Alternative feed ingredients for animals Outcomes
advertisement

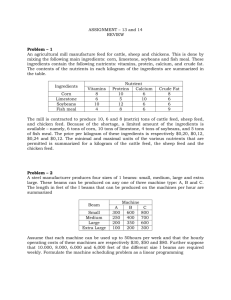
Alternative feed ingredients for animals Outcomes: Describe world food situation – competition between humans and animals, consequences Identify alternative feed ingredients and limitations Examine role of communication World Food Situation Crisis level (UN, 2010) Food prices to rise by 40% over coming decade Wheat and coarse grains to increase by between 15% - 40% Vegetable oils to increase more than 40% Food prices at highest level on record February 2011 About 1b people estimated to be undernourished Why is there crisis? Extreme weather (too much rain, heat & cold) Heat wave, drought & wildfires in Russia, Worst drought in China, Drought in US etc 1/3 of grain supplies in the U.S. used for fuel ethanol production Shrinking grain harvests due to aquifer depletion and severe erosion Running out of technology to raise land productivity Rising world population Competition between humans and animals for vital feed ingredients (energy, protein) ENERGY – Wheat, Maize (Corn), Barley, Oats, Rice, Sorghum, Rye, Triticale, Vegetable oil, Cassava PROTEIN – Soybeans, Fishmeal, Peanut meal, Competition Increasing feed cost ( normally constitute 50-75 of the total cost) About 2.4 million dogs being fed scraps as main food (PDSA) About 11,586 animals abandoned last year – more than 30 daily (RSPCA) Received 2112 calls about animal abandonment in 2010 Abandoned animals Animal welfare Alternative feed ingredients o Non conventional ingredients – legumes o Industrial bye products – biscuit waste, brewers grains, brewers yeast, molasses o Agro processing bye products – cocoa husk, palm-oil sludge, cassava peals, rice bran / husk, rice polishing, corn / maize bran o Recycling waste – activated sludge, dried poultry waste (15% fiber, 25% protein), rendered products (meat scraps from animal flesh & tissues) poultry Alternative feed ingredients (continuation) Poultry by-product meal( heads, feet, intestines, but excluding feathers 55-60% protein) Poultry feather meal(Hydrolysed 70% protein) Poultry hatchery by-product meal (egg shells, unhatched and infertile eggs, and culled chicks 22-32% protein) Agro-processing Maize de-husking Maize Harvested maize Trial 1 West African dwarf and Saanen goats Indian bamboo (Bambusa vulgaris ) and Indian almond (Terminalia catapa) suplemented with cassava peels and cassava peels mixed with maize Both plants contain acceptable levels of minerals Indian almond more acceptable than Indian bamboo and both better when supplemented with cassava peels and maize than cassava peels alone. Trial 1- continuation Indian almond Indian bamboo Trial 2 Golden Hubbard Layers Palm-oil supplementation (1- 3%) on ground dehydrated sweet potato(5%) as replacement for Maize in conventional layers diet All levels resulted in increased availability of nutrients, improved feed conversion efficiency and increased weight gain Palm oil also reduces dustiness and laxative effect of sweet potato Sweet potato (Ipomea batatas Trial 2 Cassava plant Cassava tuber and peals Cassava chips Trial 3: Detoxification & utilisation of Full Fat Soybeans Many plants contain anti-nutritional factors for protection Cotton seed – Gossypol Cassava – Hydrocyanic acid- Cyanide Cocoa – Theobromine, Caffeine Groundnuts – Prone to Aflatoxin infestation Soybeans – Trypsin inhibitors, Hemagglutinins, Sapponins, Phytic acid etc Trial 3 Full-fat soybeans for Soybeans (Glycine maxima broiler (160 Hubbard DOC) 3 processing methods compared. Cooking in water for 20 minutes better in economic terms over soaking for 6 hours before cooking for 20 minutes and soaking in water for 6 hours before roasting for 20 minutes ( wet roasting) although wet roasting gave higher terminal weights, better feed conversion etc Chickens Broiler Chicks Broiler Parent Chicks Chickens Broiler Parents Trial 4 (Bloodmeal and fishmeal as supplements to fullfat soybeans for laying hens Bloodmeal Comparing egg- production, egg-weight and haught’s unit, fishmeal is superior to bloodmeal Both of them gave better results at 5% level than 7.5% Fishmeal Trial 5 (Raw and cooked fullfat soybeans in laying diets Growth retardation and pancreatic enlargement reported for chicks were absent from hens fed raw soybeans. Satisfactory results were obtained in both cases at a level as high as 35% contrary to earlier reports. Field observations Catfish Production Hatchery waste Processing waste Feed-mill waste pellets Poultry manure Poultry meal Aquaculture Aquaculture Fish fingerling hatchery Fish feed pelletizer Snail Feed Feed mill waste Waste vegetables and fruits Kitchen waste (without salt) Pawpaw fruits and leaves Banana fruits and leaves Sweet potato leaves Feeding ruminants Cattle Sheep Cattle – 100% Grazing Cows , Heifers and Bulls Calf Feeding Ruminants (continuation) Beef cattle on 100% nomadic grazing At best grazing + concentrates (least cost / palm kernel cake or meal, brewers waste + vitamin / mineral licks Adequate veterinary care for worms, parasites including blood parasites, vaccinations Limitations of alternative feed ingredients Not available in economic quantities perhaps due to higher demand than supply Dependent on industries running at full capacity New products require toxicological tests, proximate composition and microbiology Cost driven more efficient industrial plants leaving little or no wastes Improvements Genetically modified organisms (plants and animals) Pelletising of feed over mash or crumbles Improved processing techniques (micronising, extrusion technology) Use of feed enzymes to liberate more nutrients especially from feed ingredients with high non-starch polysaccharides (NSPs) – wheat, barley, sorghum (phytase, amylase) Use of Nutricines (Anti-oxidants, emulsifiers, enzymes, flavours, organic acids (subject to legislation) The Way Forward Agricultural production and productivity needs to be stepped up Brazil is the fastest growing (40% growth in the next decade) and 20% growth expected in China, India, Russia and Ukraine Communication needs to be stepped up between Universities / Research institutions and the feed industry and other stake holders on possible alternative feeds Improved communication to the public on feeding and welfare requirements of animals, for instance few people know that it takes about £3000 to rear a rabbit through its life span Improved agricultural extension to farmers especially in emerging economies. References http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_DoqZTLnXmPk/R8NSGPF pmI/AAAAAAAAADY/XOPIaSwLEhc/s400/sweetpotato.g if accessed on 13/03/11 1330hrs http://www.infiniteunknown.net/wpcontent/uploads/2010/06/soybeans.jpg accessed on 13/03/11 1354hrs http://www.rspca.org.uk/inaction/whatwedo/decisions/overpopulation//article/EM_Overpopulation accessed 17/03/11 1626hrs References (continuation) http://img.dailymail.co.uk/i/pix/2007/04_02/dogsPA23 04_468x312.jpg accessed 12/03/11 1149 hrs http://www.crunchysanimalrescue.org.uk/images/staf f.jpg accessed 12/03/11 1335 hrs http://1.bp.blogspot.com/_3lhqKnS9Mg/S79Klfrmj_I/AAAAAAAAAtc/pKkd7eI8XSk/s 1600/One+of+Rush+Kennels+seized+dogs.JPG accessed 12/03/11 1450 hrs http://dingo.care2.com/pictures/c2c/share/22/227/74 1/2274186_370.jpg accessed 12/03/11 2144hrs References (continuation) http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2010/oct/25/impendin g-global-food-crisis accessed on 13/03/11 1154 hrs http://www.theodora.com/wfb/photos/india/bamboo_forest_ar unachal_pradesh_india_photo.jpg accessed on 13/03/11 1315hrs http://www.google.co.uk/imgres?imgurl=http://www.botany.ha waii.edu/basch/uhnpscesu/htms/npsapln2/images/combret/DN 4073x7.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.botany.hawaii.edu/basch/uh npscesu/htms/npsapln2/fish_pops/combret/tree01.htm&h=419& w=504&sz=39&tbnid=IqGCD4sBAYMrLM:&tbnh=108&tbnw=130 &prev=/images%3Fq%3Dimage%2Bof%2Bindian%2Balmond&zo om=1&q=image+of+indian+almond&hl=enGB&usg=__T0h00JkBVZzmJuUuE5UxDmltTeU=&sa=X&ei=t7V8 TcCEKc26hAfo9Oj7Bg&ved=0CCMQ9QEwBA accessed on 13/03/11 1317hrs