Buddhism
advertisement

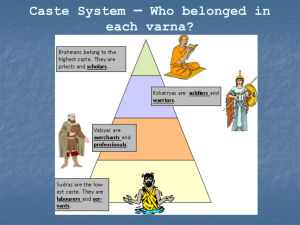
• 10/10 Focus: – Buddhism teaches that people can escape the suffering of the world by following the teachings of the Buddha • Do Now: – Describe the ultimate goal of Hinduism – How might the concept of reincarnation control people’s social behavior? • 10/14 Focus: – Buddhism developed in India but later spread into other areas, such as China. • Important Terms: – Enlightenment, Nirvana, 4 noble Truths, Eightfold Path • Do Now: – What judgment would someone who practiced Hinduism make about the past life of an untouchable? Buddhism Buddhism • Developed in India – Spread to other parts of Asia • Approx. 2,500 years old • Founded by Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha) Siddhartha Gautama • Founder of Buddhism • Born a Hindu prince in N.E. India – Nepal today – Approx. 500 BC • Lived a sheltered life in great luxury • At the age of 29 he became of aware of the hardships in life Siddhartha Gautama • Leaves his kingdom to seek enlightenment and source of suffering in the world • Lives an ascetic life for 6 years – Rejected all material things; begged for food; lived in the forest – Studies with gurus and monks – Rejects this approach and goes on his own • Sits under the Bodhi tree and meditates – Becomes enlightened – The Buddha • “The Enlightened One” The Four Noble Truths • All Life is Suffering – Buddha discovered this when he left his sheltered world and saw death and suffering in others The Four Noble Truths • Suffering is caused by self centered desire and attachment for things that are illusions The Four Noble Truths • The way to eliminate suffering is to eliminate desire The Four Noble Truths • Desire can be overcome by following the Eightfold Path – “The Middle Way” – Moderation in all things The Eightfold Path • Series of steps that lead to enlightenment and Nirvana • Nirvana – Union with the universe – Release from the cycle of reincarnation The Eightfold Path • Right Understanding • Right livelihood • Right intention • Right effort • Right speech • Right mindfulness • Right Action • Right Concentration – Accepting the reality of the four noble truths – Rid yourself of qualities you know are wrong or immoral – Avoiding lies, boasts, hurtful words – Treating others fairly – Avoiding jobs that bring harm to others – Try to abandon wrong and harmful thoughts, words, and actions – Awareness of the world around you – Ignoring temptation and discomfort during meditation • Mandala Types of Buddhism • Theravada – The best way to achieve nirvana is to become a monk and devote your life to mediation – “The small vehicle” – Southern Asia • Mahayana – – – – Not necessary to be a monk or nun Northern Asia and Japan “The Great Vehicle” Bodhisattvas • People who have found enlightenment • Tibetan Buddhism – Mix of Theravada and Mahayana – Led by the Dali Lama • 10/15 Focus: – In Buddhism, the Eightfold Path provides a way to reach nirvana. – The Eightfold Path is also known as the “middle way”. • Do Now: – Identify one of the Four Noble Truths of Buddhism. Buddhism and Hinduism Similarities • Karma • Dharma • Reincarnation Differences • Buddhists don’t accept Hindu Gods, priests, and rituals • Buddhism rejects the caste system – " Birth does not make one a priest or an outcaste. Behavior makes one either a priest or an outcaste". • Goal of Buddhism is nirvana • Goal of Hinduism is moksha Closure • What is the series of steps that Buddhists believe lead to enlightenment? • Why is the referred to as the “middle way”?