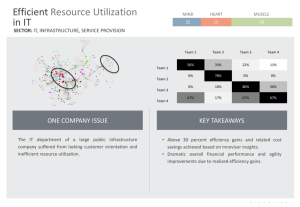
Hierarchical Power Management for Asymmetric Multi
advertisement

Hierarchical Power Management for Asymmetric Multi-Core in Dark Silicon Era Thannirmalai Somu Muthukaruppan Mihai Pricopi Vanchinathan Venkataramani, Tulika Mitra School of Computing, National University of Singapore Sanjay Vishin Cambridge Silicon Radio DAC’13 Motivation Dark silicon phenomenon ◦ A chip can have many cores but a significant fraction of them are left un-powered, or dark, at any point in time due to power and thermal limits. Asymmetric multi-core architecture as an alternative ◦ Cores with diverse power-performance characteristics. This paper Introduce a hierarchical power management framework for asymmetric multi-cores. ◦ Builds on control theory. ◦ Coordinates multiple controllers in a synergistic manner to achieve optimal powerperformance efficiency. ◦ Respects the thermal design power budget. Scenario System exceeds the Thermal Design Power(TDP). ◦ => power budgets have to be reduced. ◦ => scaling down voltage and frequency. ◦ => the QoS degrades. Reverse the process once the system load decreases. Avoid oscillations! ARM big.LITTLE TC2 ◦ Two high performance Cortex A15 and three energy-efficient Cortex A7 ◦ 3rd model(HMP) ◦ Per-cluster DVFS Impact of Active Cores on Cluster Power Heart Rate The throughput of the critical kernel of a QoS task. ◦ Ex: number of frames per second(fps) for a video encoder. Heartbeats in QoS benchmark ◦ Heart rate = heartbeats per second Feedback Based Controller Proportional-Integral-Derivative(PID) Controller de(t ) z (t ) K p e(t ) K i e(t )dt K d dt ◦ Kp, Ki, Kd : proportion, integral, derivative gain. Framework Overview Resource Share Controller Target heart rate hrref(Qi) = [hrrefmin,hrrefmax] Measured heart rate hr(Qi) Slice s(Qi) Core Utilization u(Qi), u(NQj): utilization of of QoS and non-QoS tasks. u(Ck) = Σu(Qi) + Σu(NQj): utilization of core k u(Clm) = max(u(Ck)) : utilization of cluster m DVFS Controller Target utilization uref(Clm) = max(uideal, utarget(Clm)) Chip-Level Power Allocator Hrthrottle(Qi): throttle factor of heart rate. QoS Controller Ideal Heart Rate hrideal(Qi) = [hridealmin,hridealmax] Target Heart Rate hrref(Qi) = [hrrefmin,hrrefmax] = hrideal(Qi) x hrthrottle(Qi) Load Balancer and Migrator Balancer ensures that the cores within a cluster are evenly load balanced. Migrator migrates tasks between clusters. Experimental Setting Versatile Express Development Platform ◦ 2 A15 + 3 A7 Linux Completely Fair Scheduler(CFS) Benchmarks: Asymmetric V.S. Symmetric x264 benchmark ◦ Phases with varying performance requirements during execution. HPM V.S. Linaro scheduler HPM V.S. Linaro scheduler Response under TDP Constraint Conclusion The authors present a power management framework for asymmetric multi-cores that based on multiple controllers. ◦ Exploits asymmetry among the cores through selective migration and employs DVFS to minimize power consumption while satisfying QoS constraints.