Chapter 2 - BWPhysics
advertisement

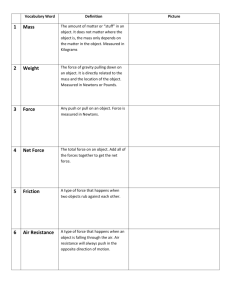
Vocabulary Words Acceleration The rate at which velocity is changing in magnitude, direction or both Average Speed Path distance divided by time interval Elapsed Time Time that passed since the beginning of an event Free Fall Motion under the influence of the gravitational force Instantaneous Speed Speed at any instant of time Rate How much something changes per unit of time Relative Regarded in relation to something else Speed How fast something is moving, distance moved over time Velocity Speed together with the direction of motion CHAPTER 3 COMPONENT One of the vectors, often mutually perpendicular, whose sum is a resultant vector. Projectile An object that moves through the air or space acted on only by gravity. Resolution The process of determining the components of a vector. Resultant The vector sum of two or more component vectors. Satellite An object that falls around Earth or some other body rather than into it. Scalar Quantity A scaled amount only. Vector An arrow whose length represents the magnitude of a quantity and whose direction represents the direction of the quantity. Vector Quantity Includes a magnitude and direction. KEY TERMS: CHAPTER 4 EQUILIBRIUM In general, a state of balance FORCE ANY PUSH OR PULL FRICTION THE FORCE THAT RESISTS RELATIVE MOTION OF OBJECTS OR MATERIALS INERTIA THE RELUCTANCE OF ANY BODY TO CHANGE ITS STATE OF MOTION KILOGRAM SI UNIT OF MOTION LAW OF INERTIA EVERY BODY CONTINUES IN ITS STATE OF REST OR MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE AT A CONSTANT SPEED UNLESS COMPELLED TO CHAGE THAT STATE BY A MASS THE AMOUNT OF MATTER IN AN OBJECT NET FORCE THE COMBINATION OF ALL OF THE FORCES THAT ACT ON AN OBJECT NEWTON SI UNIT OF FORCE NEWTON’S FIRST LAW THE LAW OF INERTIA NORMAL FORCE FOR AN OBJECT RESTING ON A HORIZONTAL SURFACE THE UPWARD FORCE THAT BALANCES THE WEIGHT OF THE OBJECT SUPPORT FORCE FORCE THAT COMPLETELY BALANCES THE WEIGHT OF AN OBJECT AT REST WEIGHT THE FORCE ON A BODY DUE TO THE GRAVITATIONAL ATTRACTION OF ANOTHER BODY Newton’s second law of motion- force and acceleration CHAPTER 5 Air resistance Friction, or drag, that acts on something moving through the air. Fluid Anything that flows, in particular, any liquid or gas. Free-body diagram A diagram showing all the forces acting on an object. Inversely When two values change in opposite directions, so that if one is doubled the other is reduced to one half, they are said to be inversely proportional to each other. Newton’s second law The acceleration produced by a net force on a body is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, is in the same direction as the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the body. Pascal The SI unit of pressure. One Pascal of pressure exerts a normal force of one Newton per square meter. Pressure Force per surface area where the force is normal to the surface; measured in Pascals. Terminal Velocity Terminal speed together with the direction (down for falling objects). Terminal speed The speed at which the acceleration of a falling object is zero because friction balances the weight. Key Terms CHAPTER SIX One of the pair of forces described in Newton’s Third Law Action Force A mutual action between objects where each object exerts an equal but opposite force on the other Interaction Whenever one body exerts a force on another body the second body exerts an equal and opposite force on the first Newton’s Third Law The force that is equal in strength and opposite in direction to the action force, which acts simultaneously on whatever is exerting the action force Reaction Force Chapter 7 Vocabulary MOMENTUM Electric charge that remains unchanged during interactions CONSERVED Colliding objects rebound without lasting deformation or heat generation ELASTIC COLLISION Product of force and time interval during which force acts IMPULSE Colliding objects become distorted and\or generate heat during the collision INELASTIC COLLISION Absence of a net external force, the momentum of an object or system of objects is unchanged LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM Product of mass and the velocity of an object -Has Magnitude and direction MOMENTUM (LINEAR MOMENTUM) Chapter 8 Vocabulary ENERGY Useful work output divided by the total work input EFFICIENCY Enables an object to do something ENERGY Pivot point FULCRUM SI unit of work JOULE Energy of motion equal to half the mass, multiplied by the speed squared KINETIC ENERGY Energy can’t be created or destroyed LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Machine made of bar that turns about a fixed point LEVER Device used to multiple forces or simply to change direction of forces MACHINE Ratio of output force to the input MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE Energy due to position or movement of something MECHANICAL ENERGY Stored and held in readiness POTENTIAL ENERGY Rate at which work is done or energy is transformed, equal to the work done or energy transformed divided by time -Measured in Watts POWER Kind of lever used to change direction of a force PULLEY SI unit of power WATT The product of a force of an object and the distance through which the object is moved WORK States that whenever work is done, energy changes WORK-ENERGY THEOREM CHAPTER 9 Shawna Foyle, Brittany Pyeritz, Mark Shandrick AXiS The straight line around which an object may rotate or revolve. A horizontal or vertical reference line in a graph CENTRiFUGAL FORCE • The outward force on a rotating or revolving body - Fictitious (made up) CENTRiPETAL FORCE • The center directed force that causes an object to move in a curved path Linear Speed • The path of distance moved per unit of time - Aka speed Revolution • Motion of an object turning around an axis outside the object Rotation •The spinning motion that takes place when an object rotates about an axis - Located within the object Rotational Speed • The number of rotations or revolutions per unit of time - Measured in revolutions per minute - RPM Tangential Speed •The speed of an object moving around a circular path CHAPTER 10 Center of Gravity •Point at the center of an objects weight distribution where the force of gravity can be considered to act Center of Mass •Point at the center of an objects mass distribution where all its mass can be considered to be concentrated Neutral Equilibrium •The state of an object balanced so any small movement neither raises nor lowers its center of gravity Stable Equilibrium •The state of an object balanced so that any small displacement or rotation raises the center of gravity Unstable Equilibrium The state of an object balance so any small displacement or rotation lowers center of gravity By Steve Schott Nick Pesanka & Jake Pulsifer VOCAB FOR CHPT. !!-!2 Ch. 11 Angular momentum Ch. 11 The production of rotational inertia and rotational velocity. Ch. 11 LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM Ch. 11 If no unbalanced external torque acts on a rotating system the angular momentum of that system is constant. Ch. 11 LEVER ARM Ch. 11 The perpendicular distance between an axis and the line of action of a force that tends to produce rotation about the axis. Ch. 11 Linear momentum Ch. 11 Product of the mass and the velocity of an object, a.k.a. momentum Ch. 11 Rotational inertia Ch.11 The reluctance of an object to change its state of rotation, determined by the distribution of the mass of the object in the location of the axis of rotation or revolution. Ch. 11 Rotational Velocity Ch. 11 Rotational speed together with a direction for the axis of rotation or revolution. Ch. 11 The rotational analog of force is _______. Hint: Tends to produce rotational acceleration. Ch. 11 Torque DUH. Moving to Ch. 12 Inverse Square law Ch. 12 The weakening of gravity with distance. Ch. 12 Which law states that: Every object attracts every other object with a force that for any two objects is directly proportional to the mass of each object. Ch. 12 Law of universal gravitation Ch. 12 Perturbatio n Ch.12 The deviation of an orbiting object from its path around a center of force caused by the action of an additional center of force. Ch. 12 Universal Gravitational Constant Ch.12 A constant G in the equation for Newton’s law of universal gravitation; measures the strength of gravity. CH 32& 33. Holl Ball Madeja & Kelsey Lloyd Electrical Forces. A force that one charge exerts on another. Electrostatics. Electricity at rest. Charge. The attracting and repelling behavior. Conservation of Charge. Charge is not created or destroyed but can be transferred. Coulomb’s Law. F = k q1 – q2 / d^2 Coulomb. SI unit for charge. Conductors. Good for the motion of electrical charges. Insulators. Poor conductors of electricity. Semiconductors. Behaves sometimes as insulators& sometimes as conductors. Superconductors. At temps near absolute zero these materials require infinite conductivity. Induced. Electrical charge that distributes on another object because of a nearby charge. Induction. The charging of an object without direct conduct. Grounding. Allowing charges to move freely along a connection between a conductor and the ground. Electrically Polarized. Charges are aligned so that one side is slightly more positive than negative. Electric field. A force field around every electrical charge or any group of charges. Electrical Potential Energy. Energy a charge has due to it’s location in an electric field. Electric Potential. Electric potential energy per coulomb at a location in an electric field. Volt. SI unit for electric potential. Voltage. Electric potential. Capacitor. A device where electrical energy can be stored. Ac current that repeatedly changes direction SI unit for electrical current An electircal device that restricts the current to flow in one direction Dc current that moves in only one direction The flow of electric charge, measured in amps The rate at which electrical energy in converted into another form of energy Resistance of a material to the flow of an electric current SI unit for electrical current The Statement that the current in a circuit is directly proportional to the voltage impressed across the circuit, and is inversely proportional to the resistance of the circiuit The difference in electrical potential Any Path along which electrons can flow Forms branches that electrical current can travel along to get to the devices Single path for the flow of electricity Devices that are connected to the same two spots so that the current can flow through each device individually A diagram of a circuit that uses symbols to show devices A circuit that in which the flow of electricity must flow through each device in turn