A293: Production, Finance and the External
advertisement

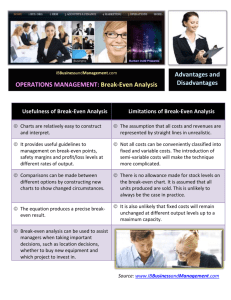
GCSE Business Studies 2015-2016 UNIT 3 Production, Finance and the External Environment The Exam - Knowledge and Key Words The Exam – A293: Production, Finance and the External Environment What will the exam be like? This is a pre-release case study examination, the teacher will give candidates a copy of the case study at the start of the unit It will last 1 hour and 30 minutes The paper is out of 90 marks The marks count for 50% of the overall grade There will be 3 main questions, each separated into a number of parts Every question will be based on the case study What will the exam test? AO1 Apply and Knowledge How well candidates can define business terms and explain business ideas. Example Testing subject knowledge and understanding. You might be asked to define the term ‘globalisation’ or explain the advantages of a competitive market. AO2 Application and Analysis How well candidates can use their subject knowledge to explain a business situation. Example Testing their ability to apply knowledge to a business context and situation. You might be asked to explain how a rise in costs may affect the break-even output of a business. AO3 Evaluation and Recommendation Using analysis to make a judgement and provide a suitable justification. Example Testing their ability to analyse a situation, identifying and explaining the advantages and disadvantages. Then making a suitable recommendation, in context, and giving reasons why you think it’s the right thing to do. You could be asked to recommend whether a business should move its production facility to another country. You might be asked to recommend if immigration has been good for a particular business. THIS EXAMINATION IS GOING TO TEST CANDIDATES ON THEIR ABILITY TO ANALYSE AND EVALUATE BASED ON THEIR SUBJECT KNOWLEDGE. Checklist of Subject Knowledge Topic Using and managing resources Types of production methods Management and control of production Production costs Economies and diseconomies of scale Calculating, plotting and interpreting break even Financial information and decision making Sources of finance Financial forecasting and analysis Cash flow forecasting Calculate, interpret and make use of revenue, cost and profit data External influences on business activity The competitive environment Competitive and monopoly markets External influences and business ethics Social costs and benefits Sustainability and business Ethical business behaviour Government and the UK Spending and taxation Rate of interest Consumer incomes effecting business Changes to population affect business Globalisation and UK business European Union and effect on trade International competition Effect of exchange rates Happy Themes of Questions This list is designed to give an idea of the main question themes that come up on the examination paper. It is not a comprehensive list, the comprehensive list will be given in class during April 2016. All of the Business Studies lessons on Unit 3 are about the subject knowledge and the issues discussed in the pre-release case study. We also do a lot of work preparing candidates for the types of questions they will get on the examination paper. When students have attended all the lessons they should feel confident that they can attempt to answer all of these questions. Which method of production should a business use to produce a particular good or service? How can a business increase its efficiency? What are economies of scale? Why do firms get them? What benefits do they bring? What are break-even charts? Why do businesses use them? What are their limitations? When will businesses use the different sources of finance? What are cash flow forecasts? Why are they useful to business? What are their limitations? What are profits? Why are they important to business? What determines how much profit you make? How do you calculate profit? What are the advantages and disadvantages of competitive markets and monopolies? How can the government control monopolies? How can businesses respond to the pressures on the environment? Why should they respond to these pressures? How can the government influence business to protect the environment more? Using examples what are ethical and unethical business practices? How are businesses affected by changes in government spending and taxation? How are businesses affected by the changes in employment and the incomes of consumers? What is economic growth and recession? How do changes in interest rates affect businesses? Is foreign competition a problem? What can UK businesses do to improve how well they compete against foreign firms? Why are education and training so important for UK business? Is immigration good or bad for UK businesses? What is globalisation? Is globalisation helping UK businesses or is it causing them problems? How can UK businesses compete better? What help can government give to businesses to improve their competitiveness? How do changes in the exchange rate of the pound sterling affect UK business? Should the UK join the Eurozone? What are the benefits and problems for UK businesses of the country’s membership of the European Union? Unit 3 Keyword List – Language for learning Added Value The process of increasing in value raw materials so that sales revenue is greater than the costs of production. Job Production The method of production where individual items are made. Batch Production The method of production where one type of product is made and then production is switched to another product. Process Production Usually an automated process suited to t h e large scale manufacture of products. Flow Production Production of one product takes place continuously using a production or assembly line. Often called mass production. Division of Labour Organisation of production into specialist tasks that are simple repetitive processes. Specialisation Occurs in production where workers specialise in carrying out one or related tasks. Mechanisation Machines controlled by workers, are introduced into t h e production process. A measure of efficiency which measures the number of products made. Productivity Lean Production A production system which ensures waste is kept to a minimum. Quality Assurance A system of ensuring quality standards are met throughout the production process. Just In Time (JIT) Stocks of materials and components are not stored but are used as they arrive at the production facility. Quality Control A system of checking the quality of finished goods. The process where all workers are responsible for quality throughout the entire production process. Total Quality Management (TQM) Sales Revenue or Sales Income Price Elasticity of Demand Fixed Costs The money a business receives from selling what it produces or provides. A measure of change in demand cause by a change in price. Costs that do not change as business changes the amount they produce. Variable Costs Costs that change as the amount the produces goes up or down. Total Costs Fixed and variable costs added together to calculate the total cost of production. Average Cost Total costs divided by the number of goods produced, so this calculates the cost to make one. Short Run A period of time, approximately 12 months in length. Fixed Assets Items owned by a business that tend to have a high value, the value will not usually change on a daily basis and will be an item the business owns for a long time. Long Run A period of time usually longer than two years. Capacity The total number of products a production facility has been set up and resourced to produce. Above Capacity A business is said to be working above capacity when it is producing more than it has been set up to do. Excess Capacity This is when a business is producing less than it is designed to. Economies of Large Scale Production These occur when a business increases its scale of production which then leads to falling average cost of production. Diseconomies of Scale When the average cost of production rises when the number of products being produced has also increased. Break-Even Level of Output The level of output by a business when it is not making any loss nor is it making any profit. It is just breaking even. Break-Even Forecast A prediction about the break-even level of output based on estimated sales and estimate costs. Margin of Safety The amount by which a business’ actual output is greater than its break-even output. Business Sponsor A business that pays money to another business. Opportunity Cost The cost of missing out on something else. This may not always be financially related. This is when the business has to compromise on options. Internal Finance Finance obtained from within the business. External Finance Finance obtained from outside the business. Interest Asset Security Time Period Income Expenditure Cash-flow The cost of borrowing, the amount of money you have to pay back on top of any borrowed money. This is the financier’s charge for lending you the money. An item of value owned by a business. Something of value which is offered to a lender to form a guarantee against a loan. If you do not repay your loan the lender can take the item of security. The length of time your finance is required for. Money which the business receives from selling its goods. The money a business will pay out. The flow of money into and out of a business. Cash-flow Forecast A statement showing the expected flow of money into and out of a business over a period of money. Balance Carried Forward The amount of cash left over at the end of a trading month. It is carried forward and used as the opening balance for the next trading month. It is sometimes called the closing balance or the balance brought forward. Balance Brought Forward The amount of cash available at the start of a trading month, it was the amount left over at the end of the previous month. It is sometimes called the opening balance. Positive Cash Flow In a trading month there has been more money flowing into the business than out. It is sometimes called a cash-flow surplus. Negative Cash Flow In a trading month there has been more money flow out of the business than in. It is sometimes called a cash-flow deficit and may mean a source of finance is needed to help with the overall cash-flow of the business. Perfect Competition A market in which there are a large number of sellers all competing against each other. Monopoly A market dominated by one seller. Patents The right to use an invention for a number of years. Copyright One of the main types of intellectual property others include designs, patents and trademarks. It is the right to prevent others copying or reproducing someone's work. The percentage of total sales in a market accounted for by one business. Market Share Monopolist A firm that accounts for at least 25% of the total sales in a market. Privatisation When an organisation owned by the government is sold off to the private sector. Cartel A group of businesses that work together to fix prices. Child Labour The use of young children in order to achieve low cost production. Ethics This is about what is morally correct and what is morally wrong. Social Responsibility An ethical framework which suggests businesses and customers have an obligation to act for the benefit of all society, the economy and the planet. Fair Trade Trade between companies in developed countries and producers in developing countries in which fair prices are paid to the producers. Human Rights This is the idea that all people should have basic rights and freedoms such as liberty, freedom of speech, equality in law, the rights to food, education and to work. Sweat Shops These are factories where people are worked very hard, often in very poor conditions and paid a low wage. Pirating Illegally copying films and music. Ethical Businesses Businesses that behave in a morally correct way. Non-renewable Resources Resources that can only be used once, such as oil. Carbon Emissions Carbon dioxide that is put into the atmosphere. Global Warming The rise in average temperatures that scientists believe is taking place. Green An adjective that describes consumers and businesses that act and make decision hat consider the effect on the environment and planet. Green businesses act to make production sustainable. Renewable Resources Resources that can be used more than once, such as wind power, or can be recreated such as crops. Sustainable Production Production that involves the use of renewable resources and recycled resources. It also minimises waste and the use of energy. Carbon Permits Permits granted under the EU Emission Trading Scheme, which allow businesses to produce a certain amount of carbon in their production process. Recycling When resources something else. are reused to produce Economic Growth A period of rising consumer incomes, demand and output. Consumers will usually spend more in this period as they have more disposable income. Demand The amount of goods and services that all customers want to buy. Recession A period of falling consumer incomes, demand and output. Customers will often limit spending as they have less disposable income. Unemployment may rise and the government may put in place measures to try and ease its affects. Unemployment Interest R ate Bank of England The number of people who are out of work. The charge made to people and businesses for borrowing money from lenders, often referred to as the cost of borrowing. The organisation that sets basic rate of interest in the UK, this influences the interest rate banks and other financial institutions charge. The BoE will change interest rates to try and control inflation. Inflation A sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time. Multiplier effect The amount by which an increase or decrease in spending on a specific product is multiplied in its effect on total spending in an economy. Taxation Charges made to people and businesses by the government. Taxes will be paid on income and spending. Take-home pay The amount of income a person receives after deductions from their gross pay for Income Tax and National Insurance Contributions. Disposable Income The amount of income left after all essential expenses have been paid for, people have the choice with what to do with this money. Business Rates The charge made to businesses by the local council. Globalisation The process by which business activities in different countries are becoming more and more connected to each other. Outsourcing When a business pays another business to carry out an activity of work for them. Such as production, accounting, marketing or cleaning. Multi-national corporations Companies that operate in different countries around the world. Global Branding When a product becomes a brand name and is sold and recognised worldwide. Inward Investment This is when a foreign business sets up factories and office in the UK. Bringing with it job opportunities and contributing to the UK economy. Protectionism The name given to methods used to protect business from the problems that international trade might bring. Exchange Rates The amount of one currency that you can buy for another currency. Stable Exchange Rate An exchange rate that does not change greatly over a period of time. Developed Countries Counties that have strong economies where most workers earn high wages and living standards are high. They usually have large tertiary (service) sector businesses. Developing Economies Poorer countries that are starting to grow, usually expanding primary and secondary businesses. Also possibly tertiary service sectors. Exports The goods and services that a country sells to another country. Imports The good and services a country buys from another country. Gross Domestic Product The total amount of goods and services a country produces. Can be used to measure the size of an economy. Innovation Developing new products and services and new ways of making products. Productivity The amount that one person can produce. Increasing productivity makes workers more efficient and can save costs. Value Added The difference between the cost of the raw materials and the value of the item when it has been produced. Value Added Tax An indirect tax on the amount by which the value of a product has been increased at each stage of its production. Infrastructure The provision of roads, railways airports, in an area or country. Immigration The movement of people from abroad to live in the UK. Ageing Population The increase in the population of those people aged over 65 years old. European Union (EU) The collection of 27 countries in Europe which trade together and aim for closer co-operation. Tariffs Taxes paid on imports that rias eth total costs of imports so that it will be harder for a foreign business to sell its goods. Quotas A limit on the amount of goods or services that can be imported. This restricts competition from foreign businesses. Social Charter Measures to protect workers in the EU from unfair working practices. Minimum Wage Part of the Social Charter, which guarantees a minimum wage kevel for workers. Eurozone A name given to the countries in the EU which have chosen to use The Euro as its currency. The Euro The currency used by 15 on the EU countries. How to answer the questions – A2E APPLY - INTRODUCTION Briefly explain the problem – Showing understanding of the terms. ANALYSE – ANALYSE – ADVANTAGES/FOR/PROS DISADVANTAGES/AGAINST/CONS Write down the advantages of the situation or reasons for doing something. Write down the disadvantages of the situation or reasons against doing something. EVALUATION – CONCLUSION/RECOMMENDATION/JUSTIFICATION Make your decision and explain how you have come to that decision. Or you can say what information is needed and what the recommendation will be dependent upon. Make sure you have fully justified why you have chosen that option. The Pre-Release Case Study June 2016 – Aaron Furniture Ltd This is the actual Case Study the exam will be based on. It is imperative students know this Case Study material implicitly. They must familiarise themselves with the Case Study as without it they cannot answer the questions on the Examination Paper. Students cannot take notes into the examination. A clean copy of the Case Study will be given to students with the Question Paper during the examination.