Writing Clear Objectives

Writing Clear Objectives
Presented by: Carroll County Public
Schools Mentoring Team
Power Point Created by: Robyn Marsden
Preface
• An important part of an effective lesson is a clear objective that informs the learner of what he or she should know and be able to do as a result of the lesson
• County wide expectations for clear objective writing are in the works
• Various sources were tapped for the information we are about to share with you and are included at the end of this presentation.
• As this is a “Professional Learning Community,” we look forward to developing our understanding of this important concept with you.
Activity
• Working in groups of 4 put these phrases together to formulate the learning objectives for today.
• What did you come up with?
Our Objectives for Today
After reviewing a power point and participating in a group discussion professional learning community members will be able to:
• List the 4 parts of the “ideal” learning objective with 100% accuracy.
• Write a learning objectives that contains a measurable verb taken from Bloom’s higher levels of thinking.
What is an objective:
• A description of a performance you want learners to be able to exhibit before you consider them competent.
• A statement that informs the learner of what he or she should know and be able to do as a result of the lesson
Why?
Writing clear objectives is important because:
• Objectives define what you will have the students do.
• Objectives provide a link between expectations, teaching and grading.
• Clear objectives help teachers foster higher level thinking skills in their students.
How: The A.B.C.D. Method
• The ABCD method of writing objectives is an excellent starting point for writing objectives (Heinich, et al., 1996). In this system, "A" is for audience, "B" is for behavior, "C" for conditions and "D" for degree of mastery needed.*
*Taken from Penn State University Online: http://tlt.its.psu.edu/suggestions/research/Write_Objectives.shtml
Audience
• Who? Who are your learners?
• As you target a specific audience with your objective make sure that you are meeting the needs of all learners in that group.
• If there are learners in that group that do not need the lesson, (they've already attained mastery) engage them in another productive activity designed to meet their needs.
(Differentiation)
Behavior
• Answers the question: What do you expect the learner to be able to exhibit as a result of the lesson?
• The behavior is the action (verb) that describes what the learner (audience) will be able to do after the instruction.
Condition
• How?
• Under what circumstances or context will the learning occur?
• What will the student be given or already be expected to know to accomplish the learning?
Degree
• How much will be accomplished?
• How well will the behavior need to be performed, and to what level?
• Do you want total mastery (100%), do you want them to respond correctly
80% of the time, etc. A common (and totally non-scientific) setting is 80% of the time.
*
Not always necessary to include in your objective
Identify the A.B.C.D. in our objectives for today:
• Who is the audience?
• What is the expected behavior? What should you know and be able to do as a result of this lesson?
• What are the conditions or circumstances under which learning will occur?
• How well must you perform today in order for the performance to be considered acceptable?
Activity
Work with a partner to dissect and classify the parts of the objectives listed on the cards.
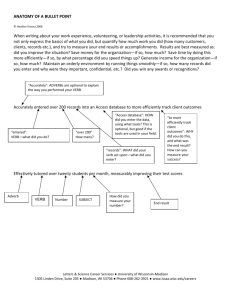
Given a paragraph in a newspaper article, the student will be able to accurately identify the grammatical subject of each sentence and explain his or her decision for all sentences given.
A-Audience B-Behavior C-Condition D-Degree the student Given a paragraph in a newspaper article, will be able to accurately identify the grammatical subject of each sentence and explain his or her decision for all sentences given.
Given a list of meteorological terms, the student will be able to accurately explain what each term means in one or two sentences for all terms given.
A-Audience B-Behavior the student Given a list of meteorological terms,
C-Condition D-Degree will be able to accurately explain what each term means in one or two sentences for all terms given.
Given a foreign language sentence written in the past or present tense, the student will be able to rewrite the sentence in future tense with no grammatical errors.
A-Audience B-Behavior the student
C-Condition
Given a foreign language sentence written in the past or present tense will be able to rewrite the sentence in future tense
D-Degree with no grammatical errors.
Given a current-events topic the student will be able to write grammatically-correct, well-crafted opinion essay of three-five pages over two to three days.
A-Audience B-Behavior the student
C-Condition D-Degree
Given a currentevents topic will be able to write a grammaticallycorrect, wellcrafted opinion essay of threefive pages over two or three days.
Given a set of current meteorological conditions taken from a weather station the student will write a weather forecast covering the next six hours.
Given the opportunity to work in a team with several people of different ethnic backgrounds, the student will demonstrate a willingness to participate and positive non-discriminatory interactions with all team members, as measured by a checklist utilized/completed by non-team members .
Given a standard balance beam raised to a standard height, the beginning student (attired in standard balance beam usage attire) will be able to walk the entire length of the balance beam
(from one end to the other) steadily, without falling off, and within a six second time span.
Given an geometric object in Photoshop software, the student will be able to use the computer mouse and lasso tool to trace a usable outline which can be used to define the object for a montage.
Quick Review: What are the
4 parts of an “ideal” objective?
• A=Audience
• B=Behavior
• C=Condition
• D= Degree
Verbs: The Key to Expressing
Desired Behaviors
•The verb in a learning objective is an action word that connotes an observable behavior.
•Bloom's Taxonomy is a way to classify instructional activities or questions as they progress in difficulty. The lower levels require less in the way of thinking skills. As one moves down the hierarchy, the activity requires higher level thinking skills.
Define
Describe
Identify
Label
List
Match
Knowledge
Remembering or Recall of
Information
Name
Outline
Recall
Recite
Select
State
Products include :
• Quiz
• Definition
• Fact
• Worksheet
• Test
•Label
• List
• Workbook
• Reproduction
•Vocabulary
Comprehension
Convert
Defend
Extend
Generalize
Discriminate Infer
Distinguish Paraphrase
Estimate
Explain
Predict
Summarize
Understanding of given information
Products include
:
• Recitation • Example
• Summary • Quiz
• Collection • List
• Explanation • Label
• Show and tell • Outline
Application
Change
Compute
Demonstrate Relate
Develop
Modify
Operate
Organize
Prepare
Solve
Transfer
Use
Using strategies, concepts, principles and theories in new situations
Products include
:
• Photograph
• Illustration
• Simulation
• Sculpture
• Demonstration
• Presentation
• Interview
• Performance
• Diary
• Journal
Analyzing
Break down Infer
Deduce
Diagram
Outline
Point out
Differentiate Relate
Distinguish Separate out
Illustrate Subdivide
Breaking information down into its component elements.
Products include
:
• Graph • Survey
• Spreadsheet • Database
• Checklist • Mobile
• Chart • Abstract
• Outline • Report
Synthesis
Categorize Devise
Compile
Create
Design
Formulate
Compose Predict
Produce
Putting together ideas or elements to develop a original idea or engage in creative thinking.
Products include
:
•Film
• Story
• Project
• Plan
• New game
•Speech
•Song
• Newspaper
• Media product
• Advertisement
• Painting
Evaluating
Appraise Judge
Compare Justify
Contrast Support
Criticize Validate
Defend
Judging the value of ideas, materials and methods by developing and applying standards and criteria.
Products include
:
• Debate
• Panel
• Report
• Evaluation
• Investigation
• Verdict
• Conclusion
•Persuasive speech
Identify the “Bloom” Verb in the following :
• will be able to accurately identify the grammatical subject of each sentence and explain his or her decision
• will be able to accurately explain what each term means in one or two sentences
• will be able to rewrite the sentence in future tense
• will be able to write grammatically-correct, well-crafted opinion essay of three-five pages
• will write a weather forecast
• will demonstrate a willingness to participate and positive non-discriminatory interactions with all team members,
• will be able to walk the entire length of the balance beam
• will be able to use the computer mouse and lasso tool to trace a usable outline
Writing an Objective
Fifth Grade: ILA Benchmarks
Benchmark: Comprehends text
Competency: Self-questions to clarify and extend meaning
What: are the fifth grade indicators?: Independently decides when to pause to monitor/clarify meaning; pauses, reflects upon, and questions the text to monitor/maintain/extend meaning
How: can the indicators be taught?: Teacher . . .continues to provide opportunities for students to independently apply their reading strategies.
Where: can the indicators be taught/observed?
• Guided Reading
• Small Group Instruction
• Literature Discussion Groups
Now it is your turn!
Using the objective you brought with you, rewrite it using the ABCD method. As you write your objective think about how you will use a “Bloom Verb” to denote the desired change in behavior.
Summary
• What are the 4 parts of the “ideal” learning objective with 100% accuracy.
• Review the learning objective that you just wrote with a partner. Can you identify the audience, behavior, condition and degree?
• As you re-read the objective, circle the measurable verb taken from Bloom’s higher level of think.
Questions?
Resources
• http://www.educationoasis.com/curriculum/
LP/LP_resources/lesson_objectives.htm
• http://workforce.cup.edu/peterson/2004cal web/Resources/WritingObjectives.doc
• http://edtech.tennessee.edu/~bobannon/wr iting_objectives.html
• http://med.fsu.edu/education/FacultyDevel opment/objectives.asp