Types of Sentences
advertisement

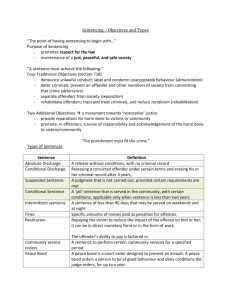
Sentencing Unit 2 Chapter 11 Factors influencing sentencing Aggravating Factors are any relevant circumstances, supported by the evidence presented during the trial, that makes the harshest penalty appropriate, in the judgment of the jurors. Mitigating Factors are any evidence presented regarding the defendant's character or the circumstances of the crime, which would cause a juror to vote for a lesser sentence. See page 281, figure 11.2 Traditional Sentences Absolute discharge Conditional discharge Probation Conditional sentence Restitution Fines & Community Service Intermittent Imprisonment Imprisonment or Incarceration Suspension of Privilege Suspended Sentence I. Absolute discharge An absolute discharge = the offender will be regarded as not having been convicted of the offence. The offender cannot be subsequently charged with the offence. (double jeopardy) However, a record is kept of the absolute discharge and can be used against the offender if the offender commits another offence. Record destroyed after one year. II. Conditional discharge Requires the offender to follow certain rules (ie. Curfew, contact, school etc.) for a specified length of time as set out in a probation order. Once the duration of the conditional discharge has passed and the conditions of the probation order have been followed successfully, the discharge becomes absolute. If not followed or new offence committed while on probation, the offender can be convicted of the original offence and sentenced. Q. When or why a conditional or absolute discharge? would be in the best interests of the offender not contrary to the public interest. Offenders excluded from consideration for a conditional or absolute discharge are those convicted of an offence punishable by a minimum term of imprisonment, a term of imprisonment of 14 years or life imprisonment. III. Probation Offenders are released into the community Must follow certain conditions as set out in a probation order. Can not be longer than three years. Offenders who break the conditions of their probation order may be charged with a breach of probation. A breach of probation is punishable by a term of imprisonment of up to two years. Probation: Mandatory conditions All probation orders contain the following : keep the peace and be of good behavior, appear before the court when required to do so by the court, and notify the court or the probation officer in advance of any change of name or address, and promptly notify the court or the probation officer of any change of employment or occupation. Probation: Optional conditions may also contain the following : report to a probation officer by a certain date and thereafter as directed by the probation officer, remain within the jurisdiction of the court unless written permission to go outside of that jurisdiction is obtained from the court or the probation officer, abstain from alcohol or drug use, abstain from owning, possessing or carrying a weapon, provide for the support or care of dependants, perform up to 240 hours of community service over a period not exceeding one year, participate in a treatment program, and comply with any other reasonable conditions set by the court. IV. Conditional sentence A prison sentence that is served in the community. Must follow a set of rules imposed by the court for a specific length of time. The prison sentence is 'suspended' as long as the offender abides by the rules imposed by the court. Closely supervised by probation officers. An alternative to incarceration for those offenders who would have been given a jail sentence of less than 2 years and who the court is satisfied will not pose a threat to public safety. V. Restitution payment made by an offender to the victim to cover expenses resulting from the crime, such as property loss or damage or personal injury. Restitution is also available to persons acting in good faith who unknowingly become victims of criminal activity. For example, a person may unknowingly purchase stolen property which is later confiscated by police. Equal to the replacement value of the property. Restitution: How much, for what? Equal to the replacement value of the property. May cover medical bills and lost income. Victims are responsible for providing documentation of expenses incurred to the court. Crime victims can make an application to the court for restitution. Restitution orders can be enforced by the civil courts. VI. Fines & Community Service A fine is the most frequently used sentencing option in Canada. 45% of convicted adult offenders in Canada are fined!! Imposed if the court is satisfied that the offender is able to pay the fine or work it off. For summary conviction offences, the maximum fine is $2000. For indictable offences, there is no limit! A victim fine surcharge…an additional payment of up to 15% of the fine. Ensuring payment of fines!! Sets out the amount of the fine, the way the fine is to be paid and the time by which the fine must be paid. Governments can refuse to issue or renew permits or licenses until the fine is paid. The payment of fines can be enforced through the civil courts. Offenders may work off their fines. (community service such as snow shoveling, cleaning up the park etc.) If an offender, without reasonable excuse, refuses to pay his/her fine or work it off within the time allotted, the offender will have to serve a term of imprisonment. VII. Intermittent Imprisonment A term of imprisonment for ninety days or less, judge can order that the sentence be served intermittently. (CCC) For example, the court may direct that the offender serve his/her prison sentence on weekends. WHY? Work, families, non-violent, dependants, etc.. When the offender is not in custody, the offender must comply with the conditions set out in a probation order. VIII. Imprisonment or Incarceration The most serious sentencing option available in Canada. Intended as a last resort to be used only where less restrictive alternatives are inappropriate. For summary conviction offences, the maximum term is six months. Some offences carry minimum incarceration terms (Ie. a second conviction for impaired driving.) VIII. Imprisonment or Incarceration The most serious penalty that can be imposed is life imprisonment. Life imprisonment is the mandatory penalty for first and second degree murder. Terms of less than two years = serve in provincial prisons. Sentences of two years or more are served in federal penitentiaries. IX. Suspension of Privilege Driver’s licence may be suspended for certain driving offences and must be suspended for impaired driving and driving while prohibited. An offender must/may be prohibited from owning or being in possession of a firearm. X. Suspended Sentence A sentence passed or given but NOT carried out. Offender MUST meet certain conditions. Only for crimes with no minimum sentence. Usually for first time offenders or minor offences. Knowledge of sentence “hanging overhead” is enough of a deterrence. Offender still has a criminal record! if the person is convicted of another offence or does not follow imposed conditions, then the person may be sentenced for the original offence.