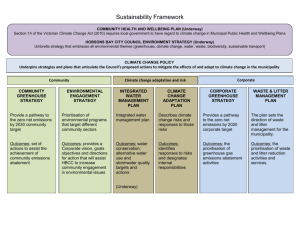
The Evolution of Environmental
Regulation
Greg Monty, Ph.D., M.I.T.
Corporate Research
Director of Technology
Copyright© 1995-2008 Underwriters Laboratories Inc. All rights reserved. No portion of this material may be reprinted
in any form without the express written permission of Underwriters Laboratories Inc. or as otherwise provided in writing.
Case Study of an S&P 500 Company
• Highlights excerpted from this companies’
Carbon Disclosure Project Questionnaire
Response (late 2007)
– Energy Use Reduction
– Recycling
– Selling Communication Technology to help policy makers
and customers reduce GHG emissions
• Risks cited
– Weather could damage their products that are installed
outdoors (due to climate change)
– Outages for customers and increased repair costs
– Rising temperatures could cause system failure if outside
operating range of equipment
p 2
Case Study continued
• Opportunities cited
– Network-based services will improve
• Telecommuting
• Tele-conferencing, video conferencing
• E-Commerce, e-banking/billing
• Distance learning
• And will reduce travel & GHG emissions for customers
– Changing technology to be less affected by weather
• Organizations involved with
–
–
–
–
California Climate Action Registry
Business Roundtable Climate Resolve Program
EPA Climate Leaders Program
Global e-Sustainability Initiative (GeSI)
• To quantify emissions improvements from communications
products
– Hosted Energy Summit for their industry in 2007
p 3
Case Study continued
• Energy steps being taken
–
–
–
–
Deploy Fuel Cell backups: mitigating outages
Cleaner energy sources
Reducing energy use
Improving energy efficiency
• Management steps being taken
– Contingency organization to deal with outage events
– Code of conduct updated 2007 (company and supply chain)
• Safe working conditions (OSHA)
• Environmentally responsible manufacturing processes
• Targets: Have not set their goals, but are planning to
p 4
Case Study continued
• Energy reduction results and activities
– 94.5M kWh reduced in 2006 in a growth year
• Powering down and removing obsolete equipment in facilities
• Installed two micro-turbines fueled by natural gas, 3.6 yr payback
period
• Installed Fuel Cells in many facilities
• Installed ‘hypalon’ roofs on buildings
– EPA Energy Star approved, highly reflective surface,
increases insulation to improve energy efficiency
• Selling off facilities no longer needed
• Other energy conservation programs
• Reviewed high-energy-use buildings and made system
improvements to reduce energy use
• Capital improvement projects for improved efficiency
p 5
Case Study continued
• Other improvements in trials
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Use of hybrid fleet for technicians
Using bio-diesel fuel for part (20%) of fleet
Increasing use of IT to reduce GHG emission
Shareholder communication is electronic
Recycle, refurbish, resell used equipment
Operate their own recovery/recycle facilities
24T paper/cardboard recycled in 2006
30% of office supply content is recycled materials
p 6
Case Study continued
• Awards
– EPA Wastewise “Partner of the year”
– Have won this award more than any other
company in their industry sector
• GHG emissions calculations
– Use EPA emissions calculations guideline
– Not 3rd-party verified
p 7
How are Environmental Regulations
Established?
• Legislative
– Directives, Laws, Guidance
• Executive
– Corporations setting ‘Policy’ and ‘Practice’
• Judicial
– Legal suits and judgments
– Court of ‘public opinion’
• Standards Bodies
– ISO, IEC/IECQ, ASTM,
– Standards Writing Bodies in various industries
• BSI, Oeko-Tex, GreenGuard, EPA, Green-e, GHG
Protocol, etc…
p 8
Acceleration: 21st Century
Environmental Requirements
• In 21st Century thus far:
– Materials
• WEEE/RoHS
– Test Standards
• Battery, Packaging, ELV
• REACH (Chemical Mgmt)
– Energy efficiency and reduction
• EuP (Design for the Environment)
– Quality Management Systems for the Environment
• ISO 14000 Portfolio, ISO14064/65
• QC 080000
• ISO 18001
• Conformity Assurance Systems
– Water Certification (source and products)
– EU, then China, Japan, Korea, ROW (but not the ‘previous
administration’-led USA)
p 9
RoHS2 Update
• Fixed Installations not mentioned
• LSIT is, but is poorly defined
• Categories 8 & 9 included
– Medical and Measurement Equipment
– In force Jan2014 (for most products)
• No new substances listed (6 original remain)
– EC considering HBCDD (flame retardant for PS),
and DEHP, BBP, DBP (plasticisers)
– EC can add substances but must apply REACH
SVHC criteria in the process
p 10
RoHS2 Update continued
• Exemption process overhauled
– Present exemptions reassessed by Oko Institut,
some changes might occur in 2009
– Exemptions to expire after 4 years, but could be
extended
– New criteria permitted: socio-economic,
availability, reliability
– EC will define portfolio required in a request for
exemption
– EC will provide detailed rules for the process to
provide ‘legal certainty’ to producers.
p 11
RoHS Update continued
• RoHS2 will become a CE marking directive
– Conformity assessment based on as-yet
non-existent, harmonized standards
– Need to test is specified: When deemed
appropriate, carry out sample testing
– Technical Files and DoCs will be required
(Decision 768/2008/EC)
• One DoC per product which lists applicable
directives
p 12
RoHS Update continued
• Timeline
– European Parliament, Council of Ministers, and EC
must agree on proposed changes
• Discussions in September 2009 after elections
– Agreement by end of 2009 or early in 2010
expected
– 18 months of transposition into National Legislation
– Entry into force in 2011/2012
• JIG-102 will be released in late Spring 2009
• China RoHS Catalog sometime in 2009
p 13
REACH Update
• REACH: Registration, Evaluation,
Authorization(Restriction) of CHemicals
• Web site for pre-registered substances
– http://apps.echa.europa.eu/preregistered/preregistered-sub.aspx
– 143,000 substances
– 65,000 companies
– Pre-registration final 01Dec2008
– Late pre-registration: must meet criteria
– 2018 is last date to register (based on tonnage)
• >1 ton/year substance
• Use EU subsidiary, importer, or ‘Only-Representative’
p 14
REACH continued
• Evaluation
– Dossier analyzed
• Risks, hazards, safe usage practices with downstream users
• Authorization
– SVHCs (substances of very-high concern)
– If listed in Annex XIV: cannot use on market
• REACH Details
– Substances, Preparations, Intended for Release, Articles
– Notification Requirements (if product contains SVHCs
>0.1%)
– Duty to inform (if SVHCs in article)
p 15
REACH is active…
1st Candidate List for SVHCs:
Anthracene PBT
4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane CMR
REACH pre-registration period is over
SVHC list will likely grow
Dibutyl phthalate CMR
Cyclododecane PBT
Cobalt dichloride CMR
Diarsenic pentaoxide CMR
PBT: Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic
CMR: Carcinogenic, Mutagenic, or Toxic to Reproduction
vPvB: very Persistent, very Bioaccumulative
Diarsenic trioxide CMR
Sodium dichromate, dihydrate CMR
5-tert-butyl-2,4,6-trinitrom-xylene (musk xylene) vPvB
Bis (2-ethyl(hexyl) phthalate) (DEHP) CMR
Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDD) PBT
Alkanes, C10-13, chloro (Short Chain Chlorinated Paraffins) PBT
Bis(tributyltin)oxide PBT
Lead hydrogen arsenate CMR
Triethyl arsenate CMR
Benzyl butyl phthalate CMR
http://echa.europa.eu/consultations/authorisation/svhc/svhc_cons_en.asp 07/18/2008
p 16
REACH Deadlines
• Jan2009: SIEF formation (substance exchange information
fora)
– Data sharing and joint registrations
• Nov2010: Registration of substances
– CMRs 1 and 2 at >1 ton/year/mfgr; or
– vT to aquatic organisms >100 ton/year/mfgr; and
– preparations intended for release from articles >1000
tons/year/mfgr.
• Dec2010: Notification of classification and labeling of
substances, including <1 ton/year.
• Dec2013: if substance is >100 tons/year, it must be
registered
• Dec2018: if substance is >1 ton/year, it must be registered
p 17
EuP Preparatory Studies
• LOT 1: Boilers and combi-boilers (gas/electric)
• LOT 2: Water heaters (gas/oil/electric)
• LOT 3: Personal Computers (desktops & laptops) and
computer monitors
• LOT 4: Imaging equipment: copiers, faxes, printers,
scanners, multifunctional devices
• LOT 5: Consumer electronics: televisions
• LOT 6: Standby and off-mode losses of EuPs
• LOT 7: Battery chargers and external power supplies
• LOT 8: Office lighting
• LOT 9: (Public) street lighting
• LOT 10: Residential room conditioning appliances (airco
and ventilation)
p 18
EuP Preparatory Studies, continued
• LOT 11: Electric motors 1-150 kW, water pumps
(commercial buildings, drinking water, food,
agriculture), circulators in buildings, ventilation fans
(nonresidential)
• LOT 12: Commercial refrigerators and freezers,
including chillers, display cabinets and vending
machines
• LOT 13: Domestic refrigerators and freezers
• LOT 14: Domestic dishwashers and washing machines
• No LOT Number : Simple Converter Boxes for digital
television
• LOT 15: Solid Fuel Small Combustion Installations
• LOT 18: Complex Set Top Boxes (with conditional
access and/or functions that are always on)
• LOT 19: Domestic Lighting
p 19
Anticipation of Federal Standards
p 20
ISO140xx…
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
ISO 14001:2004 Environmental Management Systems – Requirements with Guidance for use
ISO 14004:2004 Environmental Management Systems – General Guidelines on Principles, Systems,
and support techniques
ISO 14020:2000 Environmental Labels and Declarations
ISO 14021:2001 Environmental Labels and Declarations – Self-declared environmental claims (type II
environmental labeling)
ISO 14024:2001 Environmental Labels and Declarations – Type I environmental labeling – principles
and procedures
ISO 14025:2000 Environmental Labels and Declarations – Type III environmental declarations
ISO 14040:2006 Environmental Management – Life Cycle Assessment – Principles and Framework
ISO 14044:2006 Environmental Management – Life Cycle Assessment – Requirements and Guidelines
ISO 14050:2002 Environmental Management – Vocabulary
ISO 14064-1:2006 Greenhouse gases — Part 1: Specification with guidance at the organization level for
quantification and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions and removals
ISO 14064-2:2006 Greenhouse gases — Part 2: Specification with guidance at the project level for
quantification, monitoring and reporting of greenhouse gas emission reductions or removal
enhancements
ISO 14064-3:2006 Greenhouse gases — Part 3: Specification with guidance for the validation and
verification of greenhouse gas assertions
ISO 14065:2007 Greenhouse gases — Requirements for greenhouse gas validation and verification
bodies for use in accreditation or other forms of recognition
p 21
ANSI Monthly Chemical Telecon
• REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and
Restriction of Chemicals)
• Network on Chemical Regulation Work Group updates
from co-chairs/participants
• ChAMP (EPA Chemical Assessment and Management
Program)
• US Federal Activities
• DHS (Department of Homeland Security)
• GHS (Globally Harmonized Systems)
• RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances)
• States activity
• SAICM (Strategic Approach to International Chemicals
Management)
• EuP (Energy Using Product)
• ASTM F40 activities
p 22
Global Awareness of Environmental
Issues
• Al Gore ‘The Inconvenient Truth’
• Al Gore wins the Nobel Prize
– An inflection point in the awareness of Environmental
‘damage’
– A beginning of a real call-for-action
• Bali 2007: Bush administration is cornered into
accepting Kyoto Protocol activity over next two years
• President Clinton’s CCI (Clinton Climate Initiative)
• Carbon emissions have emerged as the ‘New
Currency’ of the 21st century
p 23
The Awareness Inflection Point?
Oslo, 10 December 07:
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate
Change and Albert Arnold (Al) Gore Jr. were
awarded of the Nobel Peace Prize "for their
efforts to build up and disseminate greater
knowledge about man-made climate change
and to lay the foundations for the measures that
are needed to counteract such change.
p 24
The Kyoto Protocol
An international agreement linked to the United
Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change.
The major feature of the Kyoto Protocol is that it
sets binding targets for 37 industrialized countries
and the European community for reducing
greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions .
p 25
Clinton Climate Initiative
Chicago
Houston
Los Angeles
New York
Philadelphia
http://www.clintonfoundation.org/cf-pgm-cci-home.htm
http://www.c40cities.org/cities/
In its first phase, CCI is working with the C40 Large Cities Climate Leadership
Group, an association of large cities dedicated to tackling climate change—to
develop and implement a range of actions that will accelerate greenhouse gas
emissions reductions.
p 26
Companies are being compared…
THE EXECUTIVE’S DAILY GREEN BRIEFING
JUNE 17, 2008
Apple, HP, Microsoft Perceived As Greenest IT
Brands
More than 70 percent of respondents to GreenFactor, a global “green” enterprise IT study said they
“probably” or “definitely” would increase their preference for a brand’s “green” products if they
were convinced of the positive impact on the environment and business. Almost 60 percent said
they would expect to pay a premium for “green” products.
http://www.environmentalleader.com/2008/06/17/apple-hp-microsoft-perceived-as-greenest-it-brands/
p 27
Green Cities are being built!
Abu Dhabi’s Masdar City, which will be the
world’s first carbon-neutral, car-free city, which
is also 100 percent powered by renewable
energy. (50,000 people)
p 28
Universities are being mobilized…
http://www.focusthenation.org/earthday.php
4 goals for your campus (see below for details)
1. Make Noise: Sign the Presidents Climate Commitment
2. Voter Registration
3. Sky Petition
4. Campus Events
Resources
— Organizer's Guide (download)
— Sky Petition (download)
— Voter Registration Guide (download)
http://www.presidentsclimatecommitment.org/html/signatories.php
p 29
Carbon emissions and the TBL
(Triple Bottom Line)
•
•
•
•
•
•
How much does your company, your suppliers, your products, and
do you personally emit (Tons of CO2/year)?
– Carbon Calculators based on Standards are emerging
– Company/Buildings/Products are being assessed
– Analytical, Certification, and Auditing services are emerging
Carbon Trading Schemes have emerged
– Cap and Trade
– buy and trade credits of Carbon emissions (RECs, TRCs)
– get taxed on your emissions? (San Francisco started already)
Companies specifying ‘Green Choice’ electricity from Utilities
Wind farms, PV, and even Nuclear is in a ‘gold rush’
The Triple Bottom Line has emerged
– People, Planet, Profit (Community, Environment, Revenue)
Corporate Social Responsibility is the ‘3BL’
p 30
Broad applicability of GHG Protocol
Principles
•
•
•
•
•
Relevance
Completeness
Consistency
Transparency
Accuracy
p 31
CSR is questioned: ‘Greenwashing?’
LOHAS:
Lifestyles of Health
and Sustainability
p 32
Air Quality, Use of Forests, Textiles
being certified
http://www.greenguard.org/Default.aspx?tabid=14
http://www.rainforest-alliance.org/forestry.cfm?id=products_companies
p 33
Air Quality, Use of Forests, Textiles,
Organic content being certified
http://www.oeko-tex.com/OekoTex100_PUBLIC/index.asp
http://www.global-standard.org/
http://www.organicexchange.org/
p 34
USGBC and LEEDs
LEEDs is the Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design
Criteria have been established to be certified to different levels
Of Green-ness in a new or redesigned buildings
http://www.usgbc.org/DisplayPage.aspx?CMSPageID=124
p 35
A competing Building Certification
system from GBI/Green Globes
Green Globes™ is a revolutionary green building guidance and assessment program that integrates
a comprehensive environmental assessment protocol, software tools, qualified assessors with green
building expertise, and a rating/certification system. Together, this combination of tools and services
integrate to offer an effective, practical and affordable way to advance the overall environmental
performance and sustainability of buildings.
The Green Globes software tools and ratings/certification system are based on the recognized and
proven Green Globes assessment protocol, thus environmental impact is comprehensively assessed
on a 1,000 point scale in multiple categories: Energy, Indoor Environment, Site Impact,
Water, Resources, Emissions, and Project/Environmental Management.
Green Globes Tools
http://www.thegbi.org/webinars/20080319/after-the-webinar.asp?EventID=474160424&FirstName=Greg&LastName=Monty&Email=greg.monty%40us.ul.com&EnrollmentID=
p 36
GHG Protocol Initiative
The Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol) is the most widely
used international accounting tool for government and business
leaders to understand, quantify, and manage greenhouse gas
emissions. The GHG Protocol, a decade-long partnership between the
World Resources Institute and the World Business Council for Sustainable
Development, is working with businesses, governments, and environmental
groups around the world to build a new generation of credible and effective
programs for tackling climate change.
p 37
Step-by-Step GHG emissions
Process
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Step 1: Secure support
Step 2: Learn/plan CO2 inventory
Step 3: Find Data
Step 4: Calculate
Step 5: Target
Step 6: Take Action!
Step 7: Report and be a leader
p 38
EPA Climate Leaders Program
http://www.epa.gov/climateleaders/partners/index.html
Dell Inc.; Manufacturing TX
Dell Inc. pledges to reduce global GHG emissions by 15 percent per dollar revenue from
2007 to 2012, and to achieve net zero global GHG emissions by 2008 and maintain that
level through 2012.
DPR Construction, Inc.; Construction CA
Greenhouse gas reduction goal is under development.
Duke Energy; Utilities NC
Greenhouse gas reduction goal is under development.
DuPont Company; Chemical DE
DuPont Company pledges to reduce total global GHG emissions by 15 percent from 2004 to
2015.
p 39
Too many standards competing for
Offset Markets?
“The voluntary offset market is awash with competing standards.
This report shows that no other standard can ensure the same
environmental and social integrity as the Gold
Standard”…http://www.tricorona.com/news/98/ (published March
10, 2008).
•Clean Development Mechanism (CDM)
•Gold Standard (GS)
•Voluntary Carbon Standard (VCS)
•VER+
•The Voluntary Offset Standard (VOS)
•Chicago Climate Exchange (CCX)
•The Climate, Community & Biodiversity Standards
(CCBS)
•Plan Vivo System
p 40
The Gold Standard
http://www.cdmgoldstandard.org/
The Cap and Trade concept requires Standards
and Certification of RECs (TRCs)
p 41
Beyond Company behavior/attributes
and Building ‘Green-ness’ lies LCA…
http://www.openlca.org/index.html
GaBi 4.2 (Just one of many tools available)
PE International GmbH
Life cycle management (LCM), Compliance checks, Life cycle assessment (LCA), Life
cycle inventory (LCI), Life cycle work environment (LCWE), Product stewardship,
supply chain management, Life cycle impact assessment (LCIA), Life cycle
sustainability assessment (LCS), Life cycle costing (LCC), Design for environment
(DfE, DfR), Life cycleengineering (LCE), Substance/material flow analysis (SFA/MFA)
Japanese, Spanish, Portuguese, Danish, Thai, Chinese, German, English
Companies (like Walmart) are now focusing on Product emissions
Expect your products to eventually need ‘emissions per item’ to be disclosed
http://lca.jrc.ec.europa.eu/lcainfohub/toolList.vm
p 42
Conclusion: Where are we headed?
• Environmental Compliance is gaining strength
and is now part of ones’ Market Access
Strategy
• The Triple Bottom Line is becoming the norm:
Profit is good, but it must be accompanied by
doing good things with the environment, and
protecting people in the community
• Each Company will need to step back, decide
what from the long list of items could be
tackled, and then tackle them…
• Look for UL’s Environmental Stewardship Mark
in the near future…
p 43