Tutorial
advertisement
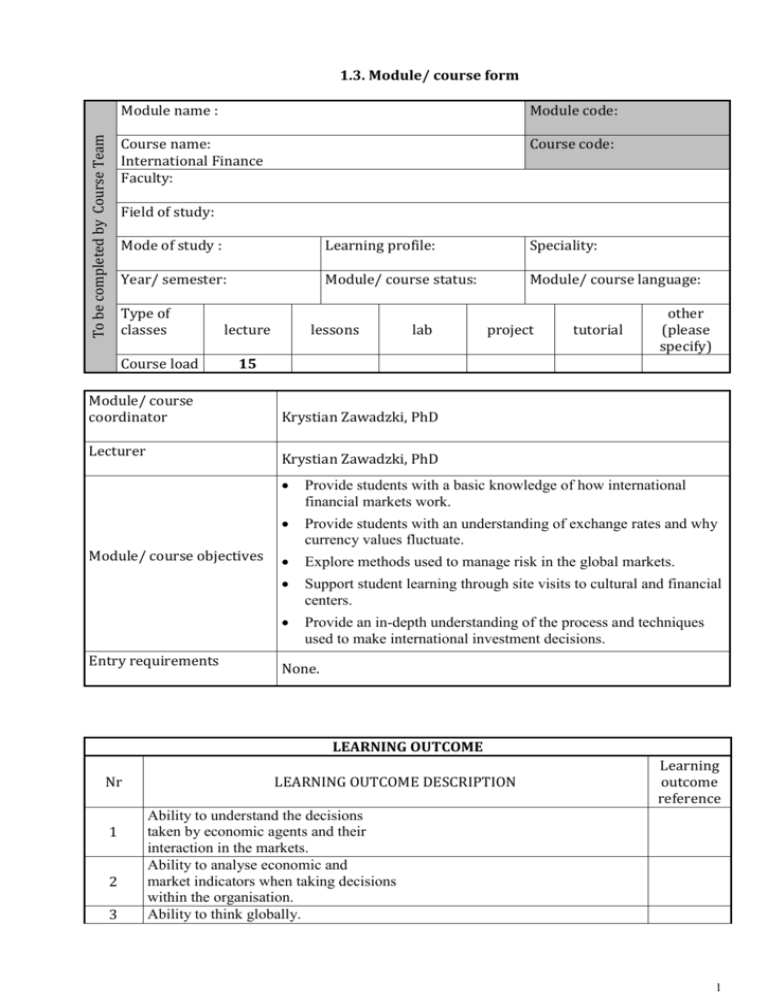
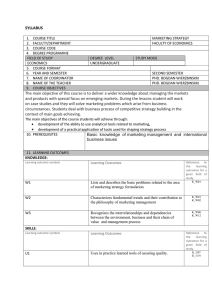
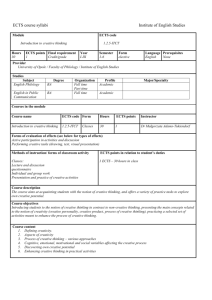
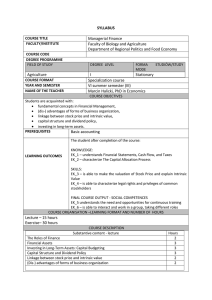
To be completed by Course Team 1.3. Module/ course form Module name : Module code: Course name: International Finance Faculty: Course code: Field of study: Mode of study : Learning profile: Speciality: Year/ semester: Module/ course status: Module/ course language: Type of classes Course load lecture lessons lab project tutorial other (please specify) 15 Module/ course coordinator Lecturer Krystian Zawadzki, PhD Krystian Zawadzki, PhD Module/ course objectives Entry requirements Provide students with a basic knowledge of how international financial markets work. Provide students with an understanding of exchange rates and why currency values fluctuate. Explore methods used to manage risk in the global markets. Support student learning through site visits to cultural and financial centers. Provide an in-depth understanding of the process and techniques used to make international investment decisions. None. LEARNING OUTCOME Nr 1 2 3 LEARNING OUTCOME DESCRIPTION Learning outcome reference Ability to understand the decisions taken by economic agents and their interaction in the markets. Ability to analyse economic and market indicators when taking decisions within the organisation. Ability to think globally. 1 4 CURRICULUM CONTENTS Lecture International Real Business Cycles International Risk Sharing and Incomplete Markets Global Imbalances Globalization and the Multinational Firm Puzzles and new directions in international macroeconomics International Price Setting The Foreign Exchange Market Exchange Rates Foreign currency futures and options International Capital Markets Risk Management and Hedging Strategies Capital Flows and Multinational Production Foreign Direct Investment International Trade Finance Final exam Tutorial Basic literature MADURA, International Corporate Finance, South Western College, 11/e, 2011 BEKAERT and HODRICK, International Financial Management, Prentice Hall, 2/e, 2011 - EUN and RESNICK, International Financial Management, McGrawHill/Irwin, 6/e, 2011 - KRUGMAN, OBSTFELD and MELITZ, International Economics: Theory and Policy,Prentice Hall, 9/e, 2011 Additional literature Teaching methods The teaching and learning processes will be based on lectures preceded and followed by independent study by students. Learning outcome number Assessment method Student presentation Activity and disussion Final exam Form and terms of an exam Written exam at the end of the semester STUDENT WORKLOAD Participation in lectures Independent study of lecture topics Number of hours 15 20 2 Participation in tutorials, labs, projects and seminars Independent preparation for tutorials* Preparation of projects/essays/etc. * Preparation/ independent study for exams Participation during consultation hours Other TOTAL student workload in hours Number of ECTS credit per course unit 6 14 5 4 64 Number of ECTS credit associated with practical classes Number of ECTS for classes that require direct participation of professors 3