Urban Geography
advertisement

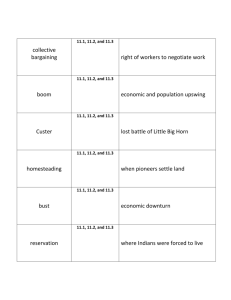
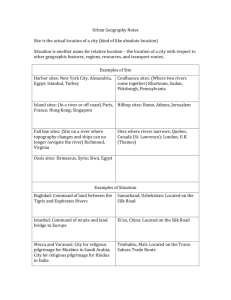
SOL 11a,b,c Site Site is the actual location of a city Situation Situation is another name for relative location – the location of a city with respect to other geographic features, regions, resources, and transport routes Harbor sites: New York Confluence sites: City; Alexandria, Egypt; Istanbul, Turkey Island sites: Paris (located on island in the Seine River), Hong Kong, Singapore Fall line sites: Richmond, Virginia Oasis sites: Damascus, Syria Khartoum, Sudan; Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Hilltop sites: Rome, Athens, Jerusalem Sites where rivers narrow: London (Thames River) and Quebec (St. Lawrence River) Baghdad – Command of Samarkand, Uzbekistan land between Tigris and Euphrates rivers Istanbul – Command of straits and land bridge to Europe Mecca, Saudi Arabia and Varanasi, India – Focal point of pilgrimage – City on Silk Road Xi’an, China – City on Silk Road Timbuktu, Mali – City on Trans-Sahara trade route Singapore – City on Strait of Malacca (maritime trade route) Cape Town, South Africa – Supply station for ships Omaha, Nebraska – City that grew up on U.S. Transcontinental Railroad Sacramento, California – City that grew up on U.S. Transcontinental Railroad Novosibirsk and Vladivostock – Cities that grew up on the Trans-Siberian Railroad Security, defense Religious centers Trade centers (local and long distance) Government administration Manufacturing centers Service centers Rio de Janeiro – Move of New York City – Changes Brazil’s capital city from Rio de Janeiro to Brasilia Pittsburgh – Early function connected to defense, then became steel manufacturing center, later shifted to diverse services in trade patterns, trade from Great Lakes via Eerie Canal, worldwide trade and financial center Mining Towns – “ghost” towns – resource depletion Nation Building – monuments Transportation/Commu nication Hubs Magnets for Migration Seed beds for new ideas and technology Universities Corporate Headquarters Media Centers Transportation problems Sprawl results in Rich and poor conversion of agricultural land to urban uses Rapid immigration results in “shantytowns” In developing countries, major cities are more connected to regions outside the country than to regions within the country neighborhoods exist in different areas isolated from one another Providing essential services (fresh water, sewage disposal, electricity, schools) Air, water, and noise pollution