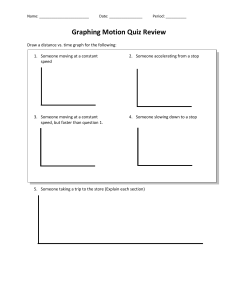
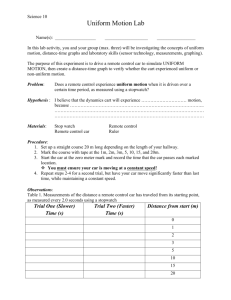
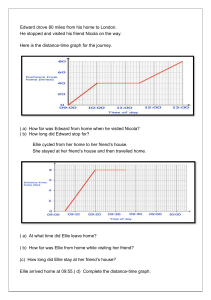
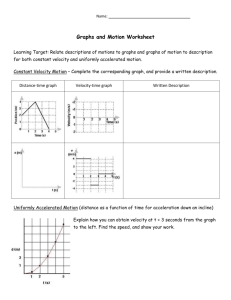
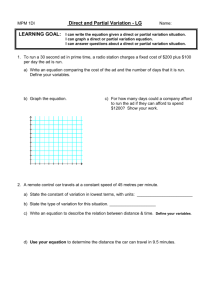
Distance/Time Graphs
advertisement

MOTION Continued • Complete the following table. Speed Distance Time A 80 cm 4s B 0.5 cm 0.2 s C 500 km 2.5 h D 15 cm 60 s 4 m/s E 8.5 s 0.8 km/h F 4h 9 m/s 45 m G 800 cm/s 6400 cm H Questions • Change: – 8 km to metres – 90 cm to metres – 180 minutes to hours – 0.5 h to seconds. – 7200 seconds to hours • A bullet travels 2200 m in 4 seconds. What is the average speed of the bullet? • A cyclist rides at a speed of 10 m s -1 for 45 seconds. What distance does she travel? • A car travels at an average speed of 70 km h -1 on a journey. What time will it take to travel a distance of 350 km? Practical applications……. • The diagram shows how an echosounder is used to find the depth of water beneath a ship. – A pulse sound which travels at a speed of 1800 m/s, is sent into the water. The reflected sound is detected 0.05 s later. How deep is the water below the ship? Distance-Time Graphs • Distance-Time Graphs show the time taken to travel a certain distance. The slope (gradient) of the graph gives information about the speed of the object. Continued…….. • A straight line represents a constant speed. • A horizontal line represents zero speed. The object is not moving. • The steeper the slope, the greater the speed. • When a distance-time graph is not a straight line, the object is changing speed. • The graph shows a journey in a car. During which section of the journey was the car travelling at greatest speed? Why?