Kepler/Newton Study Guide Johannes Kepler
advertisement

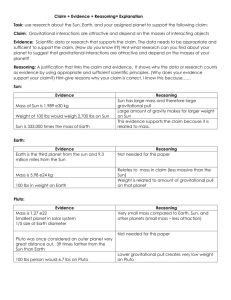
Kepler/Newton Study Guide Johannes Kepler - Laws of Planetary Motion Law 1. Planets travel in ___elliptical orbits________________. a. Perihelion - _____points where a planet is closest to sun______ b. Aphelion - ____points where a planets is farthest from sun_________________ c. Draw Fig. 22.10. Draw in the earth and label Earth at its perihelion and aphelion. Law 2. Planets sweep out equal areas in _______equal amounts of time_______________________. The speed of a planet is faster at its __________perihelion______________. Law 3. Harmonic Law - P2 = D3 P = Period - time for planet to _____orbit the sun (Earth years)______________________________ D = __distance from the sun (astronomical units)____________________________________ This means that: a. The farther a planet is from the sun, ___the longer the orbital period___________________ b. Astronomers could predict the ______distance/period given the other piece of info________________ Sir Isaac Newton - Universal Law of Gravitation 1. The force of gravity between any two objects is: a. Directly related to the ____mass of 2 objects____________________. b. Inversely related to the square of the distance _______between the center of gravity of the two objects ________________ 2. So.... what is the relationship between mass of objects and the force of gravity? Bigger mass, larger force of gravity 3. What is the relationship between distance between objects and the force of gravity? Change in force is = 1/distance, larger distance causes a decrease in force 4. Why does the speed of a planet increase as a planet approaches perihelion? The gravitational pull of the sun on the planet is greater when it is closer to the sun. 5. Why does Mercury have a greater speed than Pluto? Mercury is closer to the sun than Pluto 6. Define Escape Velocity: Minimum velocity needed to escape the gravitation pull of a planet, moon, or other body 7. Compare the escape velocity of Mars to Jupiter. Escape velocity of Mars is less than Jupiter because Jupiter is much more massive than Mar. 8. Name some phenomena caused by gravity. -tides caused by the gravitation pull of the moon on Earth -long orbits of comets KEPLER/NEWTON EXERCISES Kepler’s Law 2: Calculate the YEAR of the following planets P2 = D3 A. Mercury ‘s (Period)2 = Mercury’s (Distance)3 Mercury ‘s (Period)2 = (0.4 AU)3 Mercury ‘s (Period)2 = ___0.064_______________ *take the square root of both sides Mercury ‘s Period = ______0.2529 years____________ B. Saturn‘s (Period)2 = Saturn’s (Distance)3 Saturn‘s (Period)2 = (__9.5_______)3 Saturn‘s (Period)2 = ____857.375______________*take the square root of both sides Saturn‘s Period = _____29.28 years_____________ C. Pluto‘s (Period)2 = Pluto’s (Distance)3 Pluto‘s (Period)2 = (___39.4______)3 Pluto‘s (Period)2 = ___61162.984_______________*take the square root of both sides Pluto‘s Period = __247.3 years________________ Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation: Calculate the Gravitational Force A. If Mass increases, then Grav. Force ___increases_____________ directly. If Mass doubles, then gravitational force ______doubles_________. If Mass triples, then gravitational force _____triples__________. If Mass increases by half, then gravitational force _ increases by half______________. B. If Distance increases, then Grav. Force_____decreases_____________ indirectly. If Distance doubles, then Gravitational Force _______decreases by 1/4________. If Distance triples, then Gravitational Force ____decreases by 1/9___________. If Distance increases by four, then Gravitational Force ___decreases by 1/16____________.