Exercise No
advertisement

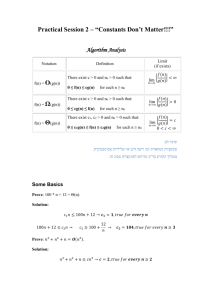
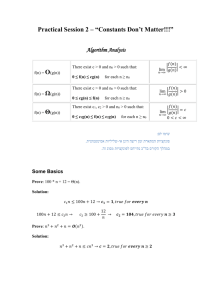
יסודות מבני נתונים – סמסטר א' – תשע"א )AVL( – עצי חיפוש בינארי מאוזנים6 תרגול Height-Balance Property For every internal node v of a tree T, the height of the children nodes of v differ by at most 1. AVL Tree Any binary search tree that satisfies the Height-Balance property. Thus, it has (log n) height, which implies (log n) worst case search and insertion times. AVL Interface The AVL interface supports the following operations in O(log n): insert, search, delete, maximum, minimum, predecessor and successor. AVL Height Lemma: The height of an AVL tree storing n keys is O(logn) Example of AVL: 44 4 2 17 78 1 3 2 32 88 50 1 48 62 1 1 Question 1 Insert the following sequence of elements into an AVL tree, starting with an empty tree: 10, 20, 15, 25, 30, 16, 18, 19. יסודות מבני נתונים – סמסטר א' – תשע"א Solution: Delete 30 in the AVL tree that you got. K2 K3 K1 K1 K2 Double rotation Question 2 Join (T1, x, T2) T1 and T2 are AVL trees (with h field in every node). x is an element and T1 < x < T2 Efficiently merge T1, x and T2 into an AVL tree. K3 יסודות מבני נתונים – סמסטר א' – תשע"א Solution: Let n1 and n2 be the number of nodes in T1 and T2 respectively. 1. In case height(T1) = height(T2) return the tree: 2. Without loss of generality we will examine the case where height(T1) > height(T2): o Find in O(log n1 – log n2) the right most sub-tree of T1 which has a height of height(T2). We will refer to this sub-tree as Ty, as y is the root. o Replace y by the following: x y T1 Ty y Ty o T2 Follow the path from x to the root of T1 and rotate the sub-tree (if needed) as the sub-tree gained one to its height, just like in insertion. Complexity of searching node y = O(|height(T1) - height(T2)|) = O( log n1-log n2 ) Complexity of the merge itself = O(|height(T1) - height(T2)|) = O( log n1-log n2 ) Total time complexity: O(|height(T1) - height(T2)|) = O( log n1-log n2 ) Question 3 Given an AVL tree T, is it always possible to build the same tree by a sequence of BST-insert and delete operations (with no rotations)? יסודות מבני נתונים – סמסטר א' – תשע"א Solution Yes, by inserting the nodes according to BFS (Breadth first search) traversal. rebuildAVL(AVL T) queue Q ← BFS(T) newT ← new BST while( ! Q.isEmpty()) n ← Q.dequque() newT.insert(n) Question 4 A cosmetician wants to represent a list of her clients’ records (by their ID). For each client we would like to mark whether he is a man or she is a woman. Suggest a data structure that supports the following operations in O(log n) time in the worst case, where n is the number of men and women in the data structure when the operation is executed: 1. Insert(k,c) - Insert a new client c with id = k to the data structure, at first mark the client as a woman. 2. Update(k) – Update client with ID = k to be a man. 3. FindDiff(k) – Find the difference between the number of women and the number of men (#of women - #of men) among all the clients with ID smaller than k. Solution: The data structure is an AVL tree T where each node x represents a person and has the following fields (in addition to the regular fields of a node in an AVL tree): 1. x.ID – ID number (the search key for T) 2. x.client – the client record 3. x.gender – 1 (woman) or 0 (man) 4. x.women- the number of all women in the sub tree rooted at x (including x). 5. x.men - the number of all men in the sub tree rooted at x (including x). Insert (k, c) create new node x x.ID = k x.client = c x.gender = 1 //(woman) x.women = 1 // (a new node is always inserted as a leaf) x.men = 0 AVL-Insert(x) for every node v in the path from x to the root do: v.women = v.women + 1 Time complexity : O(logn) O(1) O(logn) יסודות מבני נתונים – סמסטר א' – תשע"א )O(logn )Update (k ) x = AVL-search(k) // O(logn if x.gender = 1 )x.gender = 0 (man )O(1 x.women = x.women – 1 x.men = x.men + 1 for every node v in the path from x to the root do: v.women = v.women – 1 v.men = v.men +1 )Time complexity : O(logn )O(logn )FindDiff (k sum-m = 0 )O(1 sum-w = 0 search for a node with ID = k: )while (T != NULL ) if (T.ID < k sum-m += T.left.men sum-w += T.left.women )if (T.gender = 1 sum-w = sum-w + 1 else sum-m = sum-m + 1 T = T.right else T = T.left | return |sum-w – sum-m )Time complexity : O(logn שאלה ( 5אם יישאר זמן בתרגול): רוצים לבנות מבנה נתונים המתחזק אוסף 𝐒 של מפתחות ומורכב מ 𝒎 -קבוצות 𝒊𝑺 𝒎 ≤ 𝒊 ≤ 𝟏 ,כל קבוצה בת לכל היותר 𝒏 מפתחות .ניתן להניח שכל המפתחות שונים זה מזה( .ראו דוגמה). על המבנה לתמוך בכל הפעולות הבאות בזמנים הנקובים .כמות הזיכרון המותרת )𝒏𝒎(𝑶. תיאור פעולה ) Insert(i,kהכנס את מפתח 𝒌 לתוך 𝒊𝑺 זמן )𝑚 𝑂(log 𝑛 + log ) Delete(i,kמחק את המפתח 𝒌 מקבוצה 𝒊𝑺 (ניתן להניח כי 𝒌 שייך לקבוצה 𝒊𝑺) )O(1 )( MinMaxמצא את המפתח המינימלי מבין המפתחות המקסימליים 𝒎𝑴 𝑴𝟏 , … ,של 𝒎𝑺 𝑺𝟏 , … , (מצויינים ב * בדוגמה למטה) )( GlobalMaxמצא את המפתח המקסימלי מבין כל מפתחות )O(1 𝑺. )𝑚 𝑂(log 𝑛 + log ראו דוגמה. יסודות מבני נתונים – סמסטר א' – תשע"א דוגמה :אם לאחר פעולות הכנסה ומחיקה הגענו למצב הזה: 𝑆1 𝑆3 *8 6 3 𝑆2 *5 *7 2 4 1 MinMaxיחזיר את המפתח 5שהוא המפתח המינימלי מבין כל המפתחות המקסמלים ( 7 ,5ו - 8מסומנים ב *). GlobalMaxיחזיר את המפתח ,8שערכו הוא הגדול ביותר מהמפתחות בכל מבנה הנתונים. פתרון: תאור מבנה הנתונים: מבנה הנתונים יכלול את הרכיבים הבאים: עץ Tsets AVLהממוין עפ"י האינדקסים של mהקבוצות. עבור ,1 ≤ i ≤ mמכל קודקוד בעל אינדקס iבעץ Tsetsיהיה מצביע לעץ TSi AVLהמחזיק את איברי הקבוצה .Si עץ AVLנוסף Tmaxהמכיל רק את האיברים המקסימאליים בכל קבוצה. שני משתני עזר GMaxו – MMaxשיחזיקו בכל רגע נתון את הערך המקסימאלי והמינימאלי של העץ .Tmax תיאור הפעולות: ) – Insert(i,kנמצא את הקודקוד עם האינדקס iבעץ ,Tsetsניגש בעזרת המצביע שבקודקוד זה לעץ ,TSiנכניס את האיבר kלעץ .TSiאם האיבר kהוא המקסימום החדש של הקבוצה ,Siנמחק מהעץ Tmaxאת המקסימום הישן של הקבוצה Siונכניס את המקסימום החדש ,נעדכן את GMaxו – MMaxבמידת הצורך. הפעולות על העצים Tsetsו Tmax -ועדכון המצביעים ייקחו ).O(log m הפעולות על העץ TSiייקחו ).O(log n בסה"כ נקבל זמן ריצה של ).O(log m +log n ) – Delete(iבדומה להכנסה ,נמצא את הקודקוד עם האינדקס iבעץ ,Tsetsניגש בעזרת המצביע שבקודקוד זה לעץ ,TSiנמצא את kבעץ TSiונמחק אותו מעץ זה .אם מחקנו את המקסימום של הקבוצה ,Siנמצא את המקסימום החדש של קבוצה זו .נמחק מהעץ Tmaxאת המקסימום הישן של Siונכניס את המקסימום החדש ,נעדכן את GMaxו – MMaxבמידת הצורך. הפעולות על העצים Tsetsו Tmax -ועדכון המצביעים ייקחו לכל היותר ).O(log m הפעולות על העץ TSiייקחו ).O(log n בסה"כ נקבל זמן ריצה של ).O(log m +log n )( – MinMaxנחזיר את הערך שבמשתנה .GMax )( – GlobalMaxנחזיר את הערך שבמשתנה .MMax