Curriculum Design and Delivery
MEDIU
INFORMATION ON AREA 2: CURRICULUM DESIGN AND DELIVERY
2.1
Academic Autonomy
Information on Benchmarked Standards
2.1.1
Describe the provisions and practices that ensure the autonomy of the department in
curriculum design and delivery, and in allocation of resources. Provide supporting
documents where appropriate.
MEDIU aims to provide a high standard and quality of service in respect of its programmes of
study, services and facilities, as well as the spirit of enterprise.
With reference to the university’s constitution, Section 20 (3)
A School, Centre, Academy and Institute shall be responsible to the Senate in relation to
arrangement of subjects taught within the jurisdiction of that School, Centre, Academy and
Institute, following whichever relevant, and may exercise any other function given to them by
Statute, rules and regulations.
Article 2 from the Faculties and Institutes Rules states that:
The responsibility of managing the faculty, institute, or academic centre is assigned to:
-
Council of the faculty, institute, or academic centre.
-
Dean of a faculty, institute, or director of an academic centre
Faculties, institutes and centres are given the right and full responsibility to design their
curriculum in accordance with relevant requirements and needs in order to meet their set
targets.
Resources allocation is, usually, based on the following input:
-
Academic staff planning
-
Current and expected number of enrolled students
-
New planed programmes
-
Lecturer-student ratio in the field of study
-
Required facilities and equipment that is relevant to the field of study.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
1
Curriculum Design and Delivery
MEDIU
Resource allocation Review Process
The process for reviewing resource allocation may be top-down or bottom-up and involves
decisions made at the following meetings:
The University council
The University Top Management Committee (TMC)
Faculty/Institute/School Management
Recommendations from management audit, quality audit and financial audit are used, as well,
to review the allocations of resources.
2.1.2
Show the relationship between the departmental board and the senate.
The departmental board operates under faculty board, which endorse all its academic related
decisions. The faculty board, then, have to submit all endorsed decisions to the Senate for
approval before they are implemented by the department/faculty
2.1.3
How does the department ensure that the academic staff have sufficient autonomy in areas
of his expertise?
Academic staff is given the right and responsibility within the jurisdiction of their Faculty,
School, Centre, Academy and Institute to design their curriculum in accordance with their field
of expertise in order to meet their faculty objectives and serve the university targets.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
2
Curriculum Design and Delivery
MEDIU
Information on Enhanced Standards
2.1.4
State the departmental policies and practices to address conflict of interest, for example,
staff involvement in private practice, part-time employment and consultancy services.
MEDIU addresses conflicts of interest according to:
Policies of the Employment Guidelines of MEDIU
Staff may be given the permission based on case to case basis and with the permission
of the university administrator MEDIU Work Ethics
Letter of Undertaking
Oath of Integrity in Public Service
2.1.5
What are the HEP’s plans to expand the autonomy of the academic staff? What is the
department’s role and how does it support this?
MEDIU adopts a working style that encourages the academicians to be independent and selfdirected in all academic activities within the area of their expertise. MEDIU are planning for a
full program of training, workshops, and seminars to promote and expand the autonomy of
the academic staff.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
3
Curriculum Design and Delivery
2.2
MEDIU
Programme Design and Teaching-Learning Methods
Information on Benchmarked Standards
2.2.1
Describe the processes, procedures, and mechanisms for curriculum development. How are
the academic and administrative staffs involved in this process?
The curriculum development process can be divided into five main steps:
1) Needs assessment.
2) The planning session.
3) Content development.
4) Pilot delivery and revision
5) Finalising the completed curriculum package.
The steps are managed and supervised by committees that are composed from experts in the
related domain and supported by the administrative officers of the faculty.
These committees present their output to the faculty for further discussion and endorsement.
After getting the approval of the faculty, the draft will be presented to the Senate committee
of curriculum for further deliberation and endorsement of the Senate. The approved
curriculum will then be submitted to MQA for assessment and recommendation and the
approval of the Minister of Higher Education.
2.2.2
What are the various teaching and learning methods used in curriculum delivery to achieve
the programme learning outcomes? Describe them.
Teaching and learning will be through a mixture of lectures, tutorials, seminars, practical
classes, projects, supervised individual and group written work, and internship. Much of the
teaching materials will be provided in electronic form, with ALIM (Advanced Learning and
Interactive Management System). The student will progress from being guided towards the
relevant material to become more independent as they progressively adapt self-learning and
achieve the program learning outcomes. Electronic and online teaching, learning, and
assessment will be used where practical and appropriate.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
4
Curriculum Design and Delivery
2.2.3
MEDIU
Show evidence that the department have considered market and societal demand for the
programme as well as sufficient resources to run it.
The program is designed to meet the growing demand of the market for engineers locally in
Malaysia as well as abroad particularly the Muslim countries. The programme offers
mathematics and physical sciences to prepare students to further their studies in engineering
degrees at the Faculty of Engineering of MEDIU.
The university has planned sufficient resources at all levels to run the program professionally
and effectively.
2.2.4
Explain how the programme promotes critical enquiry, develop problem solving, decision
making, and analytical thinking skills, as well as encourages students to take active
responsibility for their learning, and prepares them for lifelong learning.
The program is structured to promote critical enquiry, develop problem solving, decision
making, and analytical thinking skills, as well as encourages students to take active
responsibility for their learning, and prepares them for lifelong learning via a set of welldesigned and dedicated modules throughout the program. In addition to the adopted
teaching, learning, and assessment methods (2.2.2).
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
5
Curriculum Design and Delivery
2.2.5
MEDIU
Describe the diverse learning methods and sources, within and outside the classroom,
where students acquire knowledge, mastery of skills, and develop attitudes and behaviour
in preparation for their learning, individual growth, future work and responsible citizenry
(e.g., co-curriculum).
Teaching and learning will be a mixture of lectures, tutorials, and practical sessions associated
with each module within classrooms and laboratories that are equipped with the appropriate
and latest resources, e.g. computers, software, devices and tools.
Additionally, the students will have access to the university co-curriculum programs that will
help them to gain valuable personal and professional skills, effective oral and written
communication, decision making, financial management, problem solving, ethics and
tolerance as well as personal and professional balance.
Information on Enhanced Standards
2.2.6
Show how the programme encourages a multi-disciplinary approach and co-curricular
activities in enhancing and enriching the personal development of the learner.
The programme is structured to encourage a multi-disciplinary approach and co-curricular
activities in enhancing and enriching the personal development of the learner, by an array of
MQA, University, faculty, core, and elective modules. Consequently, it is expected that, upon
completion of the course, students will be equipped to enter the engineering degree course
at the Faculty of Engineering MEDIU.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
6
Curriculum Design and Delivery
2.2.7
MEDIU
How are external sources engaged in the needs analysis for this programme? How are their
commentaries utilised to improve the programme?
MEDIU and the faculty have always engaged external sources to seek their views and opinion
on the proposed programmes at the university and the faculty level, in terms of their
marketability, acceptability, and viability. The external sources opinion and recommendation
are sought for in formal or informal manner to be subsequently incorporated in the process of
reviewing the programmes wherever/whenever relevant.
2.2.8
What are the co-curricular activities that enrich student learning experience, and foster
personal development and responsibility?
The university provides the students with opportunities to be involved in professional
societies, student design competitions, and university co-curricular activities, and help to
prepare students for professional practice.
2.3
Curriculum Content and Structure
The department is required to complete Table 1 and 2 to highlight the core subject matter essential
for the understanding of the concepts, principles and methods that support the programme
outcomes, as well as the requirements of the discipline for an award taking into account the
appropriate discipline standards and international best practices for the field.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
7
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Information on Benchmarked Standards
2.3.1
Classification of subjects (Provide information where applicable in Table 1):
Table 1: Components of the programme and its value
Subject Classification
Credit Value
1.
MQA modules
2.
Core/Major/Concentration:
Courses/modules
projects/ thesis /dissertation
9
15%
42
70%
-
5%
4.
Minor courses/modules
3
7.
Others (University)
6
Total Credit Value
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
Percentage
10%
100%
8
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
2.3.2
List the subjects offered in the programme, and include their classification.
Please arrange by year and semester offered as in Table 2.
Table 2. List of course/module offered in the programme
Semester/
Year Offered
Name and Code of
Course/Module
1
1/1
English for General Purposes
2
1/1
3
Classification
(Major/Minor/
Elective/Audit)
Credit
Value
University
3
Islamic Studies/ Moral and
Ethics
MQA
3
1/1
Mathematics I
Major
4
1/1
Mathematics II
Major
5
1/1
Mathematics III
Major
Name(s) of
Lecturer
4
4
4
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
1/1
1/1
1/1
2/1
2/1
2/1
2/1
2/1
2/1
2/1
3/1
3/1
Physics I
Physics II
Physics III
English for Academic Purposes
Major
4
Major
4
Major
4
University
3
Bahasa A/B
MQA
Malaysian Studies
MQA
Mathematics IV
Major
Mathematics V
Major
Physics IV
Major
Physics V
Chemistry
Physics Laboratory
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
3
3
4
4
4
Major
4
Minor
3
Major
2
9
Curriculum Design and Delivery
2.3.3
MEDIU
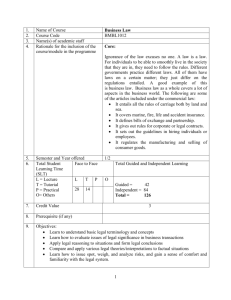
Basic information of each course/module (Provide information where applicable in Table 3.)
Table 3: Summary of information on each course/module
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
12.
Name of Course/Module
Course Code
Name(s) of academic staff
Rationale for the inclusion of the course/module in the programme
Semester and Year offered
Total Student Learning Time
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent
(SLT)
Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
O= Others
Credit Value
Prerequisite (if any)
Objectives
Learning outcomes
Transferable Skills:
Skills and how they are developed and assessed, Project and practical experience and
Internship
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
13.
Synopsis
14.
Mode of Delivery
Lecture, Tutorial, Workshop, Seminar, etc.
15.
Assessment Methods and Types
16.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
17.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
19.
Main references supporting the course
Additional references supporting the course
20.
Other additional information
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
Note: Independent Learning comprises the “Student Self Learning Time” and the “Total Assessment Time”
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
10
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Bahasa Malaysia A
2.
Course Code
MPW1113
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
MQA
To develop student’s ability in Bahasa Kebangsaan and enable
them to develop writing and speaking skills required for
communication.
5.
Semester and Year offered
2/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time
(SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 78
Total =120
28
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
3
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
Kursus ini adalah untuk membolehkan pelajar menguasai kemahiran asas bahasa Melayu dan kecekapan
berbahasa untuk berkomunikasi bagi melahirkan idea dan perasaan secara lisan dan penulisan.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Setelah mengikuti mata pelajaran ini,pelajar dapat:
1. Mengetahui sistem bunyi, sistem ejaan rumi, kosa kata dan tatabahasa Melayu;
2. Boleh mendengar dan memahami pertuturan dalam pelbagai situasi harian;
3. Boleh bertutur dalam pelbagai situasi harian.
4. Boleh membaca dan memahami bahan-bahan bacaan yang mudah.
5. Boleh melahirkan idea dan perasaan secara lisan dan tulisan.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
11
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
11.
Transferable Skills:
Enable students to develop writing and speaking skills required for communication.
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
13.
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons: Lectures
student-Lecturer discussion
collaborative and co-operative learning;
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (Participation, project, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
Synopsis:
The topics are thematically organized, task-based and student-centered. Structured speaking tasks,
incorporating systematic work on reading and writing, encourage students to express themselves more
appropriately. The reading and writing tasks are accompanied by model language and essential grammar
for different situations. The tasks and activities are generally graded in terms of difficulty and are designed
in such a way that students are gradually encouraged to be independent learners.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
Final Examination
20%
60%
Total
16.
100%
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
A6
12
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
17.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
18.
LO2
LO3
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
LO4
SLT
Details
4
2
12
18
4
2
12
18
12
6
30
48
4
2
12
18
4
2
12
18
28
14
78
120
Total
T
Indep.
L
Topic 1
Sebutan dan Intonasi
Sebutan- Prinsip sebutan, Intonasi
Intonasi pelbagai jenis ayat.
Topic 2
Sistem Ejaan
Sistem Ejaan, Bunyi huruf, Struktur suku kata.
Topic 3
Bahasa Melayu Praktis : Lisan
Bertegur sapa, Penyataan diri, Bahasa dalam situasi, Konsep masa
dan bilangan
Topic 4
Bahasa Melayu Praktis : Pemahaman
Penyataan Umum, Iklan, Papan tanda, Makluman, Arahan/larangan
Topic 5
Penulisan
Penulisan karangan, Mengisi borang
Total
19.
Main references supporting the course
1. Ab. Rahman Ab. Rahsid and Yap Kim Fatt (1999). Bahasa Kebangsaan. Kuala Lumpur: Longman.
2. Nik Safiah Karim (1981), Tatabahasa Dewan, Kuala Limpur: dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
13
Curriculum Design and Delivery
MEDIU
Additional references supporting the course
1. Ab. Rahman Ab. Rashid dan Hij. Wan Som (1995). Bahasa Melayu dalam Komunikasi dan Proses
komunikasi. Petaling Jaya: Longman Malaysia
20.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
14
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Bahasa Malaysia B
2.
Course Code
MPW1123
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
MQA
course/module in the programme
To develop student’s ability in Bahasa Kebangsaan and enable
them to develop writing and speaking skills required for
communication.
5.
Semester and Year offered
2/1
6.
Total
Total Guided and Independent Learning
Student
Learning
Face to Face
Time
(SLT)
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 84
Total =126
28
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
3
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
Untuk mempertingkatkan kecekapan berbahasa, sesuai dengan intelek pelajar untuk berkomunikasi
dengan berkesan secara lisan dan tulisan dalam konteks rasmi, kreatif dan bukan kreatif.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Setelah mengikuti mata pelajaran ini, pelajar dapat:
1. Menggunakan bahasa dengan berkesan dari segi lisan dan tulisan;
2. Berkomunikasi secara lisan dengan berkesan dari segi sebutan dan intonasi,
3. tatabahasa, kosa kata, ungkapan dan laras;
4. Memahami bahan bertulis yang beraneka jenis dan gaya, dan seterusnya mengungkapkan fikiran
secara lisan dan tulisan dengan bahsa yang betul
5. dan berkesan;
6. Merumuskan butiran dan memperluas sesuatu idea dengan cara yang
tersusun, padat dan berkesan secara lisan dan tulisan.
7. Mengarang pelbagai teks dengan bahasa yang betul dan berkesan; Berkomunikasi secara lisan dan
tulisan dengan sopan, di samping mengekalsuburkan nilai-nilai murni masyarakat Malaysia.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
15
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
11.
Transferable Skills:
Enable students to develop writing and speaking skills required for communication.
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures
student-Lecturer discussion
collaborative and co-operative learning;
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
The topics are thematically organized, task-based and student-centered. Structured speaking tasks,
incorporating systematic work on reading and writing, encourage students to express themselves more
appropriately. The reading and writing tasks are accompanied by model language and essential grammar
for different situations. The tasks and activities are generally graded in terms of difficulty and are designed
in such a way that students are gradually encouraged to be independent learners.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
Quizzes
40%
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
16.
100%
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
17.
A2
A3
A4
A5
᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃
᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃᷃
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
A6
LO4
16
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
2
12
18
Sebutan dan Intonasi
Sebutan
Prinsip sebutan
Intonasi
Komponen intonasi, Intonasi pelbagai jenis ayat
4
2
12
18
Topic 3
Isu Ejaan dan Tatabahasa
Ejaan, Pengimbuhan, Pemilihan kata, Struktur ayat
Penghubung ayat
4
2
12
18
Komunikasi Lisan
Ucapan / syarahan
Pengendalian mesyuarat
4
2
12
18
6
3
18
27
Penulisan
Ciri-ciri penulisan
Fakta, Gaya dan laras, Struktur, Bentuk wacana
Jenis-jenis teks
Jenis teks berformat- surat rasmi, kertas kerja, Jenis teks tak
berformat - cerpen
6
3
18
27
Total
28
14
84
126
Topic 2
Topic 5
Topic 6
19.
Kefahaman
Teks prosa, Teks puisi
Main references supporting the course
1. Ab. Rahman Ab. Rahsid and Yap Kim Fatt (1999). Bahasa Kebangsaan. Kuala Lumpur: Longman.
2. Nik Safiah Karim (1981), Tatabahasa Dewan, Kuala Limpur: dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
17
Total
4
Pengenalan
Asal-usul bahasa Melayu
Rumpun bahasa Melayu, Bahasa Melayu sebagai lingua franca.
Dasar dan Kedudukan Bahasa Melayu
Asas pemilihan bahasa Melayu, Perkara 152 Perlembagaan
Persekutuan, Akta Bahasa Kebangsaan, Akta Pendidikan
Status dan Fungsi Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa kebangsaan, Bahasa rasmi, Bahasa perpaduan, Bahasa ilmu
Bahasa dan Budaya
Indep.
T
Topic 1
L
Topic 4
Details
Curriculum Design and Delivery
MEDIU
Additional references supporting the course
1. Bahasa: Pengintelektualan Bhasa Melayu. Kuala Lumpur: Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka.
2. Ismail Hussein (1992). Sejarah Pertumbuhan Bahasa Kebangsaan Kita. Kuala Lumpur; Dewan
Bahasa dan Pustaka.
3. Noraini Yusoff (1991) Penulisan Berformat, Kuala Lumpur; Pustaka Pertiwi.
4. Sulaiman Masri (1995). Penulisan dalam Bahasa Melayu Baku (edisi ke-2), Kuala Lumpur; Dewan
Bahasa dan Pustaka.
5. Ab.. Rahman Ab. Rashid da Yap Kim Fatt (1995). Bahasa Melayu-Komunikasi Berkesan dan
Pengucapan Umum. Petaling Jaya: Longman Malaysia.
6. Abdullah Hassan (1980). Linguistik Am untuk Bahasa Malaysia. Petaling Jaya: Fajar Bakti Sdn. Bhd.
7. Awang Sariyan (1995) Sebutan Baku dan Ejaan Rumi. Kuala Lumpur: Synergymate Sdn. Bhd.
8. Asmah Hj. Omar (1987). Bahasa Laporan. Kuala Lumpur: Dewan Bahasa dan Pustaka.
9. Za’aba (2000) Pelita Bahasa Melayu 1. Kuala Lumpur: Dwan Bahasa dan Pustaka.
20.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
18
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Islamic Studies
2.
Course Code
MPW1143
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
MQA
course/module in the programme
This subject is MQA requirement
5.
Semester and Year offered
1/1
6.
Total
Total Guided and Independent Learning
Student
Learning
Face to Face
Time
(SLT)
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 84
Total =126
42
-
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
3
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
1. To introduce Islam as the universal civilization that contributes to the progress of human life.
2. To counter and to reject all the false accusations towards Islam and its components.
3. To inculcate and to enhance high quality of virtues of life in the daily lives of Muslim, so that a
comprehensive, balanced and prosperous life can be achieved.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to :1. Understand all the basic principles and concepts of Islam.
2. Review all the Islamic knowledge that had been learned before.
3. Apply all the Islamic teachings in their daily life.
4. Distinguish which is really bad or good according to the Islamic perspective.
5. Generate a “new life” as a Muslim after reordering his recent life.
6. Prioritize tasks between worldly affairs and hereafter in his Muslim daily life.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
19
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
11.
Transferable Skills:
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
4. Classroom lessons. Lectures
student-Lecturer discussion
collaborative and co-operative learning;
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (Participation, project, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
Quizzes
40%
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
100%
16.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
17.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
LO4
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
20
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
T
12
-
Total
L
Indep.
Details
Topic 1
Islam & Its Fundamentals
Islam as a way of Life
The Meaning of Islam, Iman & Ihsan , The Vital Teachings of Islam, alMaqosid al-Syariah, The World , view of Islam : Its Special
Characteristics, Cosmology from Islamic Perspective, Jihad in Islam.
24
36
Islam as the Civilization & Culture
Topic 2
The Concept of Culture and Civilization
The concept of Civilization, Comparison between Western
Civilization and Islamic Civilization, The uniqueness of the Islamic
Civilization, Factors of the Excellent Achievement of the Islamic
Civilization, Contribution of Islamic Civilization in various fields.
Art and the Cultural Manifestation
Philosophy, Concept and the principles of the Art and Cultures, Art
and the Cultural Manifestation.
8
16
-
30
2
4
2
4
Islamic Institutions
Topic 3
Parenting and Society
The Development of the parental institution, The Development of
Society, Islam and the Multi-racial society, The concept of the
Middle ummah
Education
Philosophy and Concept of Education, The development of the
Islamic Educational System in Malaysia
Politics and Legislation
Concepts and Principles of politics and legislation, The leadership
and the political system during the period of Prophet Muhammad
s.a.w, The Institutions of Political System and the Legislation, Syura
and Hisbah
Legislation and Judiciary system
Concepts, Principles and the Philosophy of Islamic Legislation, The
sources of Islamic Legislation, The Islamic Penal Code, The Judiciary
System, Schools of Islamic Thoughts
Economy and Finance
The Principles and the Philosophy of the Economic and Financial
system, The Fundamentals of the Economic and Financial System,
Institutions of Finance, The Products of the Islamic Financial and
Economic System.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
4
2
2
-
4
4
2
4
2
4
21
30
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
D. Islam and the current challenges
Topic 4
Social Problems, the Development and Urbanization, Science,
Technology and ICT, Globalization, Misunderstandings towards
Islam, the Unity of Ummah, The Inter Cultural Dialogue.
Total
19.
10
-
20
30
42
-
84
126
Main references supporting the course
1. ISLAM : The Practical Religion, Prof. Dr. Ala’eddin Kharofa, Kuala Lumpur, A.S Noordeen, 1992.
Additional references supporting the course
1. Global View of Islam, Mujahid Yusuf, Unitele, Unitele, 1996.
2. Religion and Civilization. India, Academy of Islamic Research and Publication, 1975.
3. Introduction to Islam, Muhammad Hamidullah, London, MHW London Publisher, 1979.
4. Islam and The Contemporary World, Choudry, G.W.. USA, Kazi Publications Inc, 1991
5. Islamic Pespectives, Sayyid Abul A’la Mawdudi.. United Kingdom, The Islamic Foundation, 1979.
6. The Concept of Vicegerency, Prof. Mohammed Haji Yacob, Johor Bahru, Badan Book Store Sdn Bhd,
1993.
7. Khasais al-Ammah lil Islam, Dr. Yusof Qardhawi, Beirut, Muassasah Risalah, 1985.
8. Tamadun Islam, Abul Hasan Ali Nadwi, Mahayudin Hj Yahaya, Siri Sejarah Fajar Bakti, 1998.
9. Pandangan Islam Tentang Keseniaan. Sidi Gazalba, Kuala Lumpur, Pustaka Antara, 1977.
10. Manusia dan Islam, Prof. Harun Din, Kuala Lumpur, Percetakan Watan Sdn Bhd, 1988.
20.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
22
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Moral Studies
2.
Course Code
MPW1153
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
MQA
5.
Semester and Year offered
1/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time
(SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
This subject is MQA requirement
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 84
Total =126
42
-
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
3
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
1. To introduce Islam as the universal civilization that contributes to the progress of human life.
2. To counter and to reject all the false accusations towards Islam and its components.
3. To inculcate and to enhance high quality of virtues of life in the daily lives of Muslim, so that a
comprehensive, balanced and prosperous life can be achieved.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
23
Curriculum Design and Delivery
10.
MEDIU
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to :1. Explain the basic concept of moral values and the types of moral values
2. Explain and criticize the moral and ethics theories
3. Recognize moral values in Religions
4. Know the current and traditional values of Malaysian society
5. Establish the reasoning of moral issues
6. Accomplish moral conflicts
7. Practices good values as a student
11.
Transferable Skills:
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures
student-Lecturer discussion
collaborative and co-operative learning;
Independent study
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (Participation, project, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
24
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
100%
16.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
17.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
18.
LO3
LO4
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
L
T
Indep.
Total
Details
4
-
8
12
6
-
12
18
Topic 1
Introduction
The importance of Moral Education – To have high moral standards
in Malaysian society through Rukun Negara, Vision 2020, Individual
Role, Responsibility and Moral Agent.
Topic 2
The Basic Concept of Ethics and Types of Moral Values
Normative approach – Distinguish between normative and
descriptive – Basic concept of values - Types of moral values
(instrumental, intrinsic, subjectivism, objectivism , relativism,
absolute
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
25
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Topic 3
Values of religion and belief
Definition of religion, purpose of religion, relation of religion and
morality such as in Islam, Christianity, Buddhism, Hinduism, Taoism,
Sikhism, and Judaism.
8
-
16
24
8
-
16
24
8
-
16
24
8
-
16
24
42
-
84
126
Topic 4
Values of insanity
Forms and dimensions of situational ethics, ethical judgement and
principle ethics such as ethical relativism and ethical reasoning
Topic 5
Moral Values of an Individual
Contents - Comprehend the needs of regulation; Form – issues or
moral dilemma, moral principle; Dimension – rasional, autonomous,
emotion , methods, cases and effects physically and mentally.
Topic 6
Conflict Resolution
Ways to solve conflict according to the constructive conflict
resolution processes – Values of analysis, hierarchy, compromise.
Total
19.
Main references supporting the course
1. Ethics: Theory and contemporary issues. Third edition. Barbara Mac Kinnon.2001. (Textbook)
Additional references supporting the course
20.
1. Moral Education, Higher Learning Education, Eow Boon Hin, Pearson Sdn Bhd,. Social Ethics: A
student's guide. Teichman , Jenny.1996
2. What is the best life?An introduction to Ethics.Art, Brad.1993
3. Environmental Ethics: An introduction to environmental philosophy.Des Jardins, Joseph r. 1993.
4. Morality and the good life: An introduction to ethics through classical sources.Solomon, Robert
C.Third edition.1999.
5. Philosophical Ethics: An introduction to moral philosophy. Beauchamp, Tom L. Second edition
1991.
6. Ethics, a contemporary introduction. Gensler, Harry J.1998
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
26
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Malaysian Studies
2.
Course Code
MPW1133
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
MQA
5.
Semester and Year offered
2/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time
(SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
This subject is MQA requirement
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 84
Total =126
42
-
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
3
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
The objective of this subject is to develop Malaysians who are loyal, patriotic and visionary. The aim of this
class is also to produce Malaysians who are proud of their country and able to meet daily challenges so that
they can live harmoniously as well as able to appreciate and understand Malaysia’s international role.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to :1. Explain Malaysia’s history and society.
2. Discuss the development of society in sense of politics, economy and socio-culture.
3. Reflect on and appreciate the sacrifices made by Malaysia's forefather who fought and
defended for the country’s independence and sovereignty.
4. Analyse Malaysia's roles and contributions in the international arena.
5. Instill patriotic values in themselves as to increase nationalism.
11.
Transferable Skills:
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
27
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures
student-Lecturer discussion
collaborative and co-operative learning;
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (Participation, project, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
100%
16.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
17.
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
LO4
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
28
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
L
T
Indep.
Total
Details
4
-
8
12
4
-
8
12
2
-
4
6
4
-
8
12
4
-
8
12
2
-
4
6
2
-
4
6
4
-
8
12
Topic 1
The Malacca Sultanate
A brief introduction on the early Malacca history
Factor contributing to the rise and full of Malacca sultanate
Topic 2
The Malacca Sultanate and foreign conquest
The Portuguese and Dutch in Malacca
The Anglo- Dutch Treaty and British intervention
Topic 3
Steps toward independence formation of Malaysia
Japanese occupation
Early political parties
Topic 4
Judicial Systems
Democracy and election
Constitution parliament
High court and federal courts
Topic 5
Social and Demongraphic structure
Population
Multi-racial society and social integration
Topic 6
Unity in Malaysia and the Education Policy
Objectives of the National Education Policy
Topic 7
Geographic and Environment features
Tourism and government commitment
Topic 8
Malaysia’s policies
Vision 2020
7th Malaysian plan
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
29
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Topic 9
Government Mega- projects
Muiltimedia super corridor
Malaysia east Asian satellite (Measat)
Kuala Lumpur International Airport
Kuala Lumpur City Center (KLCC)
4
-
8
12
4
-
8
12
4
-
8
12
4
-
8
12
42
-
84
126
Topic 10
Malaysian Culture
Tradition
Festivals
Ceremonies
Multi- racial beliefs
Etc.
Topic 11
Social Problems
Juvenile delinquency
Drug abuse
Smoking
Child abuse
Domestic violence
Teenage pregnancy
Private education
Topic 12
Other Malaysian Issues
Information technology
Urbanization
Road safety
Sports
Environmental problems
Total
19.
Main references supporting the course
1. Information Malaysia year Book 1998/99, Berita Publishing Negara Kita, institute pentadbiran.
Additional references supporting the course
1. Heritage Malaysia , new straits Time Annual 1995
20.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
30
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
English For General Purposes
2.
Course Code
LENG1013
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
Dr Mohd Faiz Bin HJ. Burhannuddin
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
University
5.
Semester and Year offered
1/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time
(SLT)
L = Lecture
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
O= Others
Total Guided and Independent Learning
To develop student’s ability in English Language and enable
them to develop writing and speaking skills required for
various types of Studies and occupational tasks.
Face to Face
L
T
28
14
P
O
-
Independent =84
Total =126
-
7.
Credit Value
3
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
Introduce students to some Basic English.
Raise students’ level of proficiency in the four language skills.
Improve students’ confidence and ability as language learners.
Serve as a transitional link to higher level English.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completion of LENG1013, students should be able to:
Listen and speak with some confidence on social matters.
Read with reasonable accuracy for pleasure.
Communicate facts and ideas reasonably accurate through writing.
Develop vocabulary that will enhance their oral and written skills and have sufficient grasp of the
language to communicate what is read.
11.
Transferable Skills:
enable students to develop writing and speaking skills required for various types of
Studies and occupational tasks.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
31
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
Class Lectures, Assignment, Interactions through discussion board, closed and open quizzes, Exams
Student learning experiences and assessment activities involve independent and group report writing
practices, oral presentations and peer assessment, where students present their reports to each other and
are involved in assessing each other’s work.
assessment activities for this course are that the student:
Writes a:
· Reports
· Translations
· Simple Essays
· Summarizations
13.
Synopsis:
LENG1013 is the first level English language subject, which is especially designed for undergraduates with
very little English. The topics are thematically organized, task-based and student-centered. Structured
speaking tasks, incorporating systematic work on reading and writing, encourage students to express
themselves more appropriately. The reading and writing tasks are accompanied by model language and
essential grammar for different situations. The tasks and activities are generally graded in terms of
difficulty and are designed in such a way that students are gradually encouraged to be independent
learners.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Lecture, Tutorial and on-line discussion
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
50%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Interactions through discussion
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
50%
Total
16.
100%
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
17.
A4
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
32
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
LO1
LO2
18.
LO3
LO4
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
Total
Details
Indep.
SLT
L
T
6
3
18
27
2
1
6
9
2
1
6
9
Reading: Friends
Topic 1
Talking about good friends and bad friends.
Grammar Points: Yes/No questions and WH-Questions.
Man’s best friend.
Read an interview about an unusual pet and answer questions.
Read a questionnaire about being a good friend.
Grammar Points: Present Perfect.
Informal correspondence.
Write simple social customs to a foreign friend.
Grammar points: Passive voice.
Online Forum.
Topic 2
Reading: My Daily Routine
Talking about Daily Routines.
Grammar points: Do- questions.
Reading about Schedules.
Grammar points: Adverbs of time.
Writing a study timetable.
Grammar points: Short forms.
Reading: Hi, how are you!
Topic 3
Saying hello.
Grammar points: Greeting expressions & Subject Verb
agreement.
Meeting and Greeting People.
Grammar points: Farewell expressions.
Writing Greeting Cards.
Grammar points: Greeting card common expressions.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
33
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Reading : Sorry I’m not in right now
Topic 4
Communication over the telephone.
Grammar points: Common phrases used in telephone
conversation.
Taking a telephone message.
Grammar points: Direct and Reported Speech.
Leaving a voice message.
Grammar points: Abbreviations in messages.
2
1
6
9
2
1
6
9
2
1
6
9
2
1
6
9
2
1
6
9
Reading: Taking a break
Topic 5
Talking about holidays.
Grammar points: Comparatives and Superlatives.
Reading about holiday get-away.
Grammar Points : Adjectives or adjectival phrases
Writing about holidays
Grammar Points: Common Phrases in postcards
Reading: This way, not that way.
Topic 6
Asking and Giving Directions
Grammar Points: Common phrases for asking
directions
Reading about directions
Grammar Points: Road directions
Written directions
Giving specific and general directions Grammar
Points: Imperatives
Topic 7
Reading: This way, not that way.
Asking and Giving Directions
Grammar Points: Common phrases for asking directions
Reading about directions
Grammar Points: Road directions
Written directions
Giving specific and general directions Grammar
Points: Imperatives
Reading: What’s a good buy?
Topic 8
Talking about bargai.
Grammar Points: Bargaining/ Negotiating expressions.
Reading about Shopping.
Grammar Points: Modals.
Cruising for shopping outlets.
Grammar points: Prepositions.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
34
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Reading/Talking about Pastimes
Grammar points: Gerunds.
Topic 9
Reading the Sports page.
Grammar points: Vocabulary to talk about pastimes.
Going to the movies.
Grammar points: Expressions to write a simple review.
2
1
6
9
6
3
18
27
28
14
84
126
Reading: Writing at the university
Types of academic essays.
Topic 10
Grammar points: Essay introductions and
Conclusions.
Researching the topic.
Grammar points: Transition words.
Writing the academic essay
Grammar points: Editing and Proofreading.
Total
19.
Main references supporting the course
1. Mohd Sallehhudin Abd Aziz & Tan Kim Hua (2008) English For General Purposes, Al Madinah
International University (Malaysia)
Additional references supporting the course
20.
1. Hartman Pamela 2007 Quest 2 Reading & Writing. McGraw HillNew York
2. Soars, J and Soars L (1996) Headway : Intermediate, Oxford University Press
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
35
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
English For Academic Purposes
2.
Course Code
LENG1023
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
Dr Mohd Faiz Bin HJ. Burhannuddin
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
University
To develop student’s ability in English Language and
enable them to develop writing and speaking skills
required for various types of Academic Studies and
occupational tasks
5.
Semester and Year offered
2/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time
(SLT)
L = Lecture
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
O= Others
Total Guided and Independent Learning
Face to Face
L
T
P
O
28
14
-
-
Independent = 84
Total =126
7.
Credit Value
3
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
None
9.
Objectives:
The objectives of this course are to allow students to;
Enhance acquisition of English vocabulary
learn some grammatical elements of the English language
write some reasonably complex sentences
read a cross section of academic materials
learn to pronounce certain English sounds
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
36
Curriculum Design and Delivery
10.
MEDIU
Learning outcomes
Upon completion of this subject, students should be able to:
use and produce words and idiomatic expressions
11.
use simple grammatical structures accurately
demonstrate the ability to write simple and complex sentences
read and understand different academic texts critically
show improvement in pronunciation of certain English words
Transferable Skills:
Enable students to develop writing and speaking skills required for various types of
Academic Studies and occupational tasks.
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
Class Lectures, Assignment, Interactions through discussion board, closed and open quizzes,
Exams
Student learning experiences and assessment activities involve independent and group report
writing practices, oral presentations and peer assessment, where students present their reports
to each other and are involved in assessing each other’s work.
assessment activities for this course are that the student:
Writes a:
Reports
Translations
Simple Essays
Summarizations
13.
Synopsis:
This is the second level English language subject. This subject is especially designed for
undergraduates with some knowledge of English. It aims to improve students’ overall language
ability. This subject is thematically based and integrated in approach. Students will also be
exposed to new words in English. They will also be exposed to important reading skills and the
ability to read a variety of academic texts. In addition, students will learn some basic sentence
structures with correct tenses. The tasks and activities for this subject are generally graded in
terms of difficulty and are designed in such a way that the students are gradually encouraged to
be independent learners.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Lecture, Tutorial and on-line discussion
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
37
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
Quizzes
Assignments
Interactions through discussion
Mid-Semester Exam
Final Examination
Total
16.
50%
10%
10%
10%
20%
50%
100%
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
17.
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
18.
LO4
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
L
T
Indep.
Total
Details
4
2
12
18
2
1
6
9
Part 1 Topics on nature and Environment
Topic 1
Topic 2
Reading ; Some Facts About Sharks
Grammar ; The Simple Tenses
Writing ; Writing in the Simple Tenses
Speaking [-s] and [-es]
Word power; Vocabulary Building
Reading ; Giant pandas
Grammar ; Simple past tense and past progressive
Writing ; sentence building
Speaking ; pronouncing words that end with [-ed]
Word power; Vocabulary Building
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
38
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Topic 3
Topic 4
19.
Reading ; Why do cats leave us
Grammar : Subject Verb Agreement
Writing : writing simple and complex sentences
Speaking ; Pronouncing the sound [r]
Word power: Vocabulary building
Reading; Facts of The World
Grammar ; Verb ‘to be’
Writing ; The Mechanics of Writing
Speaking [ea]
Word Power : Vocabulary Building
2
1
6
9
2
1
6
9
4
2
12
18
2
1
6
9
2
1
6
9
4
2
12
18
4
2
12
18
Topic 5
Part 2: Topics on academic and Technology
Topic 6
Topic 7
20.
Reading: Things That We Must Have
Grammar: Adverbs of Manner and Frequency
Writing: Sequence Connectors
Speaking: Contractions
Word Power: Vocabulary Building
Reading; A History Of Tunnels
Writing; Extracting Information
Speaking : Fixed Speech Exchanges
Word power; Vocabulary Building
Reading: Men and Inventions
Grammar: Modals
Writing : Sentence Connectors
Speaking : Questions Tag
Word Power; Vocabulary Building
Topic 8
Part 3: Topics on People and Society
Topic 9
Reading ; Ibnu Sina
Grammar: Modals
Writing: Filling in Forms; The Mechanics of Writing
Speaking: Pronouncing [s] & [sh]
Word power; Vocabulary Building
Reading: Philosophers of The Three Worlds
Grammar; Prefixes
Writing: The Mechanics of Writing
Speaking; Making requests
Word Power: Vocabulary Building
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
39
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Topic 10
Reading ; Job Advertisements
Grammar ; suffixes
Speaking; Speech Exchanges
Word Power; Vocabulary Building
Total hours
21.
2
1
6
9
28
14
84
126
Main references supporting the course:
1. Mohd Sallehhudin Abd Aziz & Normala Othman (2008) English for Academic Purposes. Al
Madinah International University (Malaysia)
Additional references supporting the course:
1. Baker, A 2000. Ship or Sheep / An Intermediate Pronunciation Course . New Edition.
Cambridge University Press
2. Glendinning, E. H. & Holmstrom, B 91992) Study Reading. Cambridge: Cambridge
University Press
3. Hillman, L, H (1990) Reading at the University. Boston Heinle & Heinle Publishers
4. Hartman Pamela 2007 Quest 2 Reading & Writing. McGraw HillNew York
5. Soars, J and Soars L (1996) Headway : Intermediate, Oxford University Press
22.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
40
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Mathematics l
2.
Course Code
PMATH1014
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
A solid mathematical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of
techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to
develop the student's mathematical knowledge and to provide
the student with all the necessary techniques and methods for
the analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
1/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time (SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 98
Total = 168
56
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
4
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
This course introduces the student to the Knowledge of algebra, factorization, solving of quadratic
equations and logarithm.
10. Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. Understand the basic concepts of mathematics in solving real life problems.
2. Solve algebraic and quadratic equations
3. Apply and use logarithms and exponent
4. Apply and use the binomial theorem
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
41
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
11. Transferable Skills:
Understand the nature of formal, symbolic representation of systems and processes by learning important
rules of algebra, factorization, solving of quadratic equations and logarithm.
12. Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13. Synopsis:
Is to enable students to understand and apply the principles of algebraic operations needed in their degree
course.
14. Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
15. Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
100%
16. Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
17. Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
LO4
42
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18. Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
T
P
Total
L
Indep.
Details
Fundamental concept of algebra
Topic 1
Real numbers and algebraic expression
Exponents
Radicals and rational exponents
Polynomials
Complex numbers
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
Equation and inequalities
Topic 2
Linear equations
Quadratic equations
Other types of equations
Linear inequalities
Quadratic and rational inequalities
Topic 3
Graphs
Graphs
Lines and slopes
Distance and midpoint formulas ; circles
Functions and graphs
Topic 4
Basic of functions
Graphs of functions
Transformation of functions
Combinations of functions; composite functions
Invers functions
Topic 5
Polynomial and rational functions
Quadratic functions
Polynomial functions and their graph
Dividing polynomial ; remainder and factor theorems
Rational functions and their graph
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
43
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Topic 6
Exponential and logarithmic functions
Exponential functions
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
56
14
-
98
168
Logarithmic functions
Properties of logarithms
Exponential and logarithmic equations
Topic 7
Trigonometric functions
Angles and their measure
Right triangle trigonometry
Trigonometric functions of any angle
Trigonometric functions of real numbers ; periodic functions
Total SLT
19. Main references supporting the course
1. Robert Blitzer, Goh Wei Wei, Heng Chai Yen, Mohd Daud Hassan, Ng Lik Neo, Tan Lai Poh, Tay Cheng
Lan, Wan Hafiza Wan Hassan, Yasothei Suppiah, Algebra & Trigonometry, 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall,
2007
2. Howard Anton, Irl C. Bivens, Stephen Davis,Calculus Late Transcendentals, 9th Edition, John Wiley &
Sons, Inc, 2010
Additional references supporting the course
1. Larson R & Hostetier, P. (2004) 6th Edition , College Algebra, Oughton Miffin Company.
2. Berry & Wainwright, Foundation Mathematics for engineers, Macmillar, 1991.
3. K.A Stroud, ‘Engineering Mathematics Mc Millan, 1998.
20. Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
44
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Mathematics II
2.
Course Code
PMTH1024
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
A solid mathematical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of
techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to
develop the student's mathematical knowledge and to provide
the student with all the necessary techniques and methods for
the analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
1/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time (SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 98
Total = 168
56
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
4
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
This course introduces the student to the Knowledge of differential calculus with good foundation in the
differentiation and its application in engineering.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:-
11.
1. explain the terms and concepts of the derivatives
2. solve the differentiation problems by using basic rules
3. solve the differentiation of trigonometric functions
4. solve the equation of the tangent and normals and extremum problems in differentiation
Transferable Skills:
Solving differentiation and trigonometric problems
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
45
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
Tutorial sessions
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
This course provides calculus topics of differentiation. The topics are completely different from those of
algebra and geometry because in these topics student will learn important rules for finding derivatives and
how to use it to analyze the rate of change of quantity. Functions will also be introduced.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
16.
17.
100%
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
LO4
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
46
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
Details
P
8
2
-
14
24
12
3
-
21
36
8
2
-
14
24
12
3
-
21
36
16
4
-
28
48
56
14
-
98
168
Total
T
Indep.
L
Topic 1
Limits
Rates change and limit laws
Calculating limits using the limit laws
One-sided limits
Topic 2
Continuity
limits at infinity
Infinity limits and vertical asymptotes
Continuity
Tangents and derivatives
Topic 3
Differentiation
The derivatives as a function
Differentiation rules
The derivatives as a rate change
Topic 4
Rules of Differentiation
Derivatives of trigonometric functions
The chain rule and parametric equations
Implicit differentiation
Related rates
Linearization and differentials
Topic 5
Application of Derivative
Extreme values of functions
The mean value theorem
Monotonic functions and the first derivative test
Concavity and curve sketching
Applied optimization problems
Indeterminate forms problems
Total SLT
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
47
Curriculum Design and Delivery
19.
MEDIU
Main references supporting the course
1. Howard Anton, Irl Bivens, Stephen Davis, Calculus, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 8th Edition, 2005
2. Howard Anton, Irl C. Bivens, Stephen Davis,Calculus Late Transcendentals, 9th Edition, John Wiley &
Sons, Inc, 2010
3. Peter V. O’Neil, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 1st Edition, Thomson, 2010
4. Dennis G. Zill, Micheal R. Cullen, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 3rd Edition, Johnes and Barlett
Publisher, 2006
Additional references supporting the course
20.
1. Peries B,M, (2004). 8th edition, Statistics. A first course, pearson perntie Hall ]
2. Stroud KA., Engineering mathematics, Mac Millan, 1998.
3. Jame SG., Modern Engineering Mathematics, 3th edition, Addlson , Wesley, 2000.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
48
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Mathematics III
2.
Course Code
PMTH1034
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
MEDIU
A solid mathematical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of techniques
in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to develop the
student's mathematical knowledge and to provide the student
with all the necessary techniques and methods for the analysis
and solutions of problems in Engineering fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
1/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time
(SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 98
Total = 168
56
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
4
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
This course introduces the students to the Knowledge of coordinate geometry and application in
engineering.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. Understand the use fullness of coordinate geometry in solving engineering related problems.
11.
Transferable Skills:
Problem solving in coordinate geometry.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
49
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
Tutorial sessions
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
This course will introduce the students to concept of polar coordinates, three dimensional geometry,
curves, loci, distance and areas in two dimensions
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
16.
100%
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
17.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
LO4
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
50
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
L
T
P
Indep.
Total
Details
12
3
-
21
36
12
3
-
21
36
16
4
-
28
48
16
4
-
28
48
56
14
-
98
168
Topic 1
Integration
Antiderivatives
An overview of the area problem
The indefinite integral
Integration by substitution
definite integral
Topic 2
The definition of area as a limit; sigma natation
The definition definite integral
The fundamental theorem of calculus
Rectilinear motion revisited using integration
Evaluating definite integrals by substitution
Topic 3
Application of the definite integrals
Volumes by slicing and rotation about an axis
Volumes by cylindrical shells
Length of plane curves
Area of surfaces of revolution
Average value of functions and its application
Work
Fluid pressure and force
Techniques of integration
Topic 4
Basic integration formulas
Integration by parts
Integration of rational functions by partial fractions
Trigonometric integrals
Improper integrals
Total SLT
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
51
Curriculum Design and Delivery
19.
MEDIU
Main references supporting the course
1. Howard Anton, Irl Bivens, Stephen Davis, Calculus, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 8th Edition, 2005
2. Howard Anton, Irl C. Bivens, Stephen Davis,Calculus Late Transcendentals, 9th Edition, John Wiley &
Sons, Inc, 2010
3. Peter V. O’Neil, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 1st Edition, Thomson, 2010
Additional references supporting the course
1. Dennis G. Zill, Micheal R. Cullen, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 3rd Edition, Johnes and
Barlett Publisher, 2006
20.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
52
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Mathematics IV
2.
Course Code
PMTH1054
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
A solid mathematical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of techniques
in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to develop the
student's mathematical knowledge and to provide the student
with all the necessary techniques and methods for the analysis
and solutions of problems in Engineering fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
2/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time
(SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 98
Total = 168
56
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
4
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
This course introduces the student to the Knowledge of integral calculus and application in engineering.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. explain the definition of integration, definite integral and indefinite integral
2. solve the integration problems by using basic rules
3. solve the integration of trigonometric functions
11.
Transferable Skills:
Problem solving and application of integral calculus.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
53
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
13.
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons: Lectures
Tutorial sessions
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
Synopsis:
This course provides calculus topics such as integration. The topics are completely different from those of
algebra and geometry because in these topics student will learn important rules for finding derivatives and
how to use it to analyze the rate of change of quantity. Integral calculus is concerned with the reverse
process of the derivatives.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
16.
100%
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
17.
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
LO4
54
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
Details
P
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
12
3
-
21
36
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
12
3
-
21
36
56
14
-
98
168
Total
T
Indep.
L
Topic 1
Conic sections
Conic sections
Eccentricity
Quadratic equation and rotations
Topic 4
Topic 3
Topic 2
polar coordinates
Polar coordinates
Graphing in polar coordinates
Area and lengths
Conic section in polar coordinates
Complex number
Complex number
Operation on complex numbers
Complex conjugate
Polar form
DeMooive’s theorem
sequences and series
Sequences
Monotone sequences
Infinite series
Topic 5
Convergence tests
The integral tests
Comparison test
The ratio and root tests
Alternating series: absolute and conditional convergence
Topic 6
Power series
MacLaurin and Taylor polynomial
MacLaurin and Taylor series
Convergence of Taylor series
Total SLT
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
55
Curriculum Design and Delivery
19.
MEDIU
Main references supporting the course
1. Howard Anton, Irl Bivens, Stephen Davis, Calculus, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 8th Edition, 2005
2. Howard Anton, Irl C. Bivens, Stephen Davis,Calculus Late Transcendentals, 9th Edition, John Wiley &
Sons, Inc, 2010
3. Peter V. O’Neil, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 1st Edition, Thomson, 2010
4. Dennis G. Zill, Micheal R. Cullen, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 3rd Edition, Johnes and
Barlett Publisher, 2006
Additional references supporting the course
20.
1. Strond, K.L, (1995). Engineering Mathematics 4th edition, Macmillan Press Ltd England.
2. Krey SR.g E (1999) advanced Engineering Mathematics 8th edition John Wiley and Sons Inc.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
56
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Mathematics V
2.
Course Code
PMTH1054
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
A solid mathematical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of
techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to
develop the student's mathematical knowledge and to provide
the student with all the necessary techniques and methods for
the analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
2/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time
(SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 98
Total = 168
56
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
4
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
This course introduces the students to the Knowledge of statistics, vector and matrices and its application in
engineering.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. Understand the use fullness of the basic principles in of statistics, vector and matrices in solving
engineering related problems.
11.
Transferable Skills:
Solving, vectors and matrices problems.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
57
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
Tutorial sessions
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
This course provides topics on vectors, statistics and matrices.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
30%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
100%
16.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
17.
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
LO4
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
58
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
L
T
P
Indep.
Total
Details
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
12
3
-
21
36
Descriptive statistics
Introduction to data
Frequency distributions
Measures of location
Measures of dispersion
8
2
-
14
24
Probability
Permutations
Combinations
Events and probability
Conditional probability
12
3
-
21
36
8
2
-
14
24
Matrices
Topic 6
Topic 5
Topic 4
Topic 3
Topic 2
Topic 1
Matrix algebra
System of linear algebra equations
Rank of a matrix
Determinants
Properties of determinants
Operation of Matrices
Inverse of matrix
Finding the inverse
Using the inverse to solve systems
Cramer’s rule
Vectors
Vector in 2-space
Vector in 3-space
Dot product
Cross product
Lines and planes in 3-space
Vector spaces
Random variables
Introduction to random variables
Discrete and continuous random variables
Expectation and variance of random variables
Discrete probability distributions
Continuous probability distributions
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
59
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
19.
Total SLT
56
14
-
98
168
Main references supporting the course
1. Walpole, Myers, Myers, Ye, Probability and Statistics for Engineers and Scientists, 8th Edition,
Pearson International, 2007
2. Howard Anton, Chris Rorres, Elementary Linear Algebra with Supplemental Applications, 1st
Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2011
3. Douglas C. Montogomery, George C. Runger, Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers, John
Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2011
Additional references supporting the course
20.
1. Stroud, K.A, (1995). Engineering Mathematics 4th edition, Macmillan, 1998.
2. Perlos, B.M (2004), 8th edition static; a first course, pearson prentice Hall.
3. G James, 2th edition, modern mathematics by a Thomas, Addison, Wesley 1992.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
60
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Physics I
2.
Course Code
PPHY1064
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
Good physics ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of
techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to
develop the student's physics knowledge and to provide the
student with all the necessary techniques and methods for the
analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
1/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time
(SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 98
Total = 168
56
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
4
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
This course introduces the student to the Knowledge of mechanics and application in engineering
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. Understand principles of mechanics.
2. Apply the knowledge to real engineering situation.
11.
Transferable Skills:
Problem solving in mechanics
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
61
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
13.
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
Tutorial sessions
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
Synopsis:
This course discuss on the graphical relationship between displacement, velocity and acceleration diagram
inconstant acceleration motion. Standard equation is then used to consider the analytical relationship. It
covers statics, the concept of equilibrium, condition of equilibrium and free body diagram. The force acting
in an object is related to the resulting acceleration hence the motion of the object using Newton’s law.
Friction is also considered bring the analysis close to a realistic one.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
100%
16.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
A5
A6
62
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
17.
18.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
LO4
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
Details
P
4
1
-
7
11
4
1
-
7
12
Total
T
Indep.
L
Topic 1
Physical Quantities
Nature of physics
Define base quantities, base units,
derived quantities, derived units
Systems of units - SI, fps, cgs.
Prefixes
Concept and calculation of Measurement
Conversion of units
Topic 2
Equilibrium of a Rigid Body
Particle
Rigid body
Constraint
Degree of freedom
Topic 3
Motion and Newton’s Laws of Motion
Motion along a straight line
4
1
-
7
12
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
Newton’s laws of motion
Motion of a connected particles
Topic 4
Kinematic
Displacement, velocity and acceleration
Constant speed and constant velocity
Graphical representation with time
Topic 5
Projectiles
Projectiles
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
63
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Topic 6
Force
Forces
Turning moment
Moment
Couple
8
2
-
14
24
12
3
-
21
36
8
2
-
14
24
56
14
-
98
168
Topic 7
Elasticity
Stress and Strain
Modules of Elasticity
Shear force
Bending moment
hook law energy stored on elasticity spring
Topic 8
Friction
Coefficient of friction
Frictional forces
Total SLT
19.
Main references supporting the course 6
th
1. Cutnell, J.D and Johnson, K.W., Physics, 6 ed., USA: John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 2004
Additional references supporting the course
1. Cheong F. C., Pre U/STPM/Matriculation, Pearson and Longman, 2004, Malaysia
2. Hutchings, R., Physics, published by Nelson,
20.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
64
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Physics II
2.
Course Code
PPHY1074
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
A solid Physical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of
techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to
develop the student's Physical knowledge and to provide the
student with all the necessary techniques and methods for the
analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
1/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time (SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 98
Total = 168
56
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
4
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
This course introduces students to the knowledge of electricity and its application in engineering to enable
students to proceed to a degree course in engineering
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. Understand The fundamental of Electricity and its application in engineering
11.
Transferable Skills:
Problem solving in electrical physics
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
65
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
Tutorial sessions
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
The basic electricity topics. Students will learn the principles of electromagnetism, current, electric power,
power factor, transformer, resistance, capacitance and current relationship.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
100%
16.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
17.
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
LO4
66
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
L
T
P
Indep.
Total
Details
12
3
-
21
36
12
3
-
21
36
12
3
-
21
36
12
3
-
21
36
Topic 1
Electromotive force and current
Origin of electricity
Charged objects and the electric force
Conductor and insulators
Coulomb’s law
Electric field
Gauss’ law
Topic 2
Electric circuits
Ohm’s Law and resistivity
Electric Power
Alternating current
Kirchhoff’s Rule
Capacitor in series and parallel
Safety and physiological effect of current
Magnetic forces and magnetic fields
Topic 3
Magnetic fields and flux
Force and torque in magnetic field
Ampere’s law
Magnetic materials
Electromagnetic induction
mutual-inductance and self-inductance
transformer
Alternating current circuits
Topic 4
Capacitors and capacitive reactance
Inductors and inductive reactance
Circuits containing resistance, capacitance and inductance
Resonance in electric circuits
Semiconductor devices
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
67
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Topic 5
Electromagnetic waves
Nature of electromagnetic waves
Energy carried by the electromagnetic waves
Doppler effect and electromagnetic waves
Polarization
Total
19.
8
2
-
14
24
56
14
-
98
168
Main references supporting the course
th
1. Cutnell, J.D and Johnson, K.W., Physics, 6 ed., USA: John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 2004
Additional references supporting the course
20.
1. Cheong F. C., Pre U/STPM/Matriculation, Pearson and Longman, 2004, Malaysia
2. Hutchings, R., Physics, published by Nelson,
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
68
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Physics III
2.
Course Code
PPHY1084
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
A solid Physical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of
techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is
to develop the student's Physical knowledge and to provide
the student with all the necessary techniques and methods
for the analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering
fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
1/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time (SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 98
Total = 168
56
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
4
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
Physics III introduce to students the knowledge of vector, static, linear kinematics, linear dynamics, circular
motion, hydrostatics and wave. Enable students to proceed further study in engineering degree course
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
69
Curriculum Design and Delivery
10.
MEDIU
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. explain and define the technical terms in physics
2. explain the basic physical concepts
3. Elaborate phenomena with physical laws, principles and models.
4. Apply physical principles in engineering
5. Solve problems using principles of physics
6. Have the critical approach towards ideas and information in analysing physical problems.
7. Assimilate the concepts and principles of physics in everyday life and in the fields of technology.
8. Apply the theory of waves in engineering applications
11.
Transferable Skills:
Understanding of basic physics and problem solving
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures
Tutorial sessions
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
This course provides an introduction to the basic physics. The subject will introduce student to vectors,
statics, dynamics, kinematics , simple harmonic motion, hydrostatic, work, power and energy.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
70
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
100%
16.
17.
18.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
LO4
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
T
P
8
2
-
Total
L
Indep.
Details
14
24
Topic 1
Vector
Define - Scalar, vector quantities
Addition subtraction and resolution of vectors
triangular method
parallelogram method
Relative velocity.
Relative acceleration
Unit vector
Definition Unit vector in Cartesian Co-ordinates i, j and k
Vector products
Dot product. A.B=
Cross product A x B =
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
71
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Topic 2
Static
Reaction, normal reaction and frictional force Fx =
Coplanar forces
Forces acting at a point/particle, static equilibrium of a point
particle acted upon by coplanar forces.
Moment
Definition - Torque = r x F
Equilibrium of rigid bodies when subjected
To coplanar forces.
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
4
1
-
7
12
8
2
-
14
24
8
2
-
14
24
Topic 3
Linear kinematics
Definition - distance, displacement, speed, velocity, average
velocity, instantaneous velocity and acceleration.
Equation of linear kinematic motion under uniform
acceleration.
Graphical evaluation
Displacement - time graph
Velocity - time graph (for calculating
Displacement, velocity and acceleration)
Topic 4
Linear Dynamics
Newton's Laws of Motion
Definition of momentum and conservation of momentum.
Define and differentiate elastic and inelastic collisions.
Topic 5
Circular Motion
Angular displacement, angular velocity, instantaneous
angular velocity and angular acceleration.
Equations of circular kinematics under uniform angular
acceleration
Work, Power and Energy
Topic 6
Work (i) define work, W = F. S (ii) work done by uniform
forces
Power: Define power P
Energy (mechanical)
define kinetic energy, and potential energy
Conservation of energy, problems involve conservation
of energy in vertical motion under gravity only
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
72
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)
Topic 7
Brief discussion on vibrations
SHM
Define SHM
Equation of SHM
Amplitude, period, frequency
Velocity of a particle in SHM
Acceleration of a particle in SHM
Examples of SHM-Spring and simple pendulum
4
1
-
7
12
8
2
-
14
24
56
14
-
98
168
Topic 8
Hydrostatic
Density- definition and units relative density
Hydrostatic pressure, atmospheric pressure distribution of
pressure in liquids, manometer. Archemedes' Principle
Total
19.
Main references supporting the course
th
1. Cutnell, J.D and Johnson, K.W., Physics, 6 ed., USA: John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 2004
2. Stev Adams, Jonathan Alldeny’ advanced . physics, Oxford university press 2000.
Additional references supporting the course
20.
1. Cheong F. C., Pre U/STPM/Matriculation, Pearson and Longman, 2004, Malaysia
2. Hutchings, R., Physics, published by Nelson,
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
73
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Physics IV
2.
Course Code
PPHY1094
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
A solid Physical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of
techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to
develop the student's Physical knowledge and to provide the
student with all the necessary techniques and methods for
the analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
2/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time (SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 98
Total = 168
56
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
4
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
This course introduces the students to the knowledge of elements inside the system of the electrical
engineering and practice what they have learn in the lectures.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. Understand principles of electrical circuits
2. Apply the knowledge to conduct circuit analysis
11.
Transferable Skills:
Problem solving in electrical circuits
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
74
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
Tutorial sessions: Practice exercises
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
This course provides an introduction to the basic techniques of circuit’s analysis and electronic circuits
design. The first part of the units introduces electrical components and the fundamental laws that govern
the behaviour of an electrical circuit. Methods of analysis will be include the use of phasors for sinusoidal
responses and Laplace transforms for more general case where there may be initial energy storage and
where there is need to determine circuit transient behaviour. In the second part of the course, a variety of
electronic circuits based on integrated circuit amplifiers will be introduced.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
16.
17.
100%
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
75
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
LO1
LO2
LO3
LO4
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
L
T
P
Indep.
Total
Details
20
5
-
35
60
20
5
-
35
60
16
4
-
28
48
56
14
-
98
168
Introduction and fundamental concept
Topic 1
Resistance
Power
Energy
Voltage and current sources
Capacitance
Self-inductance
Mutual inductance
Introduction to circuit analysis
Topic 2
Kirchhoff’s current law
Kirchhoff’s voltage law
Resistors in series and parallel
Inductors in series and parallel
Capacitor in series and parallel
Principles of superposition
Thevenin theorems
Topic 3
Circuit analysis in the sinusoidal steady state
Phasors and impedance
Series inductor –capacitor-resistor (LCR) filter
Parallel LCR filter
Total
19.
Main references supporting the course
th
1. Cutnell, J.D and Johnson, K.W., Physics, 6 ed., USA: John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 2004
Stev Adams, Jonathan Alldeny’ advanced . physics, Oxford university press 2000.
Additional references supporting the course
1. S.R. Paranjothi, 2000,” Electric Circuit Analysis”, Pearson
2. Boylested and Nashelsky, 2001,”Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory”, Prentice-Hall.
3. Cheong F. C., Pre U/STPM/Matriculation, Pearson and Longman, 2004, Malaysia
4. Hutchings, R., Physics, published by Nelson,
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
76
Curriculum Design and Delivery
MEDIU
20. Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
77
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Physics V
2.
Course Code
PPHY1104
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
A solid Physical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of
techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to
develop the student's Physical knowledge and to provide the
student with all the necessary techniques and methods for
the analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
2/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time (SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 98
Total = 168
56
14
-
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
4
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
This course introduces students to the knowledge of heat and application in civil engineering
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. Understand The fundamental of heat and its application in civil engineering
11.
Transferable Skills:
Understand the nature of Heat, heat transfer and gas behaviour
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
78
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
Tutorial sessions
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
This course provides an introduction to the principles of heat, thermodynamics and gas behaviour
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Quizzes
10%
Assignments
10%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
100%
16.
17.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
LO4
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
79
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
19.
SLT
L
T
P
Indep.
Total
Details
20
5
-
35
60
20
5
-
35
60
16
4
-
28
48
56
14
-
98
168
Topic 1
Introduction to heat
Temperature scale
Thermal expansion
heat and internal energy
mode of heat transfer
Thermodynamics
Topic 2
thermodynamics system and their surrounding
laws of thermodynamics
thermal processes
heat engines
Carnot’s principles and Carnot engine
refrigerators, air conditioners and heat pumps
entropy
Topic 3
Ideal gases
Molecular mass, the mole and Avogadro’s numbers
The ideal gas law
Kinetic theory of gases
Diffusion
Total
20.
Main references supporting the course
th
1. Cutnell, J.D and Johnson, K.W., Physics, 6 ed., USA: John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 2004
2. Stev Adams, Jonathan Alldeny’ advanced . physics, Oxford university press 2000.
Additional references supporting the course
21.
1. S.R. Paranjothi, 2000,” Electric Circuit Analysis”, Pearson
2. Boylested and Nashelsky, 2001,”Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory”, Prentice-Hall.
3. Cheong F. C., Pre U/STPM/Matriculation, Pearson and Longman, 2004, Malaysia
4. Hutchings, R., Physics, published by Nelson,
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
80
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Physics Laboratory
2.
Course Code
PPHY1112
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Major
A solid Physical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of
techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is
to develop the student's Physical knowledge and to provide
the student with all the necessary techniques and methods
for the analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering
fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
3/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time (SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 52
Total = 95
13
-
30
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
2
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
Laboratory or practical sessions enable the students to understand the theoretical physical concepts and at
the same time raise their techniques and skills in carrying out experiments as well as writing reports
properly.
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. Carry out the experiments according to instructions
2. Arrange and analyse the experimental data properly and clearly
3. Arrive at accurate experimental conclusions
4. Write the experimental reports correctly
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
81
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
11.
Transferable Skills:
Conducting experiment, analyse and report writing
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
Practical sessions: Laboratory experiments
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises, Laboratory report)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
Students will conduct experiments in the laboratory on force, friction, specific heat, electricity, electric
circuits and gases
14.
Mode of Delivery:
practical sessions
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
50%
Performance Assessment
50%
Final Examination
50%
Total
16.
17.
100%
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
LO1
LO2
LO3
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
LO4
82
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
Details
Torque-parallel forces
Torque-Non parallel forces
Topic 4Topic 5
Centripetal force
Sliding friction
Ohm’s law
Resistance in series and parallel circuits
Topic 10
1
-
2
4
7
1
-
2
4
7
1
-
2
4
7
1
-
2
4
7
1
-
2
4
7
1
-
2
4
7
1
-
2
4
7
1
-
3
4
8
1
-
3
4
8
1
-
2
4
7
1
-
3
4
8
1
-
2
4
7
Specific heat capacity
Topic 9
Topic 6Topic 7Topic 8
Simple harmonica motions
P
Total
Buoyant Force
T
Indep.
Topic 3
Topic 2
Topic 1
L
To determine the specific heat capacity of a solid by electrical
method.
Gas
To prove Charles's Law
Topic 12
Topic 11
Electricity
To determine the resistance of a given wire and emf of a cell
using potentiometer.
Kirchhoff’s rules
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
83
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Topic 13
Capacitors in series and parallel circuits
Total
19.
1
-
3
4
8
13
-
30
52
95
Main references supporting the course
1. Practical Physics by M. Somerkh, Chatto & William's (educational) Ltd.,
Additional references supporting the course
1. Ordinary Practical Physics, 2nd edition by G.L. Moss, Heinemann Educational Bks Ltd.,
2. Practical Physics by M. Somerkh, Chatto & William's (educational) Ltd.,
20.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
84
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
1.
Name of Course
Chemistry
2.
Course Code
PCHM1123
3.
Name(s) of academic staff
To be Assigned
4.
Rationale for the inclusion of the
course/module in the programme
Minor
A solid chemical ability at a basic level is essential for the
understanding of the principles and the application of
techniques in Engineering science. The aim of the module is to
develop the student's chemical knowledge and to provide the
student with all the necessary techniques and methods for the
analysis and solutions of problems in Engineering fields.
5.
Semester and Year offered
3/1
6.
Total Student
Learning Time
(SLT)
Face to Face
Total Guided and Independent Learning
L = Lecture
L
T
P
O
T = Tutorial
P = Practical
Independent = 72
Total = 122
36
-
7
-
O= Others
7.
Credit Value
3
8.
Prerequisite (if any)
none
9.
Objectives:
To enable students to acquire knowledge and understanding of scientific concepts, theories,
facts and laws in physical, inorganic and organic chemistry which forms the basis of material
science
10.
Learning outcomes:
Upon completing this course, students should able to:1. Understand basic concepts of chemistry and its applications.
2. Understand the relationship between properties of matter, bonding and structure.
3. Understand the effects of environment on materials and how to reduce these effects.
4. Understand general characteristics of engineering materials such polymers and steel.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
85
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
11.
Transferable Skills:
To develop in students the ability to handle information and solve problems related to chemical reactions
12.
Teaching-learning and assessment strategy
A variety of teaching and learning strategies are used throughout the course, including:
Classroom lessons. Lectures and Power Point presentations
Tutorial sessions: Practice exercises
Lecturer-led problem-solving sessions,
Solving assigned problems in groups and singly
Independent study.
Assessment strategies include the following:
Ongoing quizzes
Midterm tests
Performance Assessment (participation, Assigned exercises, Laboratory Report)
Lecturer Observation
13.
Synopsis:
This course covers the mole concept, atomic structure and the periodic table, chemical bonding,
thermochemistry, acids and bases, transition metals, water and polymers.
14.
Mode of Delivery:
Class Lectures / tutorial and practical sessions
15.
Assessment Methods and Types:
The assessment for this course will be based on the following:
Coursework
40%
Laboratory Report
20%
Mid-Semester Exam
20%
Final Examination
60%
Total
100%
16.
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Aims
A1
17.
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
Mapping of the course/module to the Programme Learning Outcomes
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
86
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
18.
LO1
LO2
LO3
LO4
Content outline of the course/module and the SLT per topic
SLT
L
T
P
Indep.
Total
Details
4
-
-
8
12
4
-
-
8
12
4
-
-
8
12
Topic 1
Atoms and Molecule: The concept of mole
Elements and compounds
Atoms and molecule, chemical symbols, empirical and
molecular formula
Relative atomic mass and relative molecular mass
Avogadro's number
Mole concept
Concentration and molarity; n=MV
Molar volume of gas
Stoichiometry: chemical equation; limiting reagent.
Topic 2
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
Fundamental particles in an atom, atomic number, mass
number isotope.
Introduction to quantum mechanics
Quantum numbers, energy levels (KLMN), sub level
energies, orbitals (s,p,d,f), electron configuration
Periodic Table; periodic properties: atomic size, ionization
energy, electron affinity and electronegativity.
Topic 3
Chemical Bonding
Ionic bonds, covalent bonds, dative covalent bonds and
metallic bonds; Lewis structure for ionic and covalent
compounds; general properties of ionic and covalent
compounds.
Geometrical shapes for simple covalent molecules based on
valence shell electron pair repulsion theory.
Weak intermolecular forces between covalent molecules;
Van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonding
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
87
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Thermochemistry
Topic 4
Exothermic and endothermic reactions
Heat of reaction: heat of combustion, heat of formation,
bond energy, heat of atomization, ionization energy,
electron affinity and lattice energy.
Hess law, and calculation of heat of formation, heat of
combustion, lattice energy (Born-Haber cycle)
4
-
-
8
12
4
-
-
8
12
4
-
-
8
12
4
-
-
8
12
4
-
-
8
12
Topic 5
Electrochemistry
Redox reactions: oxidation number, oxidation and
reduction; oxidizing and reducing agents; balancing redox
reactions.
Standard electrode potential, standard hydrogen electrode,
redox series
Electric cell, calculation of e.m.f. and determination of
spontaneity of reaction.
Metal corrosion: mechanism of corrosion (rusting of iron),
electrochemical cell e.g. concentration cell and galvanic
cell, prevention of corrosion: electroplating and cathodic
protection.
Topic 6
Acid and Bases
Properties of acids and bases of metal oxides and nonmetals.
Calculation of pH for strong acids, weak acids, strong base
and weak base.
Neutralization : titration curves
Topic 7
Transition metals
Properties
Extraction of ferrum and copper
Steel
Water
Topic 8
Water hardness
Sources of water hardness
Types of water hardness
Methods of removing water hardness: boiling, addition of
washing soda and ion exchange.
Estimation of water hardness: EDTA titration
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
88
MEDIU
Curriculum Design and Delivery
Carbon compounds
Topic 9
Introduction to carbon compounds (Organic)
Functional groups
Homologous series; alkane, alkene, alcohol and carboxylic
acid
Substitution reactions, addition and esterization.
Polymer
4
-
-
8
12
-
14
72
122
Topic 10
Practical
Determination of molarity and concentration of an acid or
base
Determination of the relative atomic mass of an element X
in a given compound.
Determination of heat of reaction for the decomposition of
potassium hydrogen carbonate.
To determine the positions of some ions/metal in the redox
series.
To study the reactions of Fe²+, Fe³+ and Cu²+ ions.
Determination of water hardness using EDTA titration.
Properties of alkanes, alcohol's and carboxylic acids.
Total
19.
2
2
-
-
2
2
2
2
2
36
-
14
Main references supporting the course
1. Petrucci, R.H. and Harwood, W.S. General Chemistry, Principles and Modern Applications,
Macmillan Publishing Company, New York 1993
Additional references supporting the course
21.
1. Tan Yin Toon, Kimia Fizik STPM, Edisi Kedua, Fajar Bakti 1999
2. Kho Chin He, Kimia Fizik STPM, Federal Publication 1997
3. Ramsden, E.N. A-Level Chemistry, Second Edition, Stanley Thornes (publishers) Ltd., 1990.
4. Brady, J.E. and Holum, J.R. Fundamentals of Chemistry, 3rd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, 1988.
5. Brady and Humiston, Kimia Am, Prinsip dan Struktur, Edisi Kedua (terjemahan), John Wiley &
Sons, 1983.
Other additional information
All materials will be available to the students in the library.
AL-MADINAH INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY 2010
89