Chapter 2: The Database Development Process
advertisement

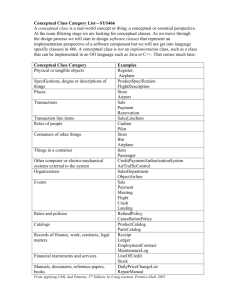
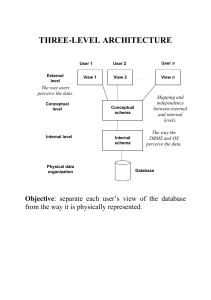
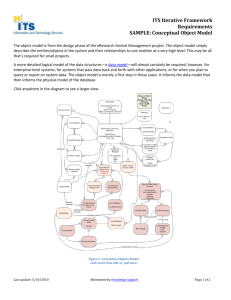
Chapter 2 The database development process Information Systems Architecture A conceptual blueprint or plan that expresses the desired future structure for the information systems in an organization. Architecture example Business Operations Customers & Suppliers External Events Integrated data warehouse CIM EDI External database access Data validation and retention Access analysis and presentation tools Information delivery system Dialogue Decision makers Customers, Suppliers A more sophisticated example... Information Systems Architecture Key • • • • • • components: data processes which manipulate data network which transports data people who perform processes and send and receive data events and points in time when processes are performed reasons for events and rules which govern data processing Information Engineering An Information Systems Architecture is developed by IS planners following a particular methodology such as Information Engineering. Information Engineering Data-oriented methodology Uses top-down planning in which specific information systems are deduced from a broad understanding of organization’s information needs, rather than relying on specific user information requests Offers perspective on relationship of information systems to business objectives Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Top-Down Planning: Bottom-Up Planning: A methodology that attempts to gain a broad understanding of the information system needs of the entire organization A methodology that identifies and defines IS development projects based upon solving operational business problems or taking advantage of business opportunities The big picture... Information engineering Information systems planning – Identify strategic planning factors (goals, CSFs, problem areas) • IT vision – Identify corporate planning objectives • Information system architecture – Develop enterprise model Systems analysis Systems design implementation Systems Development Life Cycle Project Identification & Selection Project Initiation & Planning Analysis Logical Design Physical Design Implementation Maintenance Database SDLC SDLC Identify Project Initiate and Plan Analyze Logical Design Physical Design Implementation Maintenance Database Development Activities Enterprise Modeling Conceptual Data Modeling Logical DB Design Physical DB Design/Creation DB Implementation DB Maintenance Planning Matrixes Show interrelationships between objects. Among the possibilities: • Location-to-Function • Unit-to-Function • Information System-to-Data Entity • Supporting Function-to-Data Entity • Information System-to-Objective Business Function-to-Data Entity Planning Matrix Information System-to-Objective Planning Matrix Functional Decomposition Enterprise Data Modeling The first step in database development, in which the scope and general contents of organizational databases are specified. Enterprise Data Model A model which includes: • overall range of organizational databases • general contents of organizational databases Built as part of IS planning for the organization and not the design of a particular database part of an organization’s overall information systems architecture (ISA) One Conceptual Database Modeling Determine Determine Build user requirements business rules conceptual data model • outcome is an entity-relationship diagram or similar communication tool • population of repository Enterprise Modeling Conceptual Data Modeling Logical DB Design Physical DB Design/Creation DB Implementation DB Maintenance Logical Database Design Select logical database model • commit to a database alternative Map Entity-Relationship Diagrams Normalize Specify data structures business rules Enterprise Modeling Conceptual Data Modeling Logical DB Design Physical DB Design/Creation DB Implementation DB Maintenance Physical Database Design Select DBMS Select storage devices Determine Design files and indexes Determine Specify access methods database distribution update strategies Enterprise Modeling Conceptual Data Modeling Logical DB Design Physical DB Design/Creation DB Implementation DB Maintenance Database implementation Code and test database processing programs Complete Install documentation database and convert data Enterprise Modeling Conceptual Data Modeling Logical DB Design Physical DB Design/Creation DB Implementation DB Maintenance Database Maintenance Analyze database and applications to ensure evolving information requirements are being met Tune database for improved performance Fix errors Provide data recovery when needed Enterprise Modeling Conceptual Data Modeling Logical DB Design Physical DB Design/Creation DB Implementation DB Maintenance Documentation most formal development methodologies are documentation based helps managers monitor progress and quality of project facilitates communication between team members includes models various stages are not complete until documentation is accepted Some Keys to Success... accurate requirements definition commitment effective change management manageable champion size So … Three Schema Architecture for Database Development Conceptual Schema • Analysis project phase External Schema • Analysis and Logical Design phases • (subset of conceptual schema) Internal Schema • Physical Design phase 3-schema architecture Conceptual Schema Describes the logical structure of the entire database Independent Avoids Stated of a specific DBMS details of physical design in • ERDs • metadata External Schema Also called a user view Specifications include screen formats, report formats, transaction definitions Physical Schema Describes physical structure of entire database Specifies how data from a conceptual schema are stored in secondary memory Sometimes called internal schema Specifications include physical file and data structures, storage organization, and index structures 3-schema development process Rapid application development design methodology which speeds systems delivery through a combination of speedy design iterations, data modeling, user/developer teamwork, and automated development tools. encompasses a set of techniques that can be used to build complex, strategic, and mission-critical applications in months rather than years RAD The RAD lifecycle requirements planning • conduct joint requirement planning workshop design • conduct JAD workshop construction • members of team monitor evolution, system is prototyped cutover • installation Within the time box... Requirements planning User design construction phase build and evolve prototype User review request for change Evaluate system cutover time box Barriers to overcome... poor training/ tools reluctance to leave old methods behind mindset that RAD is not adequate for largescale systems development speedy delivery does not mean low quality “creeping functionality”