Slide 1
advertisement

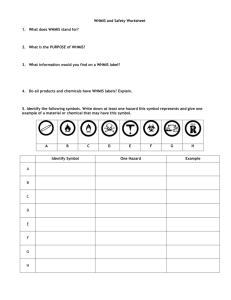
Lab Safety and WHMIS Education Lab Safety • As a senior student Lab Safety should not be new to you. However let’s review some key features. – Always keep safety in mind • • • • • Safety equipment Personal Protective Equipment Lab Equipment Lab Procedures Chemical Handling Safety Equipment • Please make sure that you know where the safety equipment is located in the classroom and know how to use it. • • • • Eye Wash Fire Blanket First Aid Kit Fire Extinguisher Personal Protective Equipment • Check labs before hand to ensure that you are wearing the proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). • Safety Goggles • Safety Aprons • Latex Gloves Lab Equipment • Ensure that you are using all Lab equipment properly and in a safe manor. • DO NOT USE BROKEN GLASSWARE • Use equipment for the purposes that it was designed for • Be aware of your surroundings • Watch sharp objects. • Be careful near hot equipment (flames, glass, etc.) • When handling hot objects use proper tongs/gloves • All broken glass goes into the glass bin, please inform the teacher. Lab Procedures • When working with equipment be sure to follow proper handling procedures. • Focusing Microscopes • Lighting Bunsen Burners • Read and Follow all lab procedures before and during lab • Do not be afraid to ask for help if confused or unsure how to use a piece of equipment Chemical Handling • Handel all chemicals as if they are dangerous. • If unsure of handling procedure please refer to text book, MSDS, or the teacher • Do not taste • When smelling waft towards you (do not smell directly) • In case of spill please notify the teacher • Follow directions for proper disposal of chemical waste WHMIS • WHMIS stands for Workplace Hazardous Material Information System. It not only identifies harmful chemicals but also lets people know how to work with them. • Three essential parts; • WHMIS Labeling • MSDS • Education and Training WHMIS Labeling • One of the most recognized parts of the labeling system is the WHMIS symbols which are recognized world wide. WHMIS Labeling CLASS A: Compressed Gas This class includes compressed gases, dissolved gases, and gases liquefied by compression or refrigeration. If the container is greater than 40 psi, the gas is a Class A product. The cylinder may explode if exposed to heat or to physical shock (Dropped). Examples: Oxygen and Acetylene in cylinders for welding, propane WHMIS Labeling • One of the most recognized parts of the labeling system is the WHMIS symbols which are recognized world wide. WHMIS Labeling CLASS B: Flammable and Combustible Material This class includes solids, liquids, and gases capable of catching fire in the presence of a spark or open flame under normal working conditions. Class B has six divisions: Division 1: Flammable Gasses Division 2: Flammable Liquids Division 4: Flammable Solids Division 5: Flammable Aerosols Division 6: Reactive Flammable Materials WHMIS Labeling • One of the most recognized parts of the labeling system is the WHMIS symbols which are recognized world wide. WHMIS Labeling CLASS C: Oxidizing Materials These materials increase the risk of fire if they come in contact with flammable or combustible materials. Examples: perchloric acid, hydrogen peroxide, permanganates, compressed oxygen WHMIS Labeling • One of the most recognized parts of the labeling system is the WHMIS symbols which are recognized world wide. WHMIS Labeling CLASS D: Division 1 Materials Causing Immediate and Serious Toxic Effects These materials can cause death or immediate injury when a person is exposed to small amounts. Examples: sodium cyanide, hydrogen sulphide WHMIS Labeling • One of the most recognized parts of the labeling system is the WHMIS symbols which are recognized world wide. WHMIS Labeling CLASS D: Division 2 Materials Causing Other Toxic Effects These materials can cause life-threatening and serious long-term health problems as well as less severe but immediate reactions in a person who is repeatedly exposed to small amounts. Health problems include immediate skin or eye irritation, allergic sensitization, cancer, serious impairments of specific body organs and systems, and reproductive problems. Examples: xylene, asbestos, isocyanines WHMIS Labeling • One of the most recognized parts of the labeling system is the WHMIS symbols which are recognized world wide. WHMIS Labeling CLASS D: Division 3 Biohazardous Infectious Materials These materials contain harmful micro-organisms that have been classified into Risk Groups 2, 3, and 4 as determined by the World Health organization or the Medical Research Council of Canada. Examples: cultures or diagnostic specimens containing salmonella bacteria or the hepatitis B virus WHMIS Labeling • One of the most recognized parts of the labeling system is the WHMIS symbols which are recognized world wide. WHMIS Labeling CLASS E: Corrosive Materials This class includes caustic and acid materials that can destroy skin or eat through metals. Examples: sodium hydroxide, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid WHMIS Labeling • One of the most recognized parts of the labeling system is the WHMIS symbols which are recognized world wide. WHMIS Labeling CLASS F: Dangerously Reactive These products may self-react dangerously (for example, they may explode) upon standing or when exposed to physical shock or to increased pressure or temperature, or they emit toxic gases when exposed to water. Examples: plastic monomers such as butadiene; some cyanides WHMIS Labeling • One of the most recognized parts of the labeling system is the WHMIS symbols which are recognized world wide. WHMIS Labeling • The WHMIS symbols should not be confused with those used in the Household Hazardous Products System; Caution Corrosive Flammable Poisonous Explosive Warning Danger WHMIS Labeling • • WHMIS product labels are used to inform the worker of dangers. They must contain the following information within a cross-hatched border.; 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Product Identifier Hazard Symbol Risk phrases Precautionary statements First Aid measures Supplier identification Reference to MSDS ACETONE ACÉTONE See Material Safety Data Sheet for this product 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Product Identifier Hazard Symbol Risk phrases Precautionary statements First Aid measures Supplier identification Reference to MSDS DANGER! EXTREMELY FLAMMABLE. IRRITATES EYES. PRECAUTIONS: Keep away from heat, sparks, and flames. Ground containers when pouring. Avoid breathing vapours or mists. Avoid eye contact. Avoid prolonged or repeated contact with skin. Wear splashproof safety goggles or faceshield and butyl rubber gloves. If acetone is present in concentrations greater than 250 ppm, wear a NIOSH-approved respirator with an organic vapour cartridge. Use with adequate ventilation, especially in enclosed areas. Store in a cool, well ventilated area, away from incompatibles. FIRST AID: In case of contact with eyes, immediately flush eyes with lots of running water for 15 minutes, lifting the upper and lower eyelids occasionally. Get medical attention immediately. In case of contact with skin, immediately wash skin with lots of soap and water. Remove contaminated clothing and shoes. Get medical attention if irritation persists after washing. Wash clothing before reuse. If inhaled, remove subject to fresh air. Give artificial respiration if not breathing. Get medical attention immediately. If swallowed, contact the Poison Control Centre. Get medical attention immediately. Do not give anything by mouth to an unconscious or convulsing person. ATTENTION! THIS CONTAINER IS HAZARDOUS WHEN EMPTY. ALL LABELLED HAZARD PRECAUTIONS MUST BE OBSERVED. B I G BIG Chemical Company / 123 Nitro Avenue, Vapour Town BC, (604)279-7408 MSDS • MSDS stands for Material Safety Data Sheets. • For every chemical held with in a workplace there should be an MSDS. • MSDS should be kept alphabetically and in a binder. • Many workplaces are going to a computer database of MSDS MSDS • MSDS are typically Split into 9 sections; 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Product Information Hazardous Ingredients Physical Data Fire and Explosion Hazard Reactivity Data Toxicological Properties Preventative Measures (PPE) First Aid Measures Preparation Information Education and Training • It is the responsibility of the Employer to provide safety Education and Training including WHMIS • WHMIS education is learning how WHMIS works, what the symbols are, what an MSDS is, etc. • WHMIS training is hands-on, job specific training on how WHMIS is implemented into the workplace, and how to work safely with hazardous materials.