Photosynthesis - Monmouth Regional High School
advertisement

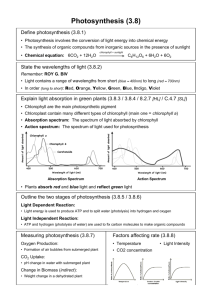
Explain how cellular respiration and photosynthesis sustain life. Diagram the process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Essential Question #5 How do organisms obtain and use energy? Cell Energy • Plants trap light energy. • Plants contain molecules that store energy in their chemical bonds. • Animals obtain energy from these molecules. Photosynthesis: Trapping the Sun’s Energy • Photosynthesis~ the process that uses the sun’s energy to make simple sugars. An Overview of Photosynthesis • Autotrophs/Producers • “self-feeders” • PLANTS, ALGAE, SOME PROTISTS, SOME BACTERIA • How do they make their own food and sustain themselves? – Convert light energy into chemical energy and use it to make their own organic molecules. • How are they the ultimate source of organic molecules for all other organisms? – They “produce” the food supply for the entire biosphere! Where does photosynthesis take place? – All green parts of a plant have chloroplasts. – What part has the most chloroplasts? • Leaves have the most! Chloroplast – Chloroplasts are concentrated in cells of the mesophyllthe green tissue of the interior of the leaf. – What molecule is responsible for the green color? • Chlorophyll- a light absorbing pigment that plays a central role in converting solar energy to chemical energy. – How does CO2 enter and O2 exit the leaf? • Stomata- (stoma, singular) “mouth” they are tiny pores – How is water delivered to the leaves? • Carried from the roots to the leaves through xylem, special veins. Chloroplast in Detail • Double membrane where reactions occur • Stroma- thick fluid within the inner compartment • Thylakoids- interconnected sacs suspended in the stroma – encloses another compartment called the thylakoid space • Grana- (granum, singlular) stacks of thylakoids Inside a Chloroplast • Photosynthesis takes place inside chloroplasts • Chloroplasts contain thylakoids, which are saclike photosynthetic membranes • Thylakoids are arranged in stacks called grana • Thylakoids contain clusters of chlorophyll and other pigments and protein known as photosystems. – This is also the location of the photosynthesis machinery• converts light energy to chemical energy • This energy is used in the stroma to make sugar. Two Phases of Photosynthesis 1. Light-dependent reactions~ convert light energy into chemical energy (ATP) 2. Calvin Cycle (Light-independent reactions)~ uses ATP to convert CO2 into simple sugars Two Main Stages of Photosynthesis A. Light Reactions (thylakoids) 1. 2. 3. 4. Chlorophyll captures the light energy Chlorophyll’s electrons get energized Electrons are passed to the electron transport chain. Energized electrons provide energy that: A. splits water (photolysis) into oxygen and 2 hydrogens, and 2 electrons. - hydrogen is used to make NADPH B. bonds phosphate to ADP to make ATP (chemiosmosis) *2 electrons are returned to chlorophyll. *NADPH and ATP will be used in the dark reactions. B. Dark Reactions (stroma) – Uses carbon from carbon dioxide , energy from ATP, and electrons & hydrogen from NADPH to make glucose. Carbon dioxide + Water Glucose + Oxygen The Light Reactions: Converting Solar Energy to Chemical Energy • Solar energy is called electromagnetic energy. ~~~~~~~~~~~It travels in waves~~~~~~~~~~~~~ • Electromagnetic spectrumthe full range of electromagnetic wavelengths (λ). Light Energy • Sunlight is a form of electromagnetic energy and travels in waves. • Wavelength- the distance between 2 waves • Different forms of electromagnetic energy have unique wavelengths. • Visible light- those wavelengths that your eyes see as different colors. Visible Light • Visible light is only a small fraction of the spectrum • Wavelengths 380 nm – 750 nm • Shorter wavelengths (i.e. gamma rays) have more energy than longer wavelengths (i.e. radio waves) • Short λ= Higher energy • Long λ= Lower energy • X-rays are short, high-energy wavelengths that can damage proteins and nucleic acids. • Shorter wavelengths have more energy than longer wavelengths. • Side Note: – wavelengths that are shorter than that of visible light have enough energy to damage important molecules in your body. This is why being exposed to UV radiation can cause sunburn and skin cancer! Pigments and Color • Pigment- a chemical compound that determines a substance’s color. • What happens when light shines on an object that contains pigments? – The different wavelengths can either be • Absorbed • Transmitted • Or Reflected, which is the color that we perceive--“see” Examples • Why do leaves appear green? – The chlorophyll reflects and transmits green light and absorbs blue-violet and red-orange light. • Why is the sky blue? – The blue wavelength is reflected, while all other wavelengths are absorbed. Why can’t you see these colors in the summer? • The plant manufactures chlorophyll, which hides the other pigments that are present in the leaves. In the fall, trees stop producing chlorophyll and the other pigments become visible. Plant Pigments Gather Light • Photosystems- clusters of chlorophyll and other molecules. • The clusters of pigments act as light-gathering panels. What happens to visible light in the chloroplast? • Light absorbing molecules in the thylakoid membranes absorb some wavelengths and reflect or transmit others. – It depends on the type of pigment! • Why do leaves appear green? • Chlorophyll a – Chlorophyll b • Absorbs mainly blue and – *Involved in light reactions* – Absorbs blue-violet and red light orange • Reflects yellow-green – Reflects green light • *Conveys absorbed energy to chlorophyll a* Other Pigments found in chloroplasts… • Carotenoids – Various shades of yellow and orange • the colors of Autumn. • Carotenoids are longer lasting, whereas chlorophyll breaks down and trees lose their green color – carotenoids pass energy to chlorophyll a – *photoprotection- carotenoids absorb and dissipate excess light energy that would otherwise • damage chlorophyll or • interact with oxygen to create oxidative molecules that could damage the molecules of the cell. • Photosystem~ cluster of pigments within the thylakoid. – Pigments~ molecules that absorb specific wavelengths of sunlight. • Chlorophyll~ pigment that absorbs all wavelengths but green. Open Notebook Quiz 1. In what organelle does photosynthesis take place? 2. What is the green pigment called? 3. What is the name of the tiny pores in leaves through which gas exchange occurs? 4. What are the reactants of photosynthesis? 5. What are the products of photosynthesis? 6. Where do the light reactions occur? 7. Where do the dark reactions occur? 8. The dark reactions (calvin cycle) requires two inputs that are supplied by the light reactions. What are these two inputs?