Walker, Severson & Feil)
http://esp.ori.org/
• DECA-P2 Deveruax Early childhood Assessment Part 2strength-based assessment along with strategy guides for
early childhood educators and families.
(LeBuffe& Naglieri, 1999)
http://www.centerforresilientchildren.org/
Resources
• Positive Behavioral Interventions and Support
at www.pbis.org
• Technical Assistance Center on Social
Emotional Intervention (TACSEI) at
www.challengingbehavior.org
• The Center on Social and Emotional
Foundations for Early Learning at
www.csefel.uiuc.edu