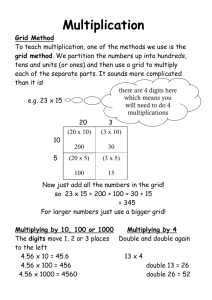
Presentation
advertisement

Grid-based System for Flood Forecasting Ladislav Hluchy Institute of Informatics SAS in co-operation with Water Research Institute, Vah River Authority and Slovak Hydrometeorological Institute Slovakia hluchy.ui@savba.sk Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Outline • • • • • • • Introduction Flood Forecasting Grid infrastructure for Flood Forecasting Use cases Grid-based Implementation Results Conclusion Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Flood Forecasting one of the Geospatial Applications • Applications that use data from Geographic Information System (GIS) • Typical applications: flood forecasting, fire simulations, environmental risk management etc. Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Flood Forecasting • Topical problem: floods have caused widespread damages in the recent years • Common interest: many countries threatened • Many potential users: governments, flood crisis teams, insurance companies, public, • Requires Grid technology Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS ANFAS Architecture Database Server GIS GISAccess Access component component GIS GIS ArcView ArcView Modelling Server Numerical Numerical Model Model ANFAS bus extension (CORBA / RMI) ANFAS bus extension (CORBA / RMI) ANFAS core component Data Data Manager Manager Map Server Map Server Model Access Model Access Component Component Model Manager Model Manager ANFAS exchange bus (Middleware : RMI, CORBA, Http) Co-operative, Co-operative, Explanatory Explanatory Component Component File File Exchange Exchange Component Component Administration Administration &&user usermanager manager Application Application Server Server HTTP Protocol HTTP Protocol Modelling Modelling preparation preparation Modelling Modelling activation activation &&follow-up follow-up Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Data Preparation Results Results exploitation exploitation ANFAS Client ANFAS Integration to ANFAS core Machine 1 ANFAS Core Server Use of the i-cluster in the ANFAS system currently hosted by EADS-MS&I Web i-cluster Machine 2 hosting RPS Controller LAN Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS SMS/FESWMS • FESWMS has been developed under funding by the U.S. Federal Highways Administration (FHWA) • FESWMS is specifically suited for modeling regions involving flow control structures, such as are encountered at the intersection of roadways and waterways. Specifically, the FESWMS model allows the user to include weirs, culverts, drop inlets, and bridge piers into a standard 2D finite element model. • As there is highway planned at the Vah River pilot site in Slovakia, the choice of FESWMS model is important • SMS provides graphical tools for defining these structures and controlling analysis using the FESWMS model. Both pre- and postprocessing capabilities are included in the interface. Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS Detailed FESWMS Solution schema structures Nonlinear solver Input files Finite element Generating matrix Nonlinear solver Linear solver write solution to the file Update solution OK Solution file Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS Parallel matrix generation Generating partial matrix Generating partial matrix Generating partial matrix PARALLEL LINEAR SOLVER Updating solution Updating solution Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Updating solution ANFAS Implementation issues Real flood modeling software is much more complicated than its mathematical model: – Mathematical model of flood is well-known (partial differential equations finite elements nonlinear solver linear solver) – Real software has to deal with • Input processing: different types input data, different variations of each type, different formats of each variation • Special cases: wetting/drying, raining/evaporation, special constructions (bridges, dams, culverts), wind effect, … • Calibration of results • Graphical user interface (GUI), visualisation • Error checking, documentation As the result, source code of real software may be hundreds times longer than source code of mathematical model Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS Remote processing Post-processing Remote processing Pre-processing Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Processing input data Parallel computational kernel Save solutions ANFAS Planned highway in the Váh pilot site Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS Main part affected by highway Bytca city Predmier village LIDAR+highway position Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS Predmier village in orthophotomap Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS Predmier village in LIDAR Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS TIN network at Predmier Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS Scenario: Water level for current terrain situation (Q-100-year) Water depth Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS Scenario: Water level for highway without bridges (Q-100-year) Water level is about 70cm higher than for situation without highway Water depth Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 ANFAS Scenario: Water level for highway with 2 bridges (Q-100-year) Water level is about 30cm higher than for situation without highway Water depth Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Why Grid? • Cooperation: requires cooperation between many organizations (meteorological institutes, river authorities) from many countries • Data management: needs large amount of data of different sources, different owners, different countries, different access right • Computation power: forecasting require large computational power for modeling and simulation Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Virtual Organization • Purpose – Shared data and computational power for flood forecasting – Cooperation between users for flood forecasting • Requirements – – – – – Identify and define clear relationships between users Authentication: certificate authorities Authorization: access right for each data/resources Collaborative tools Security Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Flood Forecasting VO Data sources surface automatic meteorological and hydrological stations systems for acquisition and processing of satellite information meteorological radars External sources of information Global and regional centers GTS EUMETSAT and NOAA Hydrological services of other countries High performance computers Storage systems Grid infrastructure meteorological models hydrological models databases hydraulic models Users Flood crisis teams meteorologists hydrologists hydraulic engineers river authorities energy insurance companies navigation Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 media public Virtual Organization for Fire Simulation Data sources GIS GIS Meteorological data source FIRE MODEL Fuel type - vegetation - canopy cover Topography -elevation -slope Weather Descriptive Numerical Parameters - wind direction, speed - temperature, rel. humidity High performance computers Storage systems Grid infrastructure Fire Modelling System FARSITE databases Users Fire Management Creation Decision Support system, prevention -Terrain, resources, - capacities Fire suppression authorities - training - operation mode Ecosystem authorities Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Universities, Insurance companies Data management • Typical data: satellite images, radar images, measured data from hydrological stations, topographical data, historical data, simulation results • Different formats, different quality, different owners, different access right • Metadata server:data description, security, replication Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 FloodVO data transfer Data sources surface automatic meteorological and hydrological stations systems for acquisition meteorological External sources of information Global and regional centers GTS and processing of radars EUMETSAT and NOAA satellite information Hydrological services of other countries Storage systems High performance computers Grid infrastructure meteorological models hydrological models Databases hydraulic models Users Flood crisis teams meteorologists hydrologists hydraulic engineers river authorities energy insurance companies navigation Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 media public DataGrid • • • • EDG Replica Manager EDG Local Replica Catalogue EDG Replication Metadata Catalogue EDG Replica Optimization Service Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 DataGrid (cont.) Storage control Metadata EDG LRC Storage Element EDG RM EDG RMC EDG ROS EDG LRC Storage Element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 EDG LRC Storage Element Grid computing • Many multidisciplinary simulations are needed for flood forecasting • For critical situations, short response times are very important • Numerical simulations are computationally intensive • Grid can offer the necessary computational power Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Visualization • Data are stored in many different formats • Unified visualization tools may simplify the userinterface • Many data for flood forecasting has spatial character => GIS software may be used as the unified visualization tool Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Portal • The unified user-interface • Allow users access to the VO remotely • Simple requirements on clients - based on standard Web technologies Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 3 current portals 1. Based on GridPort using Globus grid toolkit 2. Based on Jetspeed portal framework using DataGrid/CrossGrid services 3. Migrating Desktop - java fat client using DataGrid/CrossGrid services Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 GridPort • A set of Perl scripts that enable Perl based portal (its CGI scripts) to use grid services of underlying Globus toolkit • Wraps Globus’ command line tools • Provides session management • Provides no additional portal infrastructure Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Architecture of GridPort based portal Resource 1 Globus toolkit Resource 2 … GridPort toolkit Portal (Apache web server) (GSI, MDS, JobManager, GridFTP, …) Storage & Portal Machine Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 … User’s web browser Storage Resource n User’s web browser GridPort screenshot Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Job submission in Flood-VO XML file (parameter description) Config. file (default values of parameters) New config file globus-job-submit machine job_script config_file Job script file Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Flood-VO: Job list Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Flood-VO: Field data SHMI II SAS RDBMS Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Time Value 00:00:00 102.00000 cm 01:00:00 126.00000 cm 02:00:00 103.00000 cm 03:00:00 80.00000 cm 04:00:00 70.00000 cm 05:00:00 65.00000 cm Jetspeed • Portal framework • Server-side Java based engine (application server) • Client services are plugged using software components called portlets. • User can arrange portlets – position, size, visibility Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Jetspeed - architecture Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Application portal screenshot (Jetspeed) Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Application Portal Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Migrating Desktop (MD) • Java application (applet) running at the client computer • Provides interface to all basic grid services (authentication, job management, file management) • Application specific job parameter input and job submission is supported via application plug-ins • has built-in viewer for common picture formats (jpeg, gif, png) and text files, advanced visualization of results via application specific visualization plug-in • Being developed in the context of the CrossGrid project Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Migrating Desktop Screenshot of MD with Job submission wizard dialog Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Use case: Cascade simulation Data sources Meteorological simulation Hydrological simulation Hydraulic simulation Portal Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Model characteristics • ALADIN (meteorological model) – – – – – – Limited area model Operated by 13 Euro-Mediterranean countries ALADIN/SLOVAKIA operated by SHMI More than 1M lines of source code (mainly F90) Developed for 64 bit big-endian architecture Proprietary - requires nondisclosure agreement Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Model characteristics • ALADIN (meteorological model) – Type: MPI parallel task, possible parameter studies – multiple executions – CPU time: approximately one hour on 8 processors – I/O size: 33/180 MB per run – Scalability: on fast Ethernet up to 8 processors – Input data: boundary conditions – Output data: quantitative precipitation forecast, temperature Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Model characteristics • HSPF (hydrological model) – Type: sequential task, multiple executions (high throughput computing) – CPU time: very small (seconds - minute) – I/O size: 1-10 MB – Scalability: HTC – Input data: quantitative precipitation, temperature, topographical data – Output data: hydrograph Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Model characteristics • FESWMS (hydraulic model) – Funded by US Federal Highway Administration – Distributed in commercial package SMS by EMS-I – Source code available (direct cooperation with developer) – Optimized and parallelized by II SAS Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Model characteristics • FESWMS (hydraulic model) – Type: MPI parallel task, multiple executions with different input data – CPU time: 10min to several hours per a task – I/O size: 10-100 MB – Scalability: good for smaller number of processor (to 16). – Input data: inflow, topographical data – Output data: water levels and velocities Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 DaveF model • A time-explicit finite-volume model from the same developers as FESWMS. It is considered as the complement of FESWMS and it is best suitable for unsteady state with critical or super-critical flow (dambreaking, flash flood, flood with wetting/drying in large expanses) • DaveF uses the same graphical environment like FESWMS (SMS) and similar input/output format =>can be easily added into ANFAS system • Parallel version of DaveF has been developed for clusters by II-SAS and shows good results Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Architecture Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Login to FloodVO Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Choose simulation Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Enter input parameters Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Visualization Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Visualization Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Download simulation results Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Cascade simulation Call meteorology master script Run meteorological simulation Extract hydrological input from results Call hydrology master script Run hydrological simulation Check results if (inflow > critical flow) If yes: call hydraulics master script run hydraulic simulation Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Cascade simulation Call meteorology master script Run meteorological simulation Extract hydrological input from results Call hydrology master script Run hydrological simulation Check results if (inflow > critical flow) If yes: call hydraulics master script run hydraulic simulation Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Cascade simulation Call meteorology master script Run meteorological simulation Extract hydrological input from results Call hydrology master script Run hydrological simulation Check results if (inflow > critical flow) If yes: call hydraulics master script run hydraulic simulation Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Cascade simulation Call meteorology master script Run meteorological simulation Extract hydrological input from results Call hydrology master script Run hydrological simulation Check results if (inflow > critical flow) If yes: call hydraulics master script run hydraulic simulation Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Cascade simulation Call meteorology master script Run meteorological simulation Extract hydrological input from results Call hydrology master script Run hydrological simulation Check results if (inflow > critical flow) If yes: call hydraulics master script run hydraulic simulation Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Cascade simulation Call meteorology master script Run meteorological simulation Extract hydrological input from results Call hydrology master script Run hydrological simulation Check results if (inflow > critical flow) If yes: call hydraulics master script run hydraulic simulation Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Cascade simulation Call meteorology master script Run meteorological simulation Extract hydrological input from results Call hydrology master script Run hydrological simulation Check results if (inflow > critical flow) If yes: call hydraulics master script run hydraulic simulation Resource broker Computing element Portal Storage element Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=315 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=510 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=720 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=810 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=915 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=1005 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=1110 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=1305 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=1515 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=1710 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=1905 minutes the maximum water level Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=2100 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=2310 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=2700 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation for t=2910 minutes Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation step 1 time 0 Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation step 3 time 0:30 Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation step 4 time 0:45 Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation step 50 time 12:15 Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation step 100 time 24:45 Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Dynamic flood simulation step 150 time 37:15 Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Future work • • • • • Adding more models Performance analysis and optimization Improving data management (repositories) Adding more information about data (metadata) Adding collaborative tools Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Use case: Simulation sequence Meteorology D Meteorology CZ Meteorology SK Hydrology Hydrology Hydrology Hydrology Hydrology Hydrology Meteorology A Hydraulics Meteorology CH Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Meteorology H Flood crisis teams Experts River authorities Data providers Virtual Organization for Flood Forecasting Energy FloodGrid Computing centers Danube River basin information Insurance companies Public Navigation Media Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003 Knowledge based Flood forecasting Data Sources Actual data from observation stations (relevance) Metadata & Knowledge Repository Simulation Metadata (parameters, area, sim. method, etc) Meteorological Simulations User interaction (Semiautomatic) External Resources (Web services) Hydrological Simulations Automatic or Semiautomatic Reasoning Hydraulic Simulations Job Submission (based on evaluation of previous jobs outputs) Grid infrastructure Information about job run (relevance) Visualization/Output Processing Cracow Grid Workshop ’03, 27-29.10.2003