South Africa: The Rise of Apartheid - South-Africa-Under
advertisement

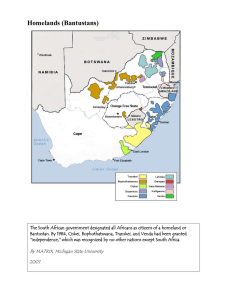
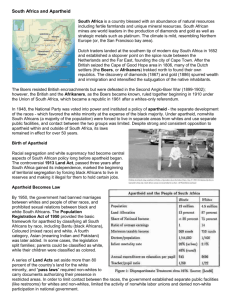
South Africa: The Rise of Apartheid Chapter 13 South Africa Section 2 Apartheid Through out the Decades After gaining independence from England, Afrikaner National Party gained majority in 1940s 1948-National Party-invented apartheid to establish white domination and separate races further 1950s – “Petty Apartheid” established – “classification and registration of Black and Coloured South Africans” 1960s- “Grand Apartheid” established - “territorial separation and police repression” 1948 Elections The national Party represented the white Afrikaners The won the election base on the slogan of Apartheid White South Africans wished to have a country that was separate from black South Africans. They created the system of Apartheid that was meant to segregate against other races and eventually have them live in separate areas of the country. Population Registration Act 1950-Population Registration Act -Divided South Africans into white, black (Africans), and colored (mixed descent) -Based on appearance, social acceptance, and descent -Blacks-forced to carry “pass books” holding fingerprints, photograph, and information on access to non-black areas 1950 Group Areas Act Created basis for ethnic government in African reserves or “homelands” Each race was assigned a different homeland Black political rights restricted to designated homeland, but had no rights in South African Parliament, which had complete control over the homelands District 6 Sophiatown Mixed Marriages Act In 1949 South African officials banned mixed marriages and relationships between different races. White South Africans believe that their race should be pure and non-diverse This devastated many families that were considered to be of mixed race Apartheid and Education Just as it was in the United States during the ‘separate but equal” laws, South Africa had segregated schools during Apartheid Black schools were dramatically inferior to those of whites Black college students were not allowed to attend white schools and black schools prepared them to become laborers Apartheid and Women Women were extremely segregated against during Apartheid They were denied land, schools, rights to vote and jobs. Their marriages and children were controlled by the government in an effort to control black populations Activity Sheet A – South African Apartheid Legislation Complete the questions Complete the Objective You may work in pairs Due on Friday South Africa and the Homelands Bantustans Between 1960 and 1985, 3.5 million Africans were moved by force Ten homelands were located to different black ethnic groups within the race: Lebowa QwaQwa Bophuthatswana KwaZulu KaNgwane Transkei and Ciskei Gazankulu Venda KwaNdebele Bantustans Homelands and Restrictions During the 1960s-1980s, South African government created a system of resettlement to remove other races from “white areas” Each territory had a chief that worked for the Afrikaner government. Many of these “leaders” were politically corrupt and greedy. Homelands were located in the most poverty-stricken and isolated regions of South Africa. Mostly populated by women and children, since men were the only ones allowed to live in the city. Homelands and Restrictions Anyone that belonged to a homeland, had their South African citizenship removed. Legally they had no rights under the South African government Homelands controlled their own systems of education, police, and healthcare. However, these were underfunded by the government Public services and amenities were segregated, and very often where not available in black homelands (i.e. movies) Churches were segregated and could forbid the entrance of black South Africans as well Independence and Territories Independence of Bantustans White South Africans removed black rights and citizenship on purpose. Apartheid government after separating races into territories, gave them the option of becoming independent from South Africa and creating their own nation. These “nations” would have no funding or support from the South African government (although they did benefit from black labor) Members of annexed homelands would have to carry passports into South Africa Independent homelands were never recognized as nations by the global community or the continent of Africa 1953- Public Safety Act and Criminal Law Amendment Act Gave government power to declare states of emergency, increasing punishments for protesting against or supporting repeal of a law: fines, imprisonment, whippings 1960-Government declared state of emergency when large group of blacks in Sharpeville refused to carry their passes Emergency lasted for 156 days, 69 people dead and 187 people wounded Who does Apartheid Benefit? A revolution was beginning… Activity Complete sheet B and study for South Africa Section 2 quiz You must complete the questions and the challenge activity You may work in pairs Both Sheet A and B are due Friday.