Research Review Activity
advertisement

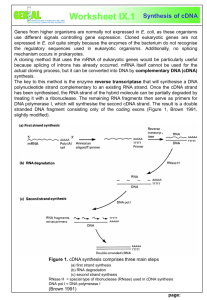
RESEARCH IN MOLECULAR GENETICS FOR FRIDAY 10/31/14 NAME _______________________________________________________________________________ Please read the handout and answer the following questions: This is important information for you to know so you may expect a quiz toward the end of next week. So do a good job. I will place this review on my website for those who like to type and have an electronic copy. It will be number four under review activities. 1.Name three things that are needed in order to study a DNA fragment? 2. What is a vector? 3. Where do plasmids replicate? 4. What do we insert into plasmids? 5. What are the basic steps to insert DNA of interest into plasmid? 6. Define the following terms: a. Digesting b. Ligating c. Transforming 7. What allows plasmids to replicate independently of the bacteria’s genome? 8. How many copies can a bacterial host make of a plasmid? 9. Describe a selectable marker and how it works 10. Describe bacterial transformation 11. Are bacterial cells the only type of cells that can be transformed? 12. What is meant by competent? 13. What makes bacteria competent? 14. What is a color screen and how does it work? 15. What is the name of our plasmid? 16. What is a polylinker or multiple cloning site? 17. What restriction sites were used to clone in the duckweed DNA into the plasmid? 18. What is a DNA library? 19. What is a genomic library? What are they used for? 20. How is a genomic library made? 21. What is a cDNA library? What is it used for? 22. Why might it be worthwhile to construct cDNA libraries under specific conditions in specific tissues or at specific times in life cycle? 23. Why is it challenging to identify ALL the cDNA’s expressed in an organism? 24. Detailed knowledge of how a cDNA library is constructed a. Why difficult to use mRNA directly? b. What is cDNA and why used? c. How is rNA isolated from Duckweed? d. How is mRNA separated from tRNA and rRNA? e. From your single stranded mRNA, how is a single strand of DNA complementary to mRNA made? f. What is reverse transcriptase? Where does it come from? g. What does revers transcriptase need to begin making a new DNA strand? h. What is the primer used? Why? i. What does primer have at the end of it? k. When reverse transcriptase reaches the end of RNA strand what does it add to the DNA strand being formed? l. After reverse transcriptase how many strands of RNA & DNA do you have? m. How can you get rid of the RNA strand? n. How to you synthesize the second strand of DNA? o. What is the primer for the second strand synthesis? 25. Describe in detail how the cDNA made is ligated into plasmid a. What restriction enzyme is used to create overhangs at each end od cDNA fragment? b. Why is it advantageous to use a restriction enzyme that recognizes an 8 base sequence? c. Why is it an advantage that the restriction enzyme can recognize different set of five bases in middle of restriction site? d. Why is it advantageous that the cDNA fragment has different overhangs at each end? e. How is cDNA pasted into plasmid? 26. Understand Fig 1-9, 1-10, and 1-11