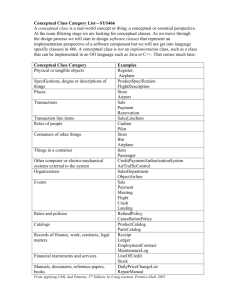
Conceptual class
advertisement

Domain Model: Visualizing concepts Larman chapter 10 Larman chapter 10 1 Artifact influence emphasizing the Domain Model Sample UP Artifacts Partial artifacts, refined in each iteration. Domain Model Business Modeling * * terms, concepts attributes, associations state changes in domain objects, attributes, associations Use-Case Model elaboration of some terms in the domain model :System foo( x ) Requirements Glossary ... bar( y ) text use cases use case diagrams system sequence diagrams system operation contracts Design Model software classes in the domain layer of the design take inspiration from the names, attributes, and associations in the domain model Design Software Architecture Doc. Software Dev. Plan Project Management Test Plan Test Larman chapter 10 Development Case Environment 2 Objectives • Identify conceptual classes related to the current iteration requirements • Create an initial domain model • Distinguish between correct and incorrect attributes • Add specification conceptual classes, when appropriate • Compare and contrast conceptual and implementation views Larman chapter 10 3 Domain Model • The Domain Model is the most important artifact to create during object oriented analysis – (a visual dictionary) • The domain model is a representation of real-world conceptual classes NOT of software components • The domain model is used as a source of inspiration for designing software objects. Larman chapter 10 4 Domain Model • A domain model is illutrated with a set of class diagrams (in which no operations are defined) • It may show: – Domain objects or conceptual classes – Associations between conceptual classes – Attributes of conceptual classes Larman chapter 10 5 Domain Model Sales LineItem concept or domain object 1 0..1 quantity Item Records-sale-of * 1..* association Stocked-in Contained-in 1 1 Sale attributes date time Store address name 1 1 1 Houses Paid-by 1 Payment 1..* Register Captured-on 1 amount Larman chapter 10 6 Domain Model Sale it is a not a picture of a software class date time oid v a oid v a visualization of a realworld concept in the domain of interest SalesDatabase software artifact; not part of domain model Sale date time software class; not part of domain model print() Larman chapter 10 7 Domain Model conceptual classes • Informally, a conceptual class is an idea, event, thing, object, person …… • Formally, a conceptual class is described by its: – Symbol – words or images representing a conceptual class – Intension – the definition of a conceptual class – Extension – the set of examples to which the conceptual class applies Larman chapter 10 8 Domain Model conceptual classes concept's symbol Sale date time "A sale represents the event of a purchase transaction. It has a date and time." concept's intension sale-1 sale-2 sale-3 concept's extension sale-4 Larman chapter 10 9 Domain Model • The primary analysis task is to identify different concepts in the problem domain and document the result in a domain model • Conceptual classes in the Sale Domain: Store Larman chapter 10 Register Sale 10 Domain Model guideline • It is better to overspecify a domain model with lots of fine-grained conceptual classes than to underspecify it ! • A Domain Model is not absolutely correct or wrong, but more or less useful, it is a tool of communication Larman chapter 10 11 Domain Model strategies to identify conceptual classes • Use a conceptual class category list (p 134-135) list of candidate conceptual classes • Identify noun phrases based upon fully dressed use cases (p 135-136) • (Use analysis patterns) Larman chapter 10 12 Domain Model Candidate conceptual classes for the Sales Domain: • • • • • • Register Item Store Sale Payment ProductCatalog Larman chapter 10 • • • • • • ProductSpecification SalesLineItem Cashier Customer Manager Receipt??? 13 Domain Model Candidate conceptual classes for the Sales Domain: • Receipt??? – Report of a sale – duplicates information found elsewhere exclude receipt – Special role in terms of business rules (the right to return bought items) include it (since returns are not considered in this iteration, receipt is excluded) Larman chapter 10 14 Domain Model Modeling guidelines 1. List the candidate conceptual classes using CCC-List and noun phrase identification technique related to the current requirements under consideration 2. Draw them in a domain model 3. Add the associations necessary to record relationships for which there is a need to preserve some memory 4. Add the attributes necessary to fulfill the information requirements Larman chapter 10 15 Domain Model ’the mapmaker’ • Use the existing names of the territory • Exclude irrelevant features • Do not add things that are not there Use the Domain Vocabulaty strategy Larman chapter 10 16 Domain Model common mistakes • If we do not think of some conceptual class X as a number or text in the real world, X is probably an conceptual class, not an attribute Sale Sale Store or... ? store phoneNumber Flight Flight Airport or... ? destination Larman chapter 10 name 17 Domain Model similar conceptual classes similar concepts with different names POST or? Register 1 Records Records * Sale Larman chapter 10 1 * Sale 18 Domain Model ’specification conceptual classes’ Item Worse description price serial number itemID ProductSpecification description price itemID Larman chapter 10 Item Describes 1 * Better serial number 19 Domain Model ’specification conceptual classes’ Flight date number time Airport Flies-to Worse 1 * Flight FlightDescription Described-by date time * name 1 Better number * Describes-flights-to 1 Airport name Larman chapter 10 20 UML Notation multiple perspectives • Essential or conceptual perspective • Specification perspective • Implementation perspective Sale Payment 1 1 Pays-for Raw UML class diagram notation used in an essential model visualizing real-world concepts. date time amount UP Domain Model UP Design Model Sale Payment amount: Money getBalance(): Money ... Larman chapter 10 1 Pays-for 1 date: Date startTime: Time getTotal(): Money ... Raw UML class diagram notation used in a specification model visualizing software components. 21 UML Notation terminology • Conceptual class – real world thing/concept • Software class – a class representing a specification or implementation perspective of a software component • Design class – a member of the UP Design Model – synonym for sw class • Implementation class – a class implemented in an objectoriented language • Class – the general term representing either a real world thing or a software thing Larman chapter 10 22 Domain Model representational gap UP Domain Model Stakeholder's view of the noteworthy concepts in the domain. A Payment in the Domain Model is a concept, but a Payment in the Design Model is a software class. They are not the same thing, but the former inspired the naming and definition of the latter. Sale Payment 1 1 Pays-for date time amount inspires objects and names in This reduces the representational gap. Sale This is one of the big ideas in object technology. Payment amount: Money getBalance(): Money 1 Pays-for 1 date: Date startTime: Time getTotal(): Money ... UP Design Model The object-oriented developer has taken inspiration from the real world domain in creating software classes. Therefore, the representational gap between how stakeholders conceive the domain, and its representation in software, has been lowered. Larman chapter 10 23 The NextGen POS Domain Model Register Item Store Sale Sales LineItem Cashier Customer Manager Payment Product Catalog Product Specification Larman chapter 10 24 Artifact influence emphasizing the Domain Model Sample UP Artifacts Partial artifacts, refined in each iteration. Domain Model Business Modeling * * terms, concepts attributes, associations state changes in domain objects, attributes, associations Use-Case Model elaboration of some terms in the domain model :System foo( x ) Requirements Glossary ... bar( y ) text use cases use case diagrams system sequence diagrams system operation contracts Design Model software classes in the domain layer of the design take inspiration from the names, attributes, and associations in the domain model Design Software Architecture Doc. Software Dev. Plan Project Management Test Plan Test Larman chapter 10 Development Case Environment 25