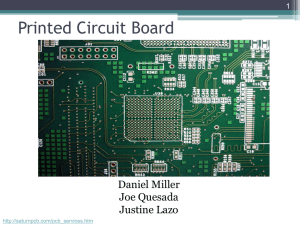
Electronics Skill
advertisement

Designing Printed Circuit Board (PCB ) (Tutorial Five) Computer and Information Engineering Lab II ECE 3102 & ECE 4102 ب ز ْدني ِّ ِّع ْلما ً َو ْر ُز ْقني ِّ فَ ْهما ِّ َر My Lord! Advance me in Knowledge and true understanding . Laboratory: Mechatronics Workshop, Room# E2-2-13.12 ب ز ْدني ِّ ِّع ْلما ً َو ْر ُز ْقني ِّ فَ ْهما ِّ َر My Lord! Advance me in Knowledge and true understanding . 2 Contents Basic PCB Skills and Tools. PCB design using Crocodile. PCB design using Eagle. 3 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Construction of Electronics Projects Need to know about…… • • • • • Types of Circuit Board . Soldering Guide. Tools required for electronics. Starter kit of components. Making a workbench for electronics. 4 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Types of Circuit Board Breadboard Stripboard Printed Circuit Board Breadboard Stripboard Printed Circuit Board 5 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Types of Circuit Board (Con.) Breadboard Temporary use, Normally for testing purpose. No soldering required . This is a way of making a temporary circuit. No soldering is required and all the components can be re-used afterwards. It is easy to change connections and replace components. Almost all the Electronics Club projects started life on a breadboard to check that the circuit worked as intended. Breadboard 6 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Types of Circuit Board (Con.) Stripboard Permanent, Soldered . Stripboard has parallel strips of copper track on one side. The strips are 0.1" (2.54mm) apart and there are holes every 0.1" (2.54mm). Stripboard requires no special preparation other than cutting to size. It can be cut with a junior hacksaw, or simply snap it along the lines of holes by putting it over the edge of a bench or table and pushing hard. Stripboard 7 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Types of Circuit Board (Con.) Printed Circuit Board Permanent, soldered . Printed circuit boards have copper tracks connecting the holes where the components are placed. They are designed specially for each circuit and make construction very easy. However, producing the PCB requires special equipment so this method is not recommended if you are a beginner unless the PCB is provided for you. Printed Circuit Board 8 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB Single sided layer • Positive board & Negative board A sample of positive board A sample of negative board the desired circuit will be the one with black color. the desired circuit will be the one with white color. 9 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) 10 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) 11 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 1 1. Circuit Schematic diagram PCB Layout 12 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 2 When the PCB layout (Using software) is finished it is printed on a Transparent Paper and becomes a PCB mask. 13 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 3 PHOTO-RESIST BOARD is a piece of glass reinforced plastic. One of the sides is copper clad with photosensitive coating. When the plastic film is peeled back this sensitive coating is revealed. After processing this will be the PCB. 14 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 4 The PCB mask (transparent page) is placed underneath the photo-resist board, touching the sensitive surface. The plastic film must be removed. PCB mask and board are then transferred to the UV light Box. Be careful to ensure that the PCB mask is the right way up, otherwise when the circuit is etched you will discover that the tracks are also the wrong way round. 15 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 5 The lid is shut and the box switched on. The photo-resist board, with PCB mask are left underneath the lid for 2 minutes (120 sec.) Note: for negative board, the exposure will be for 25 seconds 16 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 6 & 7 The photo-resist board is then placed in a tank filled with developer solution. It is important that the board is only left in the developer for approximately ten seconds. When the board is taken out of the developer it must be washed in clean water before transferring to the etching tank. Always use plastic tongs or gloves. 17 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 6 & 7 The etchant used is Ferric Chloride. This solution slowly etches away the unwanted copper, leaving the tracks only. ◦ At this stage it is important to keep checking that the PCB is completed If it is left in the tank too long the copper tracks will also be removed or damaged. 18 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 8 & 9 The last stage is drilling the holes for the components. A small PCB drill is used for this purpose. Again care is needed as a good PCB can be ruined by careless drilling. 19 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 10 Soldering Techniques 1. Use a soldering iron in good condition. Inspect the tip to make sure that it is not past good operation. If it looks in bad condition it will not help you solder a good joint. The shape of the tip may vary from one soldering iron to the next but generally they should look clean and not burnt. 2. A PCB eraser is used to remove any film from the tracks. This must be done carefully because the film will prevent good soldering of the components to the PCB. The tracks can be checked using a magnifying glass. If there are gaps in the tracks, sometimes they can be repaired using wire but usually a new PCB has to be etched. 20 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 10 Soldering Techniques (Con.) 3. Place the PCB, with its components in position, in the bull clip. This will steady the PCB when you try to use the soldering iron. 4. The heated soldering iron should then be placed in contact with the track and the component and allowed to heat them up. Once they are heated the solder can be applied. The solder should flow through and around the component and the track 21 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 10 Soldering Techniques (Con.) 5. Having completed soldering the circuit the extended legs on the components need to be trimmed using wire clippers. The circuit is now ready for testing. Below are some of the warning symbols that appear on etchants and ferric chloride solutions. They are present to warn the user of their potential danger if mishandled. Why should etchants and solutions such as ferric chloride be handle with great care ? 22 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 11 Checking & Testing 23 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Step 11 Checking & Testing (Con.) 24 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Working With PCB (Con.) Finally The Product 25 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Tools Required for Circuit Construction Soldering iron A soldering iron is a hand tool used in soldering. It supplies heat to melt the solder so that it can flow into the joint between two work-pieces. A soldering iron is composed of a heated metal tip and an insulated handle. Heating is often achieved electrically, by passing an electric current through a resistive heating element. The iron's power rating should be 15 to 25W and it should be fitted with a small bit of 2 to 3mm diameter. 26 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Tools Required for Circuit Construction (Con.) Soldering iron stand You must have a safe place to put the iron when you are not holding it. The stand should include a sponge which can be dampened for cleaning the tip of the iron. 27 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Tools Required for Circuit Construction (Con.) De-soldering pump (solder sucker) A tool for removing solder when de-soldering a joint to correct a mistake or replace a component. 28 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Tools Required for Circuit Construction (Con.) Reel of solder The best size for electronics is 22swg (swg = standard wire gauge). 29 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Tools Required for Circuit Construction (Con.) Cutters For trimming component leads close to the circuit board. 30 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Tools Required for Circuit Construction (Con.) Small pliers Usually called 'snipe nose' pliers, these are for bending component leads etc. If you put a strong rubber band across the handles the pliers make a convenient holder for parts such as switches while you solder the contacts. 31 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Tools Required for Circuit Construction (Con.) Small flat-blade screwdriver For scraping away excess flux and dirt between tracks, as well as driving screws. 32 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Tools Required for Circuit Construction (Con.) Small electric drill Ideally this should be mounted in a drill stand. We will need a range of small drill bits, but for most holes a 1mm bit is suitable. Larger holes can be drilled with a hand drill but 1mm bits are too fragile to use reliably in a hand drill. 33 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Soldering Guide: HOW TO SOLDER A few safety precautions: Never touch the element or tip of the soldering iron. • They are very hot (about 400°C) and will give you a nasty burn. • Take great care to avoid touching the mains flex with the tip of the iron. • The iron should have a heatproof flex for extra protection. An ordinary plastic flex will melt immediately if touched by a hot iron and there is a serious risk of burns and electric shock. Always return the soldering iron to its stand when not in use. • Never put it down on your workbench, even for a moment! Work in a well-ventilated area. • The smoke formed as you melt solder is mostly from the flux and quite irritating. Avoid breathing it by keeping you head to the side of, not above, your work. Wash your hands after using solder. • Solder contains lead which is a poisonous metal. 34 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Soldering Guide: HOW TO SOLDER (Con.) Always return the soldering iron to its stand when not in use. Use a damp sponge, frequently, to keep the bit clean. 35 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Soldering Guide: HOW TO SOLDER (Con.) Tinning the bit, Heating the joint and applying the solder. Tin the bit for good heat conduction. (This means putting a small blob of solder on the tip of the bit). Hold the iron like a pen. Rest your hands on the workbench to make them steady. Take precautions against the work moving (use a small vice or sticky tape). Heat the biggest part of the joint for 2-3 seconds. 36 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Soldering Guide: HOW TO SOLDER (Con.) PRACTICE MAKES PERFECT !!! 37 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Important Components 38 Basic PCB Skills and Tools Important Components (Con.) 39 Basic PCB Skills and Tools De-soldering Components Tools required: pliers, cutters, soldering iron, and solder sucker (desoldering tool). Take great care to avoid damage. Components cost a few pence, an assembled printed circuit board may be worth several hundred pounds. Ensure the iron bit is well tinned. Heat up the joint to be de-soldered until the solder runs. Apply the solder sucker and remove the solder. This should only take two or three seconds. Working on a double-sided PCB (where copper tracks are on both sides of the PCB) is more difficult and requires more care. It is often safer to cut the component leads and discard the component, then desolder the leads individually. 40 41 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Crocodile Technology 3D Crocodile is a compilation of circuit design tools and simulation tools. This application is also good for beginners who wanted to learn electronics. The simulation tools help learners / users to experiment circuit connections without being worried about component get burns because of wrongly connected. You can always replace burnt component with a new one by simply drag and drop. 42 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Creating New File 1. Click File >> New 2. Click “Rectangular PCB space” from the Parts Library pane and drag it to the scene space 43 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Working Space Parts tray Click and drag parts to PCB space 3D / PCB space Schematic space Parts tray 44 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Circuit Designing Practice Find and drag all the components below to the PCB space No. Component Value Qty 1. Resistor 470 Ohm 3 2. Resistor 10 kOhm 2 3. Capacitor 100 uF 1 4. Diode 1N914 1 5. IC 555 timer - 1 6. 4027 dual JK flip flop - 1 7. LED - 3 45 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Drawing the Schematic Draw the schematic below on the schematic space. See the circuit simulation by clicking the switch button on the schematic 46 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Crocodile Technology to Real PCB Once a circuit has been designed and simulated/tested in Crocodile Technology and any necessary alterations made, the completed circuit is ready for export to ‘real PCB’. Both Crocodile Technology and Real PCB software must be running at the same time for this to be possible. The conversion to PCB layout can be achieved through a menu in Crocodile Technology. Real PCB converts the circuit diagram effortlessly to PCB layout and usually with 100% accuracy. 47 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Working with Real PCB Real PCB can also be used to construct a circuit as a PCB layout, from scratch, by selecting components from a series of menus and drawing the tracks connecting them. It can be used by both beginners and experts to produce accurate PCBs. Quality checks can be carried out automatically and the software will also produce a bill for the components used on any PCB. The ‘Pour Copper’ menu changes the final PCB by only removing enough copper so that the tracks can be seen. This means that only the necessary copper is removed to ensure the final circuit works. This extends the life of etchant used in the etchant tank. Two more ways of presenting the PCB. The 'artwork' layout is the most likely to be printed out on a transparency, ready for conversion to PCB. The ‘real life’ layout style shows the PCB with its components. This is useful when arranging the components on the PCB, as the position of each can be check against a real life printed. 48 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Working with Real PCB (Con.) When the PCB layout is finished it is printed on a transparency and becomes known as a PCB mask. The PCB mask is transferred to the UV box, which is the next stage in the manufacture of a printed circuit board. Advantages of using circuit and PCB software: 1. Circuits can be simulated on screen without the need to build a circuit on a breadboard with real components. 2. Errors can be corrected and alterations made to the circuit by simply replacing components from menus. 3. No soldering is needed, simply move components with a mouse. 4. Using simulation software is safer than soldering with hot soldering irons and avoids dangerous fumes being produced whilst soldering. 5. Once a PCB has been designed it can be printed onto transparencies repeatedly, all to the same high quality. 6. PCB layout software is more accurate than drawing a circuit by hand. 49 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Working with Real PCB (Con.) Jumper wires exist when Real PCB finds out that there are no possibilities of copper connection. But you can always eliminate jumper wires by rearranging the components position. Try rearranging the components until a PCB artwork with minimum or no jumper wires at all. Jumper wires 50 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Working with Real PCB (Con.) Exporting to Real PCB 51 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Working with Real PCB (Con.) • For the first time, simply click “Quick” button. • Take note on the “circuit warnings” down below… 52 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Working with Real PCB (Con.) 1 2 Click this button to open Real PCB Click this button to see error log 53 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Working with Real PCB (Con.) Jumper wire Tools pane 54 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Working with Real PCB (Con.) 55 Circuit Design Using Crocodile Technology 3D Working with Real PCB (Con.) It will always be a good practice to print the artwork to a white paper first. This will allow you to check the arrangement and the orientation of the components easily. If you’ve satisfied with the artwork than print it on a transparency film to create a PCB mask. 56 USING EAGLE SOFTWARE 57 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software EAGLE Software Eagle software is used to design schematic diagram i.e. the circuit and then transfer it into a PCB layout However, Eagle does not perform analysis like PSPICE or ORCAD. circuit 58 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Creating New Project File >> New >> Project 59 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Creating New Project (Con.) 60 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Rename Project & Schematic Right click on the New Project folder icon to access the menu. Rename the project before creating a new schematic since it is not possible to change the project’s name while it is in use. 61 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software LIBRARY • Set up the library before working on the schematic . • Right click on the Library, and choose “Use all”. • Some user might drop components that he/she don’t want. This will make sure that all the components library is selected 62 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Designing Space Copy Select / Move Add Parts – This is where all the parts needed stored in the library Connecting Wires NOTE: Right hand click to rotate your parts 63 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Example: Rectifier Circuit An AC signal produced by a function generator Output will be connected to an oscillator Now construct the circuit using the schematic. 64 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Selecting Components This window will appear if ‘Add Part’ Icon is clicked. Write the type of component (Ex. DIODE), Choose the model D1N4148. 65 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Selecting Components To select the part just click OK and the part will be displayed on the schematic window. WARNING!!! NEVER CLICK "Drop". By clicking the "Drop" button, this part is deleted from the list. If you’ve clicked the "Drop" button by mistake, you can reset the library on Control Panel. 66 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Selecting Components (Con.) To position the component simply click the left mouse button anywhere on the window. Click again to get another same component. To stop the addition function of the component, strike the ESC key and click "Cancel”. OR Press STOP in the toolbar. 67 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Selecting Components (Con.) Adjust the display screen using Fit, In and Out button. To delete, click delete button, click on the parts to delete press STOP to end this operation. 68 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Wiring the parts After putting the component, wiring can be done by the Wire function. Left click the lead wire of the part and double-click at the end point which of wiring. It isn't necessary to keep to push the mouse button during wiring work. To stop this feature, press STOP button. The drawn line can be erased using the Delete button. Can also wire the components using bus icon. 69 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Wiring the parts (Con.) A circular black mark is put to the node of the wiring. This mark isn't related to the wiring of the printed board. It is to confirm the connection of the wire when the person sees the schematic. When pushing the Junction button, the circular mark which moves with the mouse pointer appears. A mark is drawn to the schematic when left clicking at the node. To stop this feature, it clicks the Cancel button. 70 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Practice Draw this circuit: A 5volt voltage regulator circuit using IC 7805 . After drawing a schematic, the mistake can be automatically detected by the ERC (Electrical Rule Check) button. 71 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software WIREPADS We need to have PADs included in schematic so that PCB can be connected to power supply, GND and the output node So, again click Add parts, search for Pad, and find wire pads. Use the ( 1,6 /0,8) package. 72 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software WIREPADS (Con.) WIREPADS 73 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Tips Can label the wire pads by clicking the icons and then select the items to rename or put values for the resistors/capacitors. Can do this in schematic diagram. 74 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Related Instructions Invoke ◦ Use when it involves ICs. ◦ It is common for an IC to have more than 1 logic circuit in it, for example, an IC for NOT gate ( 74LS04N ). ◦ There are 6 NOT the IC. Hence, allows you to other logic accordingly. gates in invoke connect circuits 75 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Electrical Rule Check (ERC) ERC is performed to check schematic transforming them into a PCB layout. Once the icon is clicked, a text file will appear producing list of errors and warnings. Correct schematic and perform ERC again. IT IS VERY SCHEMATIC IMPORTANT TO GET A before CORRECT Icon associated with ERC 76 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Example of ERC EAGLE Version 4.09r2 Copyright (c) 1988-2002 CadSoft Electrical Rule Check for C:/PROGRAM FILES/EAGLE-4.09R2/projects/test/test.sch WARNING: Sheet 1/1: POWER Pin IC1P VCC connected to +5V Board and schematic are consistent 0 errors 1 warning 77 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Starting New Project: Board File Click "Board" icon in the schematic window. When a board isn't made yet, board creating is confirmed by following dialog. 78 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Creating Board File The yellow line among the parts is the line which shows a connection among them. But, these lines are not wiring for the printed board yet. 79 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Creating Board File Need to move your parts into the frame. Click on Select all the parts, click on Right hand click the grouped parts. And then left hand click to place them in the frame. Once all parts are place in the frame, click on the Ratsnest icon. Can still rotate parts even though using in the PCB layout window. 80 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Parts Arrangement on the Board The yellow line shows a connection among the parts. The part should be arranged for the yellow line to be simpler. 81 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software What is RATNEST A Ratsnest display: ◦ the program will draw a straight line (not a track) between the pads of components which are connected on the schematic. ◦ it shows the connectivity of circuit before starting laying out tracks. ◦ At the start of board layout with all components, placed down randomly, this will appear as a huge and complicated random maze of lines. Hence the name Ratsnest. 82 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Placing Components Place all the components that need to be in specific locations. ◦ e.g. connectors, switches, LEDs Pay attention to orientation of each part placed. Give careful thought when placing components to minimize trace lengths. Put parts next to other parts they connect to. Arrange ICs in only one or two orientations: ◦ a good job here makes routing the traces much easier. ◦ Again, the orientation of each part matters too. ◦ vertically or horizontally. if possible, align each IC so that pin #1 is in the same place for each part, say, on the top ( if horizontal ) and/or left sides ( if vertical ). 83 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Design Rule Check (DRC) Firstly, set the rules for PCB layout. Examples of what can be set with a DRC: ◦ Circuit connectivity. It checks that every track on board matches the connectivity of schematic. ◦ Electrical clearance. Can check the clearance between tracks, pads, and components. ◦ Manufacturing tolerances like min/max hole sizes, track widths. A complete DRC is performed again after finishing PCB. 84 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Design Rule Check (DRC) (Con.) The default is 8 mil. Since 1 inch is 25.4mm and 1mil is 1/1000 inches, so 8mil is about 0.2mm. 40mil is about 1mm. Normally, we set it to be higher, around 16-20mil. 85 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software AUTOROUTE – connecting the parts Next, click Autorouter icon will appear. and a window Make sure your Autorouter is setup as shown 86 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Autorouting on the Board In EAGLE, a pattern is drawn using 2 layers which are component side and wiring side. The blue line is the wiring on the wiring side and the red line is wiring on the component side. 87 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software RIP - up If you don’t like the design of your PCB or if there is an error, need to re-route. Click the RipUp icon basically to cancelled PCB connections. Once clicked that, go to and a window will popped out. Click Yes Once done, rearrange the parts again, Ratsnest and Autoroute until not satisfied with PCB design. 88 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Before & After The PCB route is marked in blue 89 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Customizing the Board Since we use one sided PCB, change the red line (1top) to blue (16 bottom) without violating the board/circuit consistency. Use right click on the red line. 90 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Customizing the Board (Con.) To see exactly how the PCB board would look like, click the display icon and highlight these portions only. 91 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Before & After 92 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Other responsibilities Select the frame and move it so that it fits nicely with PCB layout. Finally, print out the PCB layout on the transparency. 93 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Customizing the board (Con.) The size of the PCB can be seen by click Info and click the frame line (length in inch). If necessary adjust the size using Move to drag the frame line. 94 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Printing the Layout File >> Export •Browse and write a filename, for example, rectifier. •Open using Paint and then print. 95 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Circuit is Framed The white lines will be the conducting lines and nodes You can add ‘copper text’ by clicking the icon. 96 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Prototype Circuit 555 timer IC. One 1N914 "switching" diode. Two 10 kΩ resistors. One 100 µF capacitor . 4027 dual J-K flip-flop. Ten-segment LED. Three 470 Ω resistors. One 6 volt battery. 97 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Pin-diagram of 555 & JK Flip-Flop (4027) 1 8 2 7 3 6 4 5 98 Circuit Design Using EAGLE Software Printing the Mask Pattern At the board, the component side pattern, the wiring side pattern, the shape of the parts and the name of the parts are drawn together. When doing print in this condition, all of them have been printed. So, it is necessary to set to print only a necessary part; the bottom copper for 1 sided PCB. Set at least tPlace, tDocu, tNames, tValues, tOrigin to OFF, set other display as necessary. And set the print setting also as below. 99 100