Anion Tests: Chemistry Lab Manual
advertisement

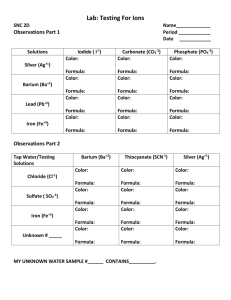
Test for Anions What is an anion? We will look at 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. The Chloride Ion ClThe sulfate ion SO42The sulfite ion SO32The carbonate ion CO32The hydrogen carbonate ion HCO3The nitrate ion NO3The phosphate ion PO43- 1. To detect the presence of chloride ions Apparatus: 1.Test Tube, 2.Spatula, 3.a chloride salt, 4.silver nitrate, 5.dilute ammonia and 6.deionised water Procedure 1. Place 2cm3 of water in test tube adding a small amount of the salt, shaking to dissolve 2. Add a few drops of silver nitrate. What happens?? 3. Add about the same amount of ammonia as water. What happens? Chloride ions Test: Add a few drops of AgNO3 to a solution of the solid A precipitate is the name given to an insoluble material that settles out of a solution Observation: A white precipitate is formed which is soluble in dilute ammonia Formula: Ag+ + Cl- AgCl The down pointing arrow means that a precipitate has formed 2+3: To detect the presence Sulfite and Sulfate ions Apparatus: 1.2 test tubes, 2. deionised water, 3. sulfate salt, 4. sulfite salt, 5. dilute HCl,6. Barium Chloride Procedure: 1. Add about 2cm3 of water to both test tubes and make up a solution of sulfite salt in one and sulfate in the other, make sure you label your test tubes! 2. Add a few drops barium chloride to each test tube to each, note what happens? Ba2+ + SO42- BaSO4 ( Barium sulfate) Ba2+ + SO32- BaSO3 (Barium sulfite) How do we distinguish between the 2? 3. Add about 2cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid to each test tube What happens? Barium sulfate is insoluble in HCl Barium sulfite is soluble Sulfate and Sulfite ions Test: Add BaCl2 solution to the test tubes, distinguish the two by adding dilute HCl Observation: A white precipitate is formed, when HCl is added to this precipitate, if the precipitate remains : sulfate if it dissolves sulfite Formulas: Ba2+ + SO42- BaSO4 ( Barium sulfate) Ba2+ + SO32- BaSO3 (Barium sulfite) BaSO4 + HCl No reaction SO3- + 2H+ SO2 + H2O 4+5: Carbonate and Hydrogen Carbonate ions Apparatus: 2 test tubes, carbonate and hydrogencarbonate salt, dilute HCl, magnesium sulfate and deionised water Procedure: 1. Place aprox 1cm of carbonate salt in a test tube, do the same and add about 2cm3 of acid into the test tubes. What happens? Distinguishing between carbonate and hydrogencarbonate 2. Add Magnesium Sulfate to a fresh solution of the salt. Precipitate forms : Carbonate No precipitate : Hydrogen Carbonate (unless boiled Carbonate and Hydrogen Carbonate Ions Test: Add dilute HCl to the solids. Distinguish the two by adding MgSO4 to a fresh solution. Observation: A gas is given off that turn limewater milky. Precipitate forms: Carbonate No Precipitate: Hydrogencarbonate (precipitate forms on boiling Formulas CO32- + 2H+ CO2 + H2O HCO3- + 2H+ CO2 + H2O Reacting with limewater Ca(OH)2 +CO2 CaCO3 + H2O Formulas Reacting with Magnesium Sulfate Mg2+ + CO32- MgCO3 Mg2+ + HCO3- Mg(HCO3)2 With boiling Mg(HCO3)2 MgCO3 + CO2 + H2O 6. To detect the presence of Nitrate ions Apparatus: Test Tube, Nitrate Salt, iron(ii) sulfate, Concentrated sulfuric acid. Procedure: 1. Place a small amount of nitrate salt in a test tube and dissolve with some deionized water. 2. Add the same quantity of freshly prepared iron(ii) sulfate 3. Carefully add some concentrated sulfuric acid, VERY DANGEROUS! Note what happens? Nitrate Ions Test: Brown Ring Test, To a solution of the solid, add a freshly prepared FeSO4 solution, add concentrated sulfuric acid Observation: A brown ring is formed at the junction of the 2 liquids Brown ring is due to the presence of nitrate ion 7. To detect the presence of a phosphate ion Apparatus: Test tube, beaker, hot plate, soluble phosphate salt, ammonium molybdate solution, concentrated nitric acid, deionized water Procedure: 1. Add a few crystals of phosphate salt to about 1cm3 of water and shake to dissolve 2. Pour in ammonium molybdate until the test tube is half full 3. Add 5 drops of concentrated nitric acid VERY DANGEROUS! What happens? 7. Phosphate ions Test: Ammonium molybdate is added to a solution of the solid. Concentrated nitric acid is added. Solution id warmed if needed Observation: Yellow precipitate is formed Phosphate ions are present