IN-Class PowerPoint
advertisement

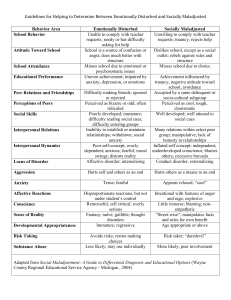
Chapter 3: Mental and Emotional Health Mr. Ramsey Do-Now Activity • Write a short paragraph describing what you think are the most important influences on someone’s personality are. This does not have to pertain to a specific person, just a general overview of influences. Skip a few lines then write down one thing you would like to learn about mental and emotional health. What is someone’s personality? • Definition: a combination of feelings, thoughts, and behaviors that make you different from everyone else. • How you would handle certain problems and situations. Self-Concept vs. Self-Esteem Self-Concept • The way you view yourself overall. • • • • Physically Your abilities How you feel you fit in As a student, friend, teams Self-Esteem • How you feel about yourself. • Do you like yourself? • Do you feel good about who you are? • Confidence around others • Responsibility How can we build Self-Esteem? • • • • • • Set realistic goals Focus on your strengths and work to improve them. Ask for help! Accept that perfection is not achievable. Remember that everyone makes mistakes. Motivate yourself. Quick-Write! • An emotion is a feeling that comes about based on different situations in life. • In two minutes, list as many different emotions (At least 5) that you can think of in your packet. Below are two examples to get you started. • Happiness • Joy Expressing Emotions • No emotion is good or bad by itself. • How you express emotion is what makes it good or bad. • The way you express emotions affects you mental/emotional, social, and even physical health. • Learning how to express emotions healthily is important to overall health. Basic Emotions to Express Anxiety • A state of uneasiness, usually associated with future uncertainty. • Talk to a family member or friend • Avoid avoidance Fear/Panic • The body’s alert system in reaction to a potential threat. • Find a support system • Keep fear/panic out of the center of attention Emotional Needs • Needs that affect your feelings and sense of well-being. • • • • • To love and be loved To belong To make a difference To be helped or help others To understand or be understood What is Stress? Positive Distress (Negative) • Stress that can help you reach your goals. • Stress that prevents you from doing what you need to do, or stress that causes discomfort. • Trying out for a sports team of school club. • Getting into an argument with a friend or family member. Fight-or-Flight Response • As your body prepares for action, it releases adrenaline, a hormone that increases the level of sugar in the blood, giving your body extra energy. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZH-AMPUnR38 Skills for Managing Stress • Relaxation • Laughter and a Positive Outlook • Physical Activity • Time Management Take-Home Challenge • Time management consists of utilizing strategies in order to use time more efficiently. One of those strategies is to write a daily planner. Create a daily planner for tomorrow from the time you wake up, to the time you will go to sleep and challenge yourself to stay on task as best as you can. • Hand your version of a daily planner next class. Do-Now Activity • Think about a time where you had to cope with the loss of a loved one. How did you feel? What did you do? Would you have liked someone to help you in some way? Write a paragraph describing the experience. If you have not had a loss in your life, think about how you would help a friend who has lost a loved one and discuss that topic. Coping With Loss • Grief: the sorrow or sadness caused by the loss of a loved one. • Grief Reaction: the process of dealing with the feelings that follow the loss of a loved one. • Stages of Grief: • • • • • Shock Anger Yearning Depression Acceptance Chapter 4: Mental and Emotional Disorders What is a disorder? • A disorder is a disturbance in the normal function of a part of the body. • Think about it… Do you feel that a disorder can be as problematic as a physical disorder? Anxiety Disorder • • • • We know what anxiety is. And we know what a disorder is. So what do you think an Anxiety Disorder is? Intense anxiety or fear keeps a person from functioning normally. Phobias • An exaggerated fear of a specific situation or object • • • • Heights Spiders Small spaces Flying Common Disorders • Mood Disorder: A disorder in which a person undergoes changes in mood that seem inappropriate or extreme. • Major Depression: When people lose interest in life and can no longer find joy in anything. • Schizophrenia: a severe mental disorder in which people lose contact with reality. Suicide • Intentional taking of one’s own life. Therapy • Individual Therapy: a single person and a therapist meet alone to discuss problems. Offers the most privacy and is usually used for first timers. • Group Therapy: a single therapist meets with several people who have the same problem. This teaches group members to offer support and show empathy towards one another. • Family Therapy: a therapist seeks to improve troubled family relationships. Mental Health Providers • Psychologist: a mental health professional who is licensed by the state lived in to perform therapy. • Clinical Social Worker (CSW): certified mental health professional with a master’s in social work. • Psychiatrist: medical doctor with a specialty in mental health problems. This is the only provider that can provide medication for disorders. You fell in love with bridges, but never touched the water. You fell in love with gardens, but never touched a flower. You fell in love with seasons, but never watched the snow melt. You fell in love with everyone else, except yourself. Chapter 10: Nutrition Do-Now Activity • Write down everything that you had for breakfast this morning. Underneath that list of food and drink, write a few sentences describing whether or not you feel it was a healthy breakfast and why. What is Nutrition??? • The study of nutrients and how the body uses them. So… What are Nutrients? • Substances in foods that your body needs to grow, have energy, and stay healthy. Appetite vs. Hunger Appetite Hunger • Psychological desire for food • The body’s physical need for food Influences on Food Choices • • • • • • • Taste preference Look, feel, smell Family traditions Culture Environment Media Emotions Nutrients for Wellness • Carbohydrates: sugars and starches that occur naturally in foods (mainly plants) • Proteins: nutrients that your body uses to build, maintain, and repair cells and tissues. • Fats: promote healthy skin and growth and consist of two different kinds. • Saturated Fats: solid at room temperature and are bad for your health. (butter, cheese, fatty meats) • Unsaturated Fats: Remain liquid at room temperature and should be included in your diet. (olive oil, nuts, avocados) • Vitamins: substances that help your body fight infections and use nutrients • Minerals: elements that help form healthy bones and teeth • Water My Plate Eating a Variety of Foods Quick Write! • Based on the information just covered, create a healthy dinner time meal that you feel is healthy and could also be enjoyable. Use the second page of you’re my Plate in order to create the meal. Balancing Calories with Physical Activity • Calorie: a unit of heat that measures the energy from food and measures how much energy your body uses. • Most teens need around 2,000 calories per day in order to perform regular activities. • If you eat more calories than your body uses you could begin to gain weight. • What factors could make it so you would need more calories in your diet without gaining weight? • Physical activity (moderate or intense) • Body type and size Nutrition Facts Label Foodborne Illness • Sickness resulting from eating food that is not safe to eat any longer. • Ways to prevent foodborne illness: • • • • • Wash your hands and use clean utensils Separate raw and cooked foods Cooks food until completely done Chill or freeze when necessary When in doubt, throw it out Breakfast Tips • EAT BREAKFAST!! • After a night’s sleep your body needs fuel to kick start your energy producing mechanisms. • Round out the meal with fruits Lunch and Dinner Tips • Vary your proteins • Limit fats, sugars, and salt • Balance out the plan by creating a food log. Healthy Snacking • Avoid snacking right before meal time. • Choose healthy snacks. • Choose nutrient dense (a large amount of nutrients per calorie) Eating Healthy While Eating Out • Make sure to control the portion sizes that you eat. (i.e. No 20 oz. steaks from Longhorn) • Try ordering a healthy appetizer choice as the meal. (Cheese fries or onion rings are not healthy) • If the restaurant’s portion sizes are large, try eating half of it and taking the rest home for another meal. • Select foods that are grilled rather than fried. Take-Home Challenge • Further your research: The nutrition guidelines we are learning about are a fairly general and basic guideline for the majority to live by. However, there are many different diets a person can choose to partake in due to health, moral, or a variety of other reasons. Pick one of the 8 diets provided and create a short review of that diet. What does it consist of? When did it become popular? Is it successful? Etc. This is a critical thinking question so you must USE YOUR BRAINS. • • • • Atkins Mediterranean Weight Watchers The Zone Diet -Vegan -Raw Food -Vegetarian -Jenny Craig •Test next week!!! •Study the packet!!!