Introduction To Financial Statements
advertisement

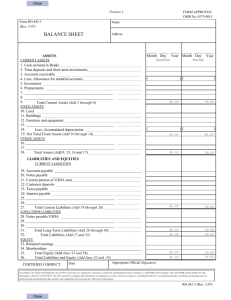
Introduction To Financial Statements Financial Statement • Financial Statements are the statements which show the financial performance and financial position of the business. It includes Trading Account, Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet. • Trading Account- Trading Account shows gross profit earned or gross loss incurred. It is credited with sales, other direct incomes and closing stock. It is debited by direct expenses, i.e., opening stock, purchases, carriage inwards, etc. • Profit and Loss Account- Profit and Loss Account shows net profit earned or net loss incurred. It is credited with gross profit and other incomes and debited with indirect expenses. The difference between the totals of two sides is either net profit or net loss. • Balance Sheet- Balance Sheet shows the financial position of the business. It is a statement to which balances of assets, liabilities and capital accounts are transferred. Expenditure • Capital Expenditure- Capital Expenditure is that expenditure which gives benefit of enduring nature, i.e., the benefit of which extends to a period or periods beyond the accounting period • Revenue Expenditure- Revenue Expenditure is that expenditure the benefit of which is exhausted within the accounting period. • Deferred Revenue Expenditure - Deferred Revenue Expenditure is expense or loss incurred by the firm which are written off in more than one accounting period. They are categorised as Fictitious Assets. Receipts • Capital Receipts- Capital Receipts are those receipts which are not received in the normal course of business, such as capital introduced, loan received, etc. • Revenue Receipts- Revenue Receipts are those receipts which are received in the normal course of business, such as revenue from sale of goods and services. • Grouping- Grouping means placing items of one nature under a common head. • Marshalling- Marshalling is arranging the assets and liabilities in a particular order, i.e in order of liquidity or permanance. • Contingent Liability- Contingent Liability is a liability that becomes payable on the happening of an event and not otherwise Adjustements • Adjusted Entry- It is an entry passed in the books of accounts to give effect to transactions that should have been recorded in the books of accounts but are not recorded. • Closing Stock- It is the value of stock in hand at the end of the accounting year. It is valued at cost or net realisable value (market value) whichever is less. • Outstanding Expenses- They are expenses incurred during the year benefit of which is consumed or exhausted in the same year but have not been paid. For example, salary payable for the month of March is provided not being paid. • Prepaid Unexpired Expenses- They are the expenses that have been paid but the benefit of which is not consumed or exhausted during the year. • Accrued Income- It is the income which has been earned but not received. • Income Receive in advance or unearned income- It is the income which has not been earned but received during the accounting year. • Depreciation- It is the fall in value of fixed asset due to usage, afflux of time, obsolescence or accident. • Bad Debts- It is the debt that has become irrecoverable. • Bad Debts Recovered- It is the debt which had been earlier written off as bad debt and has been recovered. • Doubtful Debts- Debts which are doubtful of recovery, i.e., recovery is not certain. • Provision for doubtful Debts;- It is the amount set aside out of present debts to meet bad debts in future. • Provision for doubtful Debtors- It is the amount set aside out of present debts to allow discount to debtors in future. Classification of Liabilities • Non-Current Liabilities: These liabilities are those liabilities which are not payable by the business in the next year. They mainly include long-term loans, borrowings or debentures, etc. Funds from this source are used for acquiring fixed assets. • Current Liabilities: These liabilities are payable by the business within a year. Examples are trade creditors, bills payable, expenses outstanding, bank overdraft, etc. • Owner's Funds: The amount owing to the proprietors as capital is a class by itself. It includes undistributed profits and reserves besides capital. It is equal to the net assets of the business and is defined as the difference between assets and liabilities. • Contingent Liabilities: Contingent Liability is a liability that becomes payable on the happening of an event. In case, the event does not happen, no amount is payable. Such liabilities are not accounted and are not shown in the Balance Sheet; they are disclosed by way of a note. Examples of contingent liabilities are: • 1. Liabilities in Respect of Bills Discounted: If the firm got its bills receivable discounted with bank, the primary liability will be that of the acceptor. If the acceptor does not pay, then it becomes firm's liability. • 2. Guarantee for Loan: If the firm has stood surety for a loan, it will be liable to pay the amount if the other person fails to meet his obligation. • Disputed Claims: If some other party has lodged a claim against the firm, the firm will be liable to pay if the claim succeeds. INCOME STATEMENT • Income Statement is a summary of accounts that affects the profit or loss of an enterprise. Many accounts shown in the Trial Balance relate to expenditure or income. These accounts either increase or decrease the profit. Accounts that increase the profit are shown on one (credit) side while accounts that decrease the profit, i.e., losses and expenses are shown on the other (debit) side. The statement so prepared is known as an Income Statement. An Income Statement has two parts, namely, • 1. Trading Account: It shows gross profit or gross loss for the accounting period; and • 3. Profit and Loss Account: It shows net profit or net loss for the accounting period. METHODS OF PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS • Horizontal Form: Under this form of presentation, the financial statements are presented in "T" form, which we have already discussed in this Chapter. The final accounts in the above illustrations have been prepared in horizontal form. • Vertical Form: Under this form of presentation, the financial statements are presented in a single column statement in a purposeful sequence.