Lecture 5 - Methods.info
advertisement

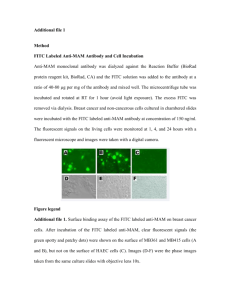
Practical molecular biology PD Dr. Alexei Gratchev Prof. Dr. Julia Kzhyshkowska Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Kaminski Course structure 08.10 Plasmids, restriction enzymes, analytics 09.10 Genomic DNA, RNA 10.10 PCR, real-time (quantitative) PCR 11.10 Protein analysis IHC 12.10 Flow cytometry (FACS) Nomenclature FACS – Fluorescence Assisted Cell Sorting FACS analysis Flow cytometry Flow cytofluorometry Applications Medicine Immunophenotyping of blood cells Diagnostic of various hematologic diseases Transplantation Research Cell cycle analysis Expression analysis Phagocytosis, endocytosis Cytokine production analysis History 1950-1960 Cytophotometry. UMSP-1 (Zeiss) 5-10 min/cell 1969 Pulse cytophotometry. ICP-11 (Phywe, Göttingen) (in 1976 purchased by Ortho-diagnostics (USA) and later disappeared from the market) 1970 Cytofluorograph (Ortho-Diagnostics) Mercury lamp excitation (480-500nm) 2 fluorescent parameters PMT detectors (no scatter detectors) >1000 cells/sec Argon laser (488 nm) as a light source 1976 Dual laser instrument (DKFZ, Heidelberg) 1986 First sorter (PARTEC, Münster) 1990-1993 Cell sizing option (Bruker-Odam, France) Principle of flow cytometry Hydrodynamic focusing of the cells in the focused laser beam Optical scheme of a flow cytometer 4 colour flow cytometer Optical system of BD FACSAria II 2 laser flow cell Fluorophores Fluorophores Parameters collected FSC – Forward scatter (correlates with the cell size) SSC –Sideward scatter (correlates with the cell granulation) FL – Fluorescence signal (min 3, max 12 channels) Concentration of cells (only with some flow cytometers) Size of the cell (only with some flow cytometers) Flow cytometry results Compensation problem 4 colour compensation Compensation Measure cells labelled with single antibody Determine the percentage of the signal in wrong detector Generate compensation matrix Modern cytometers perform compensation automatically Experiment planning Antibody has to be highly specific Antibody has to be tittered Select correct fluorophores (low expression – bright fluorescence, high expression – weak fluorescence) Think about the abundance of the cell population you want to analyse Controls Non stained cells Cells stained with single antibodies/dyes (for compensation purpose) Cells stained with unspecific isotype control – unspecific antibodies of the same isotype as your test antibodies, labeled with the same fluorophore with the same efficiency Cell staining Prepare cell suspension Add antibody Incubate Wash Measure Experiment today a) b) c) d) e) f) 2 µl CD14 FITC Ab 2 µl CD16 APC Ab 2 µl CD14 FITC Ab + CD16 APC Ab 2 µl Isotype FITC 2 µl Isotype APC 2 µl Isotype FITC + 2 µl Isotype APC g) Non-labelled cells Questions?