Writing Business Letters
advertisement

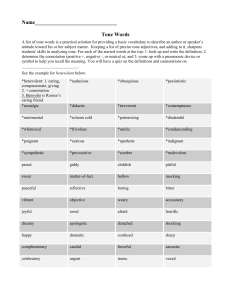
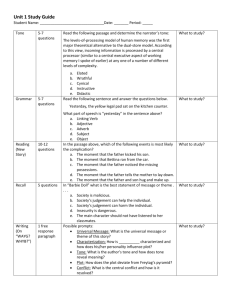
Writing Business Letters Purpose of business correspondence Realistic and maximum aims Transmittal of information Audience appraisal Development of arguments Layout of a business letter Seven basic parts: Writer’s name and address Date(write month in full) Inside address(recipient’s) Attention line-(optional)addresses specific person Greeting-salutation Body of the letter Complimentary close-use “Yours faithfully” for unknown receiver& use “Yours sincerely” for a person you have addressed in the opening. Writer’s signature& job title/designation Types of layout Full block layout-against the left margin/modern style Full block layout with centered letterhead-Initial details centered, body follows full block format Modified block layout-conservative style/uses right and left alignment Formatting a business letter Single space between words/Double space par. Use open style of punctuation(omits punctuation accept in the body) or mixed style of punctuation(places punctuation after greeting and closing words) Divide the letter in appropriate paragraphs Use an average paragraph length of six lines Use not more than 15-20 words /sentence& one idea/sentence Always use full stops more than commas. Plain English writing style A business letter should ideally be written: in a simple, appealing and straight forward style in a clear and concise manner following the ‘you’ approach-user centered/empathetic x x x approach While writing a business letter, avoid the use of: highly technical jargon/discourteous tone long sections of unbroken text/ lengthy sentences clichéd openings/new ideas in the closing par. Tone in business writing What is tone? Writer’s attitude towards the reader and the subject/message Affects the reader in the same way as a tone of voice in everyday exchanges Prepares the ground for transmittal of message Conveys your intent to the reader Must have a purpose to fulfill What sort of tone should I use? Be confident: Not: You must agree that I am qualified for the position. But: My qualifications in the areas of translation and customer service meet your job requirements. Be courteous and sincere: Not: You didn't read the instructions carefully, thus your system has shut down. But: The system may automatically shut down if any installation errors occur. Use appropriate emphasis and subordination: Emphasize primary idea-short sentence can stand alone/subordinate secondary details Use non-discriminatory language: chairperson, to whom it may concern Stress the benefits for the reader-write from the reader’s perspective Write at an appropriate level of difficulty-avoid too many complex/passive structures, or technical jargon Appropriate tone/audience analysis Bob is writing a cover letter for a position as a Sales Representative for a newspaper. He is unsure that he will be able to succeed at such a position, and uses phrases such as: "I hope that you will contact me..." "I know that my qualifications are not very impressive, but...“ Clearly, Bob is not assuming an appropriate tone. He must consider that: He is applying for a position as a Sales Representative. He wants the employer to ask him to come in for an interview. The employer will look for highly motivated and confident individuals. If Bob were to consider these things he may rewrite his cover letter to include such phrases as: "You can reach me at 555-2233; I look forward to hearing from you." "My qualifications make me an excellent applicant for this position..." The tone of the message has changed drastically to sound more confident and self-assured "What is my intent upon writing?" Suzy is writing a job acceptance letter to an employer but is unsure of the tone she should take in the message. She has decided to accept the position. When she asks herself, "What is my intent upon writing?" she answers, "I want to accept the position, thank the company for the offer, and establish goodwill with my new co-workers." As she writes the letter she quickly assumes a tone that is appreciative for the offer and enthusiastic about beginning a new job. Types of business letters Good news or neutral letters An inquiry An order refusal A request A credit refusal An acknowledgement An adjustment refusal A letter of introduction Refusing an invitation or Persuasive letters Sales letters Job applications Collection letters request Writing plan The direct order of information-good news letter/persuasive letter The indirect order of information-bad new letter References • Ober, Scott. Contemporary Business Communication. 2nd Edition. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 1995. • Dwyer, Judith. 2008,The Business Communication Handbook,8th ed. Pearson • The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University