A.P. Psychology 3-C (C) - Heritability and Molecular Genetics
advertisement
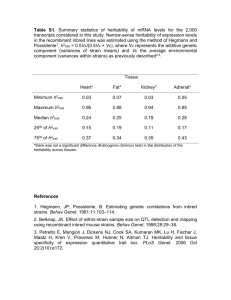
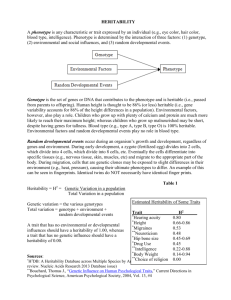
Unit 3-C (C): Heritability and Molecular Genetics Mr. McCormick A.P. Psychology Do-Now (In Journal) How much of your behavior do you attribute to biology? How much of your behavior do you attribute to your environment? Why? Heritability Heritability: The proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes Varies, depending on populations and environments being studied Measured from 0-1: 0 [0%] (low heritability): Influenced by environment 1 [100%] (high heritability): Influenced by genes E.g.: If the heritability of intelligence in a given population/environment is 40% (moderately low), then genetic influence explains 40% of differences in intelligence among that specific population Herit: Inherit Ability: Capability Heritability: Genetic or Environmental Differences? Observe the image of “Plant Heritability” What can explain variations of height among plants grown in the left flower pot? What can explain variations of height among plants grown in the right flower pot? Describe the Heritability (High/Low) of height variations among plants grown in the left flower pot. Describe the Heritability (High/Low) of height variations among plants grown in the right flower pot. What can explain variations of height among plants grown in both the left and right flower pots? Describe the Heritability (High/Low) of height variations among plants grown in both the left and right flower pots. Heritability Can you think of a real-life example, in which differences within a specific population were highly due to environment (low heritability)? Can you think of a real-life example, in which differences within a specific population were highly due to genetics (high heritability)? Nature Vs. Nurture Genes and environments work together in influencing human thought and behavior: Genes may predispose individuals to various physical and psychological traits, though one’s environment may affect the extent to which these traits develop Interaction: The interplay that occurs when one factor (heredity) affects another factor (environment) E.g. Someone with a predisposition to aggression may elicit others to treat them more defensively Nature Vs. Nurture Can you think of an example of an interaction between a “Nature” factor and a “Nurture” factor? Molecular Genetics Molecular Genetics: The subfield of biology that studies the molecular structure and function of genes “Bottom Up” approach to understanding biopsychology E.g. Identifying genes that influence one’s introversion vs. extroversion Homework Chapter 4 Quiz: “Nature, Nurture, and Human Diversity” Unit 3 Test: “Biological Bases of Behavior” Chapter 6 Outline: “Sensation and Perception” Unit 3 Project: “3-D Brain Model”