WHMIS
advertisement

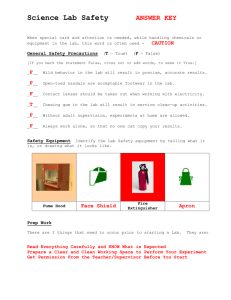
Self Directed Lesson on: WHMIS WHMIS stands for Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System WHMIS is a Canadian created system that came into effect on October 31, 1988 The point of WHMIS is to help employers and workers understand the dangerous properties of chemicals and workplace materials Components of WHMIS Components of WHMIS include labeling stickers, Material Safety Data Sheets that explain the stickers and worker training The 8 Classes of WHMIS In WHMIS, there are 8 key classes of Hazardous Materials These classes are labeled A, B, C, D1, D2, D3, E and F Each class of WHMIS deals with a different type of Hazardous Material and each symbol represents the danger that could occur if the material is mishandled Class A Class A : Compressed Gas Compressed gases are dangerous because they have the potential to explode or leak Many compressed gases are also combustible and would carry that WHMIS symbol as well Common examples of compressed gas include: propane, welding gases, oxygen, helium and aerosols Class B Class B: Flammable and Combustible Material Flammable material is material that will easily burn or catch fire at normal temperatures Combustible material is material that will catch on fire at above normal temperatures Common examples of flammable and combustible materials include: propane, kerosene, spray paint, varnish, turpentine, acetylene, diesel, gasoline and WD40 Class C Class C: Oxidizing Materials An oxidizing material will help another substance burn but does not usually burn itself Oxidizers can provide oxygen for the fuel or can cause a material that does not usually burn to catch fire Common examples of oxidizing materials include: oxygen, nitric acid, bleach and chlorine Class D – D1, D2 and D3 Class D1 Class D2 Class D3 Class D1: Materials Causing Immediate and Serious Toxic Effects These are materials that are poisonous or cause serious effects such as coma or burns within minutes of exposure Materials in this class may also cause serious long term health effects as well Common materials causing immediate and serious toxic effects are: carbon monoxide, cyanide, arsenic, and even Tide and Mr. Clean Class D2: Materials Causing Other Toxic Effects These are materials that cause effects such as allergies, cancer, reproductive problems and chronic illnesses These materials can cause mutations, irritations and carcinogens Common materials causing other toxic effects are: asbestos, lead, mercury and nicotine Class D3: Biohazard and Infectious Materials Biohazardous materials include viruses, fungi, parasites and bacteria and are usually toxic organisms These materials are usually found in labs, hospitals or veterinary clinics Common examples of biohazardous materials include: HIV/AIDS virus, salmonella, hepatitis, anthrax and ebola Class E Class E: Corrosive Materials Corrosive materials are materials that can cause severe and immediate burns Many corrosives can not only damage human skin, but material (clothing), containers (plastics etc.) and even metal Common corrosives include: acids (Ex. hydrochloric and battery acid), chlorine and ammonia Class F Class F: Dangerously Reactive Materials Dangerously reactive materials have 3 different requirements: 1. They react with water to make a toxic gas 2. It will react itself if bumped, dropped or upon a temperature increase 3. It can create a polymer, decompose or condense easily These materials are very chemically unstable Common dangerously reactive materials are: ozone and nitroglycerine Why do I care about WHMIS? The point of WHMIS is to help keep you safe while you are on the job The WHMIS symbols work with the Material Safety Data Sheets to tell you all the dangerous properties of the materials you are about to handle Worker training ensures that employees know what safety measures to take when handling material Remember, even the most harmless looking products can be hazards – so it is important to pay attention to WHMIS symbols at all times! = References Pictures from http://www2.worksafebc.com/Topics/WHMIS Information adapted from http://www.ccohs.ca (Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety) and http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Workplace_Hazar dous_Materials_Information_System (Wikipedia)