quantum theory
advertisement

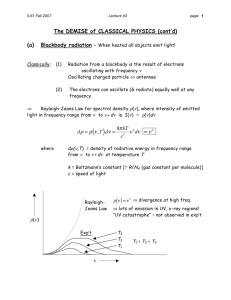
Quantum Theory By: Lucas, Steven, Brandon and Kristen Vocabulary • Spectra: the range of colors that a object will give off when it is heated or burned. • Blackbody: An object that will absorb all light and can radiate it will almost no gaps in its spectrum. • Discrete: Apart from, or separate from others of its kind. Vocab cont… • Quantum: a discrete amount of energy, given by the product of Planck's constant(h) and the frequency of the radiation (f) • Empirical equation: an equation that fits the observed data but is not based on any theory • Postulate: a claim, something said without proof of consept. Properties of light • The color of light is determined by the its wavelength. • Increasing or decreasing the temperature of an object will change the color of the light it emits. • Each color of light can only have a a set number of different energy levels. Blackbody radiation • When a blackbody is heated it follows a color path until it reaches a certain temperature limit. • The pattern stops once you reach the ultraviolet end of the spectrum. Max Planck QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. • A German physicist that is credited with creating the founding for quantum theory. • He won the Nobel Prize in 1918 for his work in quantum mechanics. • Now he is known for: 1. Planck’s postulate 2. Planck’s constant 3. Planck's law of black Planck’s constant and postulate • He used pervious theory about blackbody radiation and experiments done with the blackbody radiation spectrum to derive this constant. • H= 6.626 068 96 x 10^(-34) j*s • His postulate Allows use to find the energy of light at any frequency • E=nhv • n is a discrete value that depends on the color of light you are dealing with, h is Planck's constant and v is the