Identification of prosodic near minimal pairs in spontaneous speech
advertisement

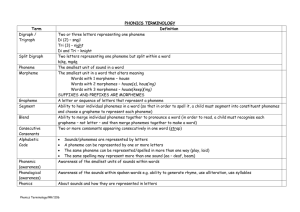
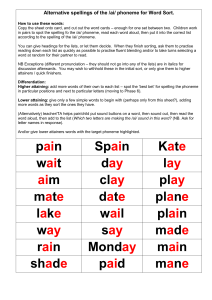
Identification of prosodic nearminimal Pairs in Spontaneous Speech Keesha Joseph Howard University Center for Spoken Language Understanding (CSLU) Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) Portland, Oregon, USA josephk@cslu.ogi.edu August 10, 2010 Agenda Background Information Research Questions Data and Subjects Research Activities Conclusion and Future Work Questions? Background Information van Santen et al. 2009/2010 Very structured tasks tested a child’s ability to make distinctions in focus and stress Video Time!! Some acoustic features were different in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) versus Typically Developing (TD) subjects Problem: Tasks situation is structured and artificial. Would we find the same outcome in spontaneous speech? Background Information The tasks used prosodic minimal pairs. A prosodic minimal pair is a 2-syllable phrase with the same phoneme sequence but the stress is on a different part of the phrase. blue COW vs BLUE cow A near minimal pair has similar (but not identical) phonetic content where the phoneme classes are the same but the phonemes might not be. Different Phrases: my dad vs my bag Same phoneme classes and vowels but different phonemes nas_aI_vst_@_vst vs nas_aI_vst_@_vst Research Questions Can we find minimal pairs in spontaneous speech? Can we find near minimal pairs if there are not many minimal pairs found in spontaneous speech? How do we find near minimal and minimal pairs? How can we evaluate whether our method of finding minimal pairs works? Data and Subjects 5 kids with Autism Spectrum Disorder and 5 kids with Typical Development Transcripts of ADOS diagnostic interviews were used as examples of spontaneous speech Festival Speech Synthesis software was used to convert the ADOS interview transcripts to phonetic transcriptions Research Activities Changed consonants in a string of phonemes to their respective phoneme class (Unvoiced Stops, Voiced Stops, Unvoiced Fricatives, Voiced Fricatives, Affricates, Liquids, Nasals, Glides) This process finds near minimal pairs Example: ufr_>_liq_ufr_3r_vst could either be f_>_9r_T_3r_d (four thirt|y) or f_>_9r_f_3r_g (for forg|et) Research Activities 1. Create a script to find phonetic strings the follow a CVC+VC pattern. C = Consonant V = Vowel C+ = Consonant 2. Create a file for each subject with all possible phonetic strings that follow a CVC+VC pattern. 3. Sort on phonetic strings to find groups of potential near minimal pairs. These phonetic strings are called potential near minimal pairs 4. Manually searched through potential near minimal pairs to find actual near minimal pairs. Research Activities Use Praat to listen to sentences of the ADOS to find actual near minimal pairs. Rule out criteria: The interviewer was speaking over that potential minimal pair The kid was making a lot of noise (i.e. hitting the table while speaking) The kid was whispering or not close enough to the microphone A Potential Near Minimal Pair is an Actual Near Minimal Pair only if: The items of the pair have a contrasting stress pattern. Consonant Phoneme Class and Vowel Phoneme Pairs Actual NMP Actual NMP / Potential NMP # of Actual NMP found in an hour Subject Words Potential NMP OGI-007 1471 518 1.5 4 .77% 2.7 OGI-013 1324 426 2 3 .70% 1.5 OGI-016 2242 667 2.5 1 .15% .4 OGI-027 2166 789 2 2 .25% 1.0 OGI-033 3427 1531 4 4 .26% 1.0 OGI-042 2305 896 2.5 3 .33% 1.2 OGI-064 1308 1042 1.5 2 .19% 1.3 OGI-065 2115 744 2.5 4 .54% 1.6 OGI-082 1203 397 1.5 3 .76% 2.0 Time(hours) Research Activities We decided to collapse vowels into classes to find more potential near minimal pairs For example my_dad under these vowel classes: Height nas_diph_vst_low_vst Backness nas_diph_vst_front_vst Length nas_long_vst_short_vst For comparison, also looked at exact phonemes for minimal pairs m_aI_d_@_d All Pairs for OGI-082 Type of Pairs # of Potential Near Minimal Pairs Exact 390 Phoneme Class / Individual Vowels (27) 397 Vowel Class: Height (5) 423 Vowel Class: Backness(5) 428 Vowel Class: Length(3) 531 Conclusion and Future Work Surprisingly small number of potential NMPs even with broad phoneme classes. This method for finding near minimal pairs is feasible with well trained annotator. The length of time it took to find such pairs decreased with experience Future Work Further broadening of phoneme classes. Alignment of phonemes to waves for these pairs. Run the analysis of van Santen et al. 2010 to see if the results found in that paper are also in spontaneous speech. THANKS! Emily Tucker Prud’hommeaux Jan van Santen CSLU Staff and Interns Thanks for making this an experience I wont forget! Questions?