PowerPoint Presentation - Adult Learners
advertisement

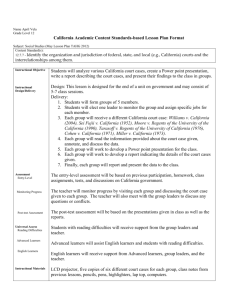
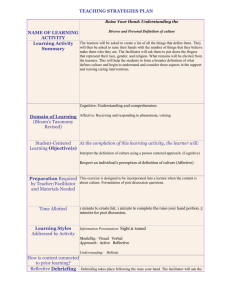
Training Adult Learners Training Techniques 1 Contents • Training is a System • Strive to Improve • Characteristics of Adult Learners • The Trainer’s Role • Teaching Adults • Learning Styles • Instructional Strategies • Instructional Media 2 Contents • Do’s • Planning and Preparation • Preparation Skills • Delivery Skills • Facilitator Responsibilities • Fatal Mistakes • Dont’s • Answering Questions • Difficult Questions and Learners 3 Training is a System Instructors Learning Environment Adult Learners Instructional Materials 4 Why the Systems Approach? • Focused – what the worker needs to know – what the worker needs to be able to do • Linked – instruction and outcomes • Reusable 5 Systems View • Preparation • Implementation • Evaluation • Revision Learners Materials Instructors Environment 6 Strive to Improve • Use the input from student evaluations to improve your future performance • Update your materials to keep them current • Continue to improve your knowledge of the subject matter 7 Characteristics of Adult Learners • Adults are capable of lifelong learning • Adults want to know why it’s important (purpose) and how they can use it • Adults like to participate in decision making regarding learning/training – Choices 8 Characteristics of Adult Learners • Learn in their own ways • Are not children • Need organization • Preconceptions and abilities • New vs. Old learning 9 The Trainer’s Role • Facilitator • Presenter • Coach 10 Facilitator Responsibilities • Optimal lighting for viewing and changes in lighting as necessary • Ensuring the room temperature is comfortable for the students 11 Facilitator Responsibilities • Setting the initial mood of the group • Creating an effective climate for learning • Motivate students to participate in the learning process • Be accepting of comments, avoid getting defensive 12 Facilitator Responsibilities • Control disruptive students • Offer yourself as a resource • Allow for limited debate and/or challenges of the ideas presented • Discuss how the learning can be applied in real world applications 13 Facilitator Responsibilities • Make yourself available at the beginning of breaks and after class to field individual student questions • Always treat the learners with respect • Avoid stereotypes 14 Teaching Adults • More effective retention given more than one training method • Reading • Hearing • Seeing • Seeing & Hearing • Talking & Writing • + Doing 10% 20% 30% 50% 70% 90% 15 Teaching Adults • Explain what you plan to tell or do • Tell them and/or do • Tell them what you told them or did • Learner explains and does 16 Learning Styles • Active – Participate – Field tips – Hands-on – Presentations • Passive – Read – Listen – Observe 17 Instructional Strategy • Characteristics of workers • Presentation • Practice • Feedback • Testing 18 Instructional Strategy • Talking Head • Demonstrations • Discussions • One-on-one 19 Instructional Media • • • • • • • Power Point Slides Overheads Videos DVDs Flip charts Etc. 20 Do’s • Positive mental attitude • Dress appropriately • Be enthusiastic • Be energetic • Avoid excessive slang and vernacular 21 Do’s • Speak up • Be yourself • Practice what you preach • Watch your body language • Be the best ‘you’ that you can be 22 Do’s • Be prepared • Be sensitive • Acknowledge learners • Use your sense of humor • Be respectful 23 Do’s • Be accessible and approachable • Be responsive • Allow learners to lead • Be flexible • Maintain your schedule 24 Planning and Preparation Facilities –Location –Accommodations –Speakers –Food and beverage for breaks Set-up and test all equipment before the start of the session –Arrange student seating if necessary 25 Planning and Preparation Learning Environment – Room - suitable classroom space for training • Size • Setup – tables and chairs for all attendees – plus two extra tables at the rear reserved for the trainers) – Temperature 26 Planning and Preparation Arrive at the training location early •Become familiar with the facility: –Security –Exits –Restrooms –Emergency procedures –Contact person –Rules 27 Planning and Preparation Administrative – Related paper work • Sign in forms/registration forms • Schedule • Evaluations • Etc. 28 Planning and Preparation Equipment and Supplies – Audiovisual equipment • Hotel • Rented • Personal Extra batteries and lamps Power strip(s) Extension cord(s) 29 Planning and Preparation Audiovisual and equipment that includes – Computer – LCD projector – VCR/TV – Microphone (if needed for the size room secured) – Overhead transparency projector – Whiteboard & markers – Flipcharts & markers – 35mm slide projector – Projection screen 30 Planning and Preparation Equipment and supplies – Transparencies – Markers – Flip charts – Paper – Pens and pencils – Handouts 31 Preparation Skills • Know your audience • Communicate the session objectives at the outset of your presentation • Be familiar enough with your materials so as to avoid reading directly from slides 32 Preparation Skills • Supplement the information that will be on the slides with real world examples, court decisions, news articles, drawings etc.. • Expect to be nervous • Do an extensive review of your material so you are thoroughly familiar with the topic you are going to present 33 Preparation Skills • The better you know your subject the more confidence you will have • The more you practice the better you will be • Try your presentation out on family or co-workers 34 Delivery Skills • Make sure you speak so that students in the back have no trouble hearing you • Enunciate your words clearly • Avoid saying uhm….. • Avoid distracting mannerisms such as jingling change or playing with your hair 35 Delivery Skills • Involve the participants by encouraging and asking questions • Start on time; make sure that established breaks, lunch and ending times are adhered to 36 Delivery Skills • Pace your delivery according to the allotted time and the material to be covered • If working from a syllabus, make sure you cover everything that is on it, or explain changes 37 Delivery Skills • Keep close tabs on the climate of the class • Recognize your strengths and weaknesses • Work to maximize your strengths and minimize your weakness 38 Delivery Skills • Don’t pretend to know all the answers • If you don’t know something: – Discuss the question with the class – Let the student know you will get the answer, but be sure to remember to follow up 39 Fatal Mistakes • Poor first impression • No objectives • Dull, dry and boring • Frozen in one spot • Weak eye contact • Poor visual aids 40 Fatal Mistakes • Weak close • No humor • Poor preparation • No audience involvement • No enthusiasm or conviction • Poor facial expression 41 Don’ts • Don’t be too formal • Don’t be a know it all • Don’t be unprepared • Do not talk down to learners • Do not use profanity • Don’t be distracting 42 Don’ts • Don’t loose control • Don’t catch people unprepared • Don’t be afraid to say you do not know • Don’t avoid eye contact 43 Answering Questions • Repeat the question – Answer now/later – Redirect – Discussion • Don’t bluff – You know – You don’t know 44 Difficult Questions and Learners • Argumentative individual • Loaded questions • Long-winded • No good answer 45 Summary • Training is a System • Strive to Improve • Characteristics of Adult Learners • The Trainer’s Role • Teaching Adults • Learning Styles • Instructional Strategies • Instructional Media 46 Summary • Do’s • Planning and Preparation • Preparation Skills • Delivery Skills • Facilitator Responsibilities • Fatal Mistakes • Dont’s • Answering Questions • Difficult Questions and Learners 47 Summary • The instructor does not know everything. • Remember – you are leading a group. 48 Questions 49 References Bassi, L. J. & Van Buren, M. E. (1999). Sharpening the leading edge: The State of the Industry Report reveals the steps companies must take to ascend to the top of the training field. American Society for Training and Development: Alexandria, VA. Carey, L. & Dick, W. (1996). The systematic design of instruction. (4th ed.). New York: HarperCollins Publishers, Inc. Chrétien, J. (May/June 1995). Effective Training Techniques, OH&S Canada (11) 3. 29-33. 50 References Grimaldi, J. V. & Simonds, R. H. (1989). Safety management. (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Irwin. Handley, W. (1977). Industrial Safety handbook. ed.). London: McGraw-Hill Book Company (UK) Limited. (2nd Johnson, D. (1998). Adult educators need to have enthusiasm. Adult Learning (9) 4, 11-14. 51 References McMaster, S. (2000).Training Made Easy for Health, Safety, and Environmental Trainers. McMaster Training Associates ©. Krause, T. R. (1997). The behavior-based safety process: Managing involvement for an Injury-free culture. (2nd ed.). New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold. Saccaro, J. A. (1994). Developing safety training programs: Preventing accidents and improving worker performance through quality training. (2nd ed.). New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold. 52 Adult Learners WORKSHOP 53 Its Your Turn You will now have a chance to apply what you have learned. The task is to design an ergonomics training program for your workers. What topics would you include? 54 Group Exercise • Each group will develop a training module – Lesson Plan – Method – Workshops/exercises – Training Aids/Examples – Evaluation 55 Training Adult Learners Training Techniques 56