Exploring Earth's Surface
advertisement

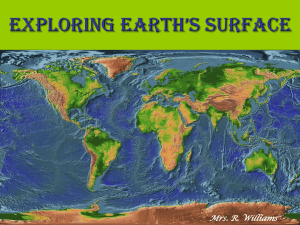
Exploring Earth’s surfacE Topography Topography is the shape of the land. An area’s topography may be flat, sloping, hilly, or mountainous. The topography of an area includes the area’s elevation, relief, and landforms. A topographic map is a map showing the surface features of an area. Elevation The height above sea level of a point on Earth’s surface is its elevation. elevate: to raise or lift something to a higher position. Relief The difference in elevation between the highest and lowest parts of an area is its relief. Example: The difference between these two points would be the relief of this area Landforms A landform is a feature of topography, such as a hill or valley, formed by the processes that shape Earth’s surfaces. Different landforms have different combinations of elevation and relief. Types of Landforms Landforms vary greatly in size and shape-from level plains to high mountain peaks. We will be learning about three main types of land forms: mountains, plains, and plateaus. Mountains A mountain is a landform with high elevation and high relief. They usually occur as part of a mountain range. A mountain range is a group of mountains that are closely related in shape, structure, and age. Mount Everest K2 (Mount Godwin Austen) Mount McKinley Plains A plain is a landform made up of nearly flat or gently rolling land with low relief. A plain that lies along a seacoast is called a coastal plain. A plain that lies away from the coast is called an interior plain. North Dakota Lower Coastal Plain of Georgia Upper Coastal Plain of Georgia Plateaus A landform that has high elevation and a more or less level surface is called a plateau. A plateau is rarely perfectly smooth on top. Streams and rivers may cut into the plateau’s surface. Columbia Plateau in Washington Colorado Plateau Balochistan Plateau of Pakistan Landform Regions A large area of land where the topography is made up mainly of one type of landform is called landform region. Models of Earth Maps and Globes Maps and globes show the shape, size, and position of Earth’s surface features. A map is a flat model of all or part of Earth’s surface as seen from above. A globe is a sphere that represents Earth’s entire surface. A political map shows boundaries. Maps and Globes A map’s scale relates distance on a map to a distance on Earth’s surface. Scale is often given as a ratio. Mapmakers use shapes and pictures called symbols to stand for features on Earth’s surface. A map’s key, or legend, is a list of all the symbols used on the map with an explanation of their meaning. Earth’s Grid To find a point on Earth’s surface, you need a grid. A grid uses lines to make rows and columns on a map. The rows go from side to side and the columns go up and down. Most maps and globes show a grid. To locate positions on Earth’s surface, scientist use units called degrees. A degree (°) is 1/360 of the distance around a circle. Earth’s Grid Halfway between the North and South poles, the equator forms and imaginary line that circles the Earth. The equator divides the Earth in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. A hemisphere is one half of the The Prime Meridian makes sphere that makes up Earth’s a half circle from the North surface. Pole to the South Pole. It passes through Greenwich, England. Places to the east of the Prime Meridian are in the Eastern Hemisphere and places to the west are in the Western Hemisphere. Don’t forget, it is always a good idea to study!!