Cnidarian Reproduction
advertisement

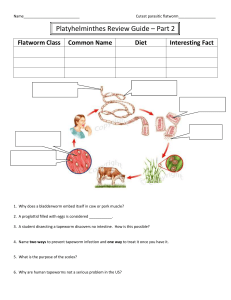
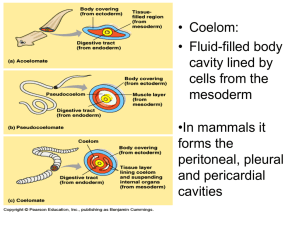
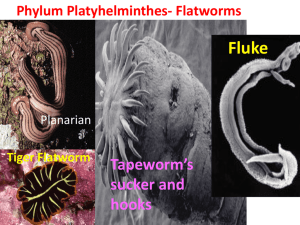
Cnidarian Reproduction Asexually – budding (polyp form) Sexually –have separate male and female medusae that produce gametes that join through external fertilization to produce polyps. Flatworms Platyhelminthes Bilateral Symmetry Free-living in freshwater or parasitic in a host Has all three layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm) Acoelomate – no body cavity. An Important Group Many nasty parasitic infections. Dugesia Tapeworms Flukes Flatworm Feeding Free living flatworms are scavengers. Parasitic flatworms use specialized structures (usually with hooks) to attach to a host. Respiration & Excretion Excretion - Flame cells remove excess water Respiration - Oxygen diffuses into body cells directly. Flatworm Nervous Systems First appearance of cephalization. Primitive brain. Eyespots Flatworm Reproduction Sexually - Hermaphrodites – internal fertilzation. Asexually – fission – when damaged, regenerates new body parts. Proglottids – found in tapeworms – each is shed off individually.