Plastic Laminates
advertisement

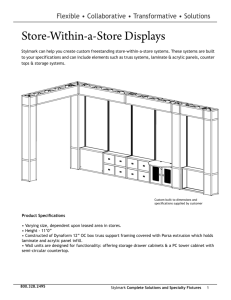
Plastic Chelsea Glynn • Plastic is referred to as a synthetic material which means that it is synthesized from oil, starch, or sugar. • It is moldable • It is most commonly derived from petrochemicals, which are chemical products from petroleum. History • The first man-made plastic was revealed by Alexander Parkes at the 1862 Great International Exhibition in London. • In 1869 a plastic that succeeds is celluloid. It was synthesized from cotton fiber and the plant material camphor, originally to make a cheaper substitute for ivory billiard balls. • In 1897 the discovery of casein plastics, produced by reacting casein (milk protein) with formaldehyde. • Cellulose acetate, a thermoplastic, was introduced as a molding compound in 1927. • The demand for plastics has increased steadily; plastics are now accepted by designers and engineers as basic materials along with the more traditional materials. Description • Two broad distinctions of types of plastics are thermoset plastics and thermoplastics. • Thermoset plastics cannot have their shape altered after production • Thermoplastics are plastics that can be softened and formed with heat. Acrylic • One thermoplastic material that is commonly used is acrylic. • Acrylic is mainly used in its solid, clear form. It is chemically clear, colorless resin, but it can have color introduced into the material before forming. • It can be heat formed at about 350°F. • It is available in sheets and rods that can be bonded together. • Acrylic is considered for locations where glass would be too heavy or the breakage too dangerous. Solid Surfacing • Solid surfacing products are nonporous, thermoplastic or thermoset materials. • This material can be worked with the same kinds of tools used to cut and shape wood. • It is used to make sinks, countertops and other moldable objects. Engineered Stone • Engineered stone is natural quartz combined with polyester resins. • It is typically available in 4 –foot widths and 10-foot lengths. • It is resistant to scratching, burning and staining. • Engineered stones are nonporous and they can be used where natural stone is prohibited, such as food service and health care applications. • It is cheaper and more chemically resistant than acrylic. Plastic Laminates • Plastic laminate is layers of paper bonded together with resins to produce a surfacing veneer. • Two types are high pressure and low pressure laminate. • High pressure laminate is kraft paper saturated with phenolic resin. • Low pressure laminate is a melamine resin-saturated paper with a color or a gravure print decorative surface. Thermally Fused Foils • Foils are a cellulosic paper soaked with melamine, acrylic, and urea resins. • Once the foil is cured it can be printed (photographic wood grain is common) and embossed (many sheen levels are created with texture). • Surface textures can be molded to imitate the texture of materials. Decorative and 2D Foils • Solid colored, pattern less thermofoil is referred to as 2D foil, low pressure laminate, or melamine. • Considered an economy material and used when cost is a primary consideration. • Sensitive to heat Rigid Thermofoils • Applied to Medium Density Fiberboard substrates that have contours, raised panels, curves and intricately shaped edges. • They are called 3D thermofoils because they conform to complicated shapes. • They create a seamless surface for environments where precise maintenance is important, such as healthcare, childcare, or educational buildings. Application • Laminates should be bonded to substrates • Laminate details for an exposed edge may require some attention because the thin material is just a surface and the side of the sheet will be shown. • Screws and other mounting hardware may be used to hold thicker surfaces in place. • Glues that are specified may fuse the surfaces together by chemically interacting with the material. Application • Acrylic items can be self supporting and the seams can be chemically welded or fused. • For high-pressure plastic laminate, the structure designed will be built from a different material and covered with laminate sheets. • The substrate for thermofoil is particleboard or medium density fiberboard but they are mostly laminated to plywood. Maintenance • Plastic can shrink and grow with temperature so it should be fully acclimated to the site conditions before installing. • Acrylic is damaged by window cleaners containing ammonia. • Acrylic tends to attract and show dust, so it must be dusted frequently. • All plastic surfaces need to be protected from scratching. • Damage to plastic laminate is usually permanent. Organization of the Industry • Manufacturers sells to distributors or dealers and dealers selling to trades. • It is uncommon for end users to purchase the material. Sustainability • Thermoset plastics are not currently recyclable. • Thermoplastic resins are recyclable but the industry lacks the tools to recycle them. • Bio-based plastics are under development, they come from renewable resources and some can biodegrade under the right conditions. • Petro-free resin is one example of a bio-based plastic used in the making of a solid surface. • Plastic certification: ASTM D6400-04 Cost • Laminates are one of the most economical surfacing materials. • The plastics are not expensive so the greater cost will come from fabrication and installation. • Custom-cast plastics will be more expensive. High Pressure Laminate Detail Manufacturers • EVCO Plastics • CW Plastics • Rex Plastics • Mack • Ameri-Kart Video • Plastic Injection Molding https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eUthHS3MTdA