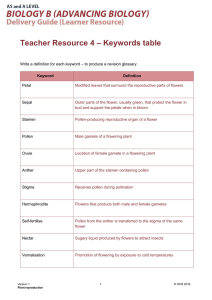
Plants & Cells Notes # 5 Compare and classify organisms into major
advertisement

Plants & Cells Notes # 5 Compare and classify organisms into major groups on the basis of structure. Describe the life cycle of flowering plants. Angiosperms are plants that produce seeds that are enclosed in a fruit. They are classified as flowering plants. The flower is the structure that contains the reproductive organs of the flowering plant. The life cycle: 1. Germination: Inside of a seed is a baby plant, known as an embryo. The embryo has the beginnings of roots, stems, and leaves. The seed coat opens and the embryo plant begins to grow. Light is not needed for germination because the embryo uses stored food inside the seed as energy to grow. 2. The seed grows into a new plant and develops roots, stems, and leaves. The root anchors the plant in the ground, absorbs water and nutrients from the soil, and can store food. The stem supports the plant, holds the leaves up so they are exposed to the sun, and carries substances between the roots and leaves. The stem also stores food and can carry out photosynthesis if green. The leaves hold chlorophyll, collect sunlight for photosynthesis, exchange gases, control water loss (transpiration), and can store food. 3. The plant eventually develops flowers. The flowers start out as buds, enclosed in leaflike structures called sepals. When the sepals open and expose the flower, this means that the plant is ready to reproduce. 4. The female part of the plant is known as the pistil. The base of the pistil is the ovary. Inside the ovary are ovules, structures that contain egg cells. When the egg cell gets fertilized, it will become the seed’s embryo. 5. The male parts of the flower are known as stamens. Anthers, located at the top, produce pollen grains. This pollen contains sperm cells. The anthers are held up by thin stalks called filaments. 6. Pollination: Pollen must be transferred from the stamen to another plant’s stigma. The stigma is on the top part of the pistil. It is sticky so that pollen grains can get easily trapped on it. 7. A slender tube, called a style, connects the stigma to the ovary. The pollen grows a tube down the style into the ovary. 8. Fertilization: The sperm cells move through the pollen tube and join with the egg cells. Each ovule develops into a seed. The fertilized egg becomes the seed’s embryo. Other parts of the ovule develop into the seed coat and stored food. 9. The ovary ripens and develops into a fruit to protect the seeds. This helps in seed dispersal. The cycle starts again. GERMINATION GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOWER POLLINATION FERTILIZATION DEVELOPMENT OF FRUIT WITH SEEDS