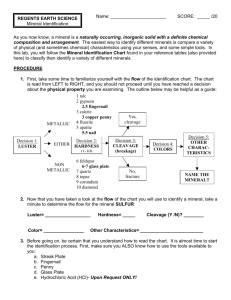
WELCOME TO THE ARIZONA MINING AND MINERAL MUSEUM*S
advertisement

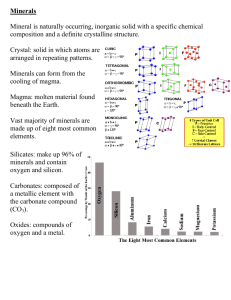
Where do Minerals Come From? pg 16 Minerals from Magma Magma comes from the mantle and cools. When it cools , it forms into minerals If it cools slowly, it forms large crystals. If it cools fast, it forms small crystals. Minerals from Solutions Minerals can dissolve into a solution. When enough minerals are in the solution, they stick together and precipitate. They form a solid while still in the solution. Minerals can also crystalize when the solution evaporates (called evaporates) WELCOME TO THE GLENDALE COMMUNITY COLLEGE MINERAL IDENTIFICATION PROGRAM presented by: Susan Celestian - Curator of the Arizona Mining and Mineral Museum Stan Celestian - Photographer © copyright 2002 TABLE OF CONTENTS Mineral Definition……………….……Slide 4 Hardness……………………………………..9 Cleavage……………………………….…...13 Fracture……………………………..…..….20 Streak………………………………………22 Luster…………………………..……….….24 Color…………………………………….…29 Specific Gravity…………………………...32 Taste……………………………………….41 Magnetism…………………………………42 Diaphaneity………………………………..46 Double Refraction…………………………50 Reaction to HCl (acid)…………………..…51 Crystals………………………………….…52 Isometric……………………………….…..54 Hexagonal……………………………….…58 Tetragonal………………………………….62 Orthorhombic…………………………..….66 Monoclinic………………………………...71 Triclinic……………………………………74 Resources………………………………….77 Introduction to Mineral Identification Basics Welcome to the fascinating world of Minerals. The purpose of this CD is to present you with some of the basic techniques used to identify minerals. This Power Point Presentation can also be viewed in the “edit” mode. Here you can view the many notes associated with the slides. Mineral Identification Basics What is a Mineral? There is a classic four part definition for mineral. Minerals must be: Naturally occurring Inorganic Possess a definite crystalline structure Have a definite chemical composition Cubic Fluorite Crystal Mineral Identification Basics What is a Mineral? Naturally Occurring Tourmaline Crystal from Brazil Minerals are not synthetic - they are produced by the natural geological processes working on Earth. For example, steel, brass, bronze and aluminum are not considered minerals in that they are not found in nature. Technically speaking, synthetic gemstones are not considered minerals. This area of mineralogy has a hazy boundary in that synthetic stones are in every way the same as the natural stones. But because they are produced in laboratories, they do not meet the classic definition of a mineral. Also note that many synthetic gemstones are “doped” with a fluorescent dye to distinguish them from natural stone. Mineral Identification Basics What is a Mineral? Inorganic Minerals are NOT produced by organic processes. As a result things like pearls, coral, coal and amber are not considered minerals. Also included in this “NOT a Mineral List” are Barite Rose - A flower like growth of Barite crystals. teeth, bones, sea shells and even kidney stones. Mineral Identification Basics What is a Mineral? Internal Structure Minerals are the result of atoms joining together through electrical bonds to produce a definite internal structure. It is the nature of the atoms and the strength of the chemical bonds that determine many of the minerals’ physical and chemical properties. Crystalline Pattern of Halite Red = Sodium Halite (salt) from Searles Lake, CA Green = Chlorine Mineral Identification Basics What is a Mineral? Definite Chemical Composition Halite - NaCl For every atom of Sodium there is an atom of Chlorine. Minerals can be expressed by a chemical formula. The internal order of minerals means that there is a definite relationship in the number of atoms that makes up the mineral. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES HARDNESS HARDNESS is defined as the resistance a mineral has to being scratched - its “scratchability”. Hardness tests are done by scratching one mineral against another. The mineral that is scratched is softer than the other. Pyrite Crystals Hardness of 6.5 Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES HARDNESS In this photo, a quartz crystal has been rubbed across a glass plate. The result is that the glass plate was scratched. The quartz is therefore harder than the glass. Quartz is harder than glass. HINT: In doing a hardness test try to pick a smooth or flat surface on the mineral to be scratched. Try to pick a point or a sharp edge on the mineral that you think will do the scratching. Glass is usually a good place to start because it is in the middle of the hardness table, it has a flat, smooth surface and it is easily obtained. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES HARDNESS Care must be taken on some minerals that crumble easily. Remember that hardness is the resistance a mineral has to being scratched - NOT how easily it breaks apart. The physical property related to the ease in which a mineral breaks is tenacity. Also be sure to determine the hardness of a mineral on a fresh surface whenever possible. Some minerals have a tendency to oxidize or corrode. These surface deposits usually have a different hardness than the fresh mineral. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES HARDNESS MOH’S SCALE OF MINERAL HARDNESS 6. FELDSPAR 1. TALC 7. QUARTZ 2. GYPSUM 8. TOPAZ 3. CALCITE 9. CORUNDUM 4. FLUORITE 10. DIAMOND 5. APATITE OTHER MATERIALS COMMONLY USED: 2.5 - FINGERNAIL 3 - COPPER PENNY 5.5 - GLASS 6-6.5 - STEEL FILE Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES CLEAVAGE CLEAVAGE is the property of a mineral that allows it to break repeatedly along smooth, flat surfaces. These GALENA cleavage fragments were produced when the crystal was hit with a hammer. Note the consistency of the 90o angles along the edges. These are FLUORITE cleavage fragments. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES CLEAVAGE Within this crystalline pattern it is easy to see how atoms will separate to produce cleavage with cubic (90o) angles. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES CLEAVAGE These pictures show different cleavage angles and the quality of cleavage. Fluorite has cleavage in four directions Mica A thin has sheet perfect of Muscovite cleavage inseen ONE on direction. edge. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES CLEAVAGE Common salt (the mineral HALITE) has very good cleavage in 3 directions. These 3 directions of cleavage are mutually perpendicular resulting in cubic cleavage. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES CLEAVAGE Rhombohedral Cleavage - 3 directions CALCITE Even these tiny fragments have rhombohedral cleavage. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES CLEAVAGE Blocky Cleavage 2 directions Orthoclase feldspar has good Note that the faces in the circle are at cleavage in 2 directions. Orthoclase Feldspar different levels. By adjusting the lighting, The appearance of this specimen is all ofblocky the parallel faces will reflect asimultaneously. hint that it has cleavage. that This resultsThe in aclue flash of the cleavagefaces is the lightspecimen from all has the parallel . fact that numerous faces will reflect light at the same time. Each face is parallel and light will reflect of each face producing a flash of light. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES CLEAVAGE TALC has micaceous cleavage. That is to say that it cleaves like mica (1 perfect direction) but, in talc the crystals are so small that they cannot easily be seen. Instead the effect is that the talc “feels soapy”. The second picture shows some of the talc that has cleaved onto the fingers. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES CLEAVAGE FLUORITE cleavage octahedron Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES FRACTURE FRACTURE is defined as the way a mineral breaks other than cleavage. This is a piece of volcanic glass called OBSIDIAN. Even though it is NOT a mineral, it is shown here because it has excellent conchoidal fracture. If you try this yourself, use caution. Conchoidal fracture in obsidian can produce extremely sharp edges. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES FRACTURE This Quartz crystal has been struck with a hammer to show how the external form of the crystal does not repeat when broken. This is a good example of conchoidal fracture. Note the smooth curved surfaces. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES STREAK STREAK is defined as the color of the mineral in powder form. Streak is normally obtained by rubbing a mineral across a “streak plate”. This is a piece of unglazed porcelain. The streak plate has a hardness of around 7 and rough texture that allows the minerals to be abraded to a powder. This powder is the streak. Hematite on Streak Plate Hematite has a reddish brown streak. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES STREAK Sphalerite is a dark mineral, however, it has a light colored streak. Next to the reddish brown streak of hematite is a light yellow streak. This is the streak of the sphalerite. Light colored streaks are often difficult to see against the white streak plate. It is often useful to rub your finger across the powder to see the streak color. Sphalerite has a light yellow streak. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES LUSTER LUSTER is defined as the quality of reflected light. Minerals have been grossly separated into either METALLIC or NONMETALLIC lusters. Following are some examples: Native Silver has a Metallic Luster Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES LUSTER METALLIC Stibnite Pyrite Galena Marcasite Mineral Identification Basics NON-METALLIC LUSTER VITREOUS Olivine - Peridot Quartz Wulfenite Spinel Mineral Identification Basics NON METALLIC LUSTER Miscellaneous Lusters Asbestos - Silky - Pearly Graphite has a greasy orApophyllite submetallic luster and easily marks paper. Sphalerite - Resinous Limonite - Dull or Earthy Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES LUSTER The moral to this story is to look at a fresh surface whenever possible. This piece of Native Copper is severely weathered. It does not look metallic. This is the same piece but the left side has been buffed with a steel brush. Note the bright metallic luster. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES COLOR The COLOR of a mineral is usually the first thing that a person notices when observing a mineral. However, it is normally NOT the best physical property to begin the mineral identification process. Following are some examples of color variation within mineral species followed by minerals that have a distinctive color: Various colors of CALCITE. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES COLOR Amethyst Ionic Iron Clear - Without Impurities Hematite Inclusions Various colors of Quartz. Chlorite inclusions End Day 1 Mineral Identification Basics INDICATIVE COLOR Azurite Turquoise Rhodochrosite Sulfur Malachite Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES TASTE IT IS NOT RECOMMENDED THAT A TASTE TEST BE PERFORMED ON MINERALS AS A STANDARD PROCESS. SOME MINERALS ARE TOXIC. However, the mineral HALITE is common salt and has a unique taste. Halite cubes from Trona, CA include picture of salt and salt shaker Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES MAGNETISM MAGNETISM is the ability of a mineral to be attracted by a magnet. This most commonly is associated with minerals rich in iron, usually magnetite. This is a piece of MAGNETITE with a magnet adhering to it. Magnetite is strongly magnetic in that a magnet will easily be attracted to it. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES MAGNETISM More sensitivity is achieved if instead of a large sample, small pieces are used. In this way, even weakly magnetic minerals will be attracted to the magnet. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES MAGNETISM This is a sample of “black sand” from Lynx Creek, Arizona. Its dark color is due to its high concentration of magnetite. See what happens when a magnet is place beneath the bottom right portion of the paper. This technique is used to separate out much of the unwanted material in the search for gold in placer deposits. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES MAGNETISM LODESTONE is a variety of Magnetite that is naturally a magnet. Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES DIAPHANEITY The manner in which minerals transmit light is called DIAPHANEITY and is expressed by these terms: TRANSPARENT: A mineral is considered to be transparent if the outline of an object viewed through it is distinct. TRANSLUCENT: A mineral is considered to be translucent if it transmits light but no objects can be seen through it. OPAQUE: A mineral is considered to be opaque if, even on its thinnest edges, no light is transmitted. Quartz with Spessartine Garnets Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES DIAPHANEITY TRANSPARENT: A mineral is considered to be transparent if the outline of an object viewed through it is distinct. Topaz from Topaz Mountain, Utah Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES DIAPHANEITY TRANSLUCENT: A mineral is considered to be translucent if it transmits light but no objects can be seen through it. Sylvite from Salton Sea, California Backlit Apophyllite Crystals Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES DIAPHANEITY OPAQUE: A mineral is considered to be opaque if, even on its thinnest edges, no light is transmitted. Schorl - The black variety of Tourmaline Mineral Identification Basics DOUBLE REFRACTION DOUBLE REFRACTION: Is a property shared by many minerals ( but not those in the isometric crystal system). It is best displayed in the mineral CALCITE. This image clearly shows the double image below the calcite Mineral Identification Basics CHEMICAL PROPERTIES REACTION TO HYDROCHLORIC ACID Some minerals, notably the carbonates, react to cold dilute HCl. In this illustration a piece of CALCITE is shown to react (fizz) after HCl is applied. Calcite Reacts to HCl Density How much mass is in a given volume. D = m/v Mineral Identification Basics PHYSICAL PROPERTIES CRYSTALS A CRYSTAL is the outward form of the internal structure of the mineral. The 6 basic crystal systems are: ISOMETRIC TETRAGONAL Drusy Quartz on Barite MONOCLINIC HEXAGONAL ORTHORHOMBIC TRICLINIC Mineral Identification RESOURCES For lots of useful images of minerals and more facts about minerals, check out this web site: http://www.gc.maricopa.edu/earthsci/imagearchive/index.htm This copyrighted Power Point CD was produced strictly for educational purposes. Any attempt at using the images within this program for monetary gain is illegal. The authors have given permission to use the program or parts of it, providedTHE credit is given to the Arizona Mining and Mineral Museum, its Curator - Susan Celestian and the photographer Stan Celestian. END