PLANTS review Chapter 29, 30, & 35-39
advertisement

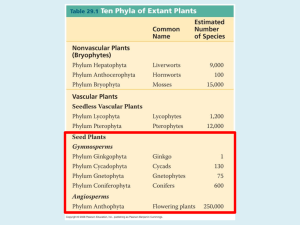
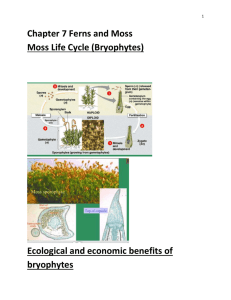
PLANTS review Chapters 29, 30, 38 Bryophytes & Pteridophytes Gymnosperms & Angiosperms Angiosperm Reproduction One of the four main types of land plants that contains mosses and lacks vascular tissue BRYOPHYTES Which is the dominant stage in the life cycle of this group? sporophyte gametophyte gametophyte One of the four main types of land plants that contains ferns and has vascular tissue Pteridophytes Which is the dominant stage in the life cycle of this group? sporophyte gametophyte sporophyte One of the four main types of land plants that contains flowering plants and possess vascular tissue Angiosperms Which is the dominant stage in the life cycle of this group? sporophyte gametophyte sporophyte One of the four main types of land plants that contains the conifers, have “naked” seeds, and vascular tissue Gymnosperms Which is the dominant stage in the life cycle of this group? sporophyte gametophyte sporophyte The mutualistic association of plant roots and fungi mycorrhizae 90% of all plant species today are in which group? Angiosperms (flowering plants) Evidence suggests that land plants evolved from which group of protists 500 million years ago? Green algae (Charophytes) What evidence suggests that land plants evolved from green algae 500 million years ago? •Both produce cellulose for cell walls in same unique way •Both only groups with peroxisomes (to reduce effects of photorespiration) •Similar sperm structure •Make cell plates during mitosis is similar way •Nuclear and chloroplast DNA closely related If a plant is “nonvascular” it means it doesn’t have _____________ xylem or phloem The female gametangia in plants is called the __________ archegonia archegonia antheridia All land plants have a life cycle that consists of two multicellular stage called ALTERNATION OF GENERATIONS Another key feature of plants is the production of gametes in multicellular organs called gametangia The gametophyte stage is haploid __________ haploid diploid The male gametangia in plants is called the __________ antheridia archegonia antheridia The zygote produced by fusion diploid of sperm and egg is ________ haploid diploid What advantages did becoming terrestrial provide plants? Increased sunlight (unfiltered by water) More carbon dioxide in air than water soils rich in nutrients fewer predators The sporophyte stage is diploid __________ haploid diploid What challenges did plants face when they became terrestrial? Lack of water, dessication, lack of structural support against gravity The sporophyte divides using meiosis _________to produce spores. mitosis meiosis The antheridia in the gametophyte produces____________ Multiple sperm The gametophyte divides using _________to produce gametes. mitosis mitosis meiosis The archegonia in a gametophyte a single egg produces _____________ Which plant group requires water for their sperm to swim to the egg? All seedless plants Bryophytes & Pteridophytes Structures in the sporophyte stage where meiosis occurs to produce spores sporangia Spores produced by plants are haploid ____________ haploid diploid The megasporagium, megaspore, and protective tissue around them make an _________ ovule What are the 5 crucial adaptations that led to the success of seed plants? •Reduced gametophytes • • • • (protects antheridia/archegonia) Heterospory (2 types of spores) Ovules (protect egg/developing zygote) Pollen (no need for water) Seeds Megaspores produce Female gametophytes ______________ The production of TWO types of spores seen in seed plants heterospory is called ___________ Microspores produce male gametophytes ______________ A pollen grain contains ____________ 2 sperm nuclei Identify the following flower parts stamen3 Anther 1 filament 2 petal 4 stigma 5 7 Carpel style ovary 6 10 8 sepal 9 ovule In angiosperms and gymnosperms a male gametopyte = a Pollen _______ grain What advantages do seeds have compared to spores? Seeds are multicellular with several layers of tissue protecting embryo Seeds have supply of stored energy so embryo can wait for good germination conditions and use stored energy for early growth Plants with “naked” seeds are called __________ Gymnosperms In a flowering plant the mature ovaries are called _________ fruits Angiosperm that has one cotyledon in the seed, parallel leaf veination, scattered vascular tissue and flowering parts in multiples of threes monocot Give an example of the above Corn, orchids, lilies, grasses Angiosperm that has two cotyledon in the seed, net leaf veination, vascular tissue in a ring and flowering parts in multiples of fours or fives Eudicot (dicot) Give an example of the above Roses, peas, beans, oaks Flowering plants are classified in the PHYLUM ANTHOPHYTA ______________ The stamens with anthers are the _________ part of a flower. male male female carpel The ________ in a flower is made up of the stigma, style, and ovary. haploid Plant pollen is _________ haploid diploid Gymnosperms have seeds often exposed on modified leaves cones called _________ The carpel including the stigma and style is the female _________ part of a flower. male female CONTRAST MONOCOTS & DICOTS MONOCOTS Number of cotyledons in seed Vein pattern one parallel Flower parts in multiples Multiples of 3’s of ? Location of scattered vascular tissue Examples Corn, orchids, lilies, grasses DICOTS two net Multiples of 4’s & 5’s In ring Peas, beans, roses, oaks Mosses, hornworts, and liverworts belong in which group of plants? Bryophytes (nonvascular plants) As plants evolved from algae to angiosperms which generation increases in dominance? sporophyte Most angiosperms are monoecious _____________ meaning they have both male and female parts on the same flower. Ferns, horsetails, club mosses belong in which group of plants? Pterophytes Ginko, cycads, Ephedra, and conifers belong in which group of plants? Gymnosperms Plants with male and female flowers on separate plants are dioecious called _____________ Flowering plants belong in which group of plants? Angiosperms How do monoecious plants prevent self pollination? Male and female parts may be physically separated (anthers/stigma at different heights) or mature at different times. Double fertilization is only seen in which group of plants? Angiosperms Seed leaves are called _____________ cotyledons CONTRAST PLANT REPRODUCTION Bryophytes Pteridophytes Mosses Ferns Dominant generation gametophyte sporophyte sporophyte (tree) sporophyte Alternate generation sporophyte gametophyte (small) gametophyte (pollen/ovule) Wind, insects carry pollen gametophyte Example How sperm move Relationship of gametophyte & sporophyte Requires water to swim Requires water to swim Sporophyte grows on top of & provided nourishment by female gametophyte Sporophyte grows out of female archegonium of gametophyte; receives nourishment; independent at maturity Gymnosperms Angiosperms Ginko, conifers Flowering plants (pollen, ovary) Wind, animals carry pollen Gametophyte Gametophyte reduced in size; reduced in size; relies on relies on sporophyte sporophyte for protection for protection and nourishment and nourishment Many angiosperms and their pollinators show which pattern of evolution? coevolution 3 n Endosperm is __ Match the derived characters with the correct branch points in the diagram embryos 7. _______________________ Flowers Embryos Seeds Vascular tissue Vascular tissue 8. _______________________ seeds 9. ________________________ flowers 10. _______________________ From:Campbell and Reece Chap 30 Self quiz Flowers that have both male and female parts are called ____________ monoecious Tell what happens to the 2 sperm nuclei in double fertilization One sperm fertilizes the egg and becomes the embryo; the 2nd sperm nuclei fertilizes 2 polar bodies and becomes the endosperm Plants that produce flowers that have either male or female parts, but not both are called _____________ dioecious fruits Mature ovaries = __________ In angiosperms diploid cells in pollen sacs (microsporangia) undergo ________ meiosis to make haploid microspores mitosis meiosis In angiosperm reproduction, the male gametophyte = Pollen _________ grain In an angiosperm seed the embryonic root is called the radicle __________ In angiosperm reproduction, sporophytes seeds grow into __________ gametophytes sporophytes In angiosperms diploid cells in pollen sacs (microsporangia) undergo meiosis to microspores make haploid _________________ In angiosperm reproduction, the female gametophyte = Embryo _________ sac In angiosperms diploid cells in ovules undergo meiosis to make 4 haploid _________________ megaspores In angiosperms, the ovule develops seed into the _______ and the ovary develops into the __________ fruit The transfer of pollen from the anther of a flower on one plant to the stigma of a flower on another pollination plant is called _____________ The shoot tip with miniature leaves attached inside a seed is called the _________ epicotyl Tell some mechanisms that prevent plants from self pollinating Dioecious flowers- pollen making and egg making flowers are on separate plants Monoecious flowers- male and female parts are physically separated by height or mature at different times Molecular barriers-biochemical block prevents pollen from same plant from developing pollen tube and fertilizing own egg