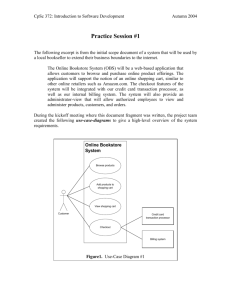
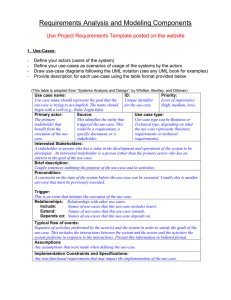
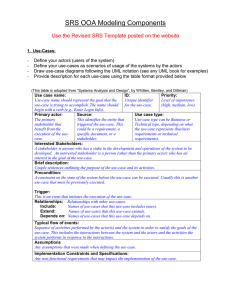
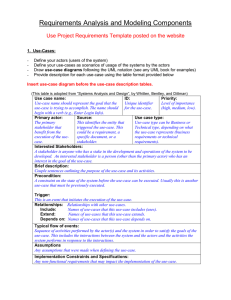
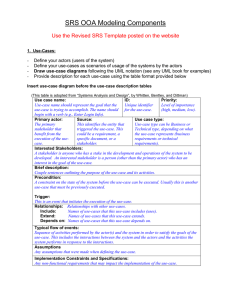
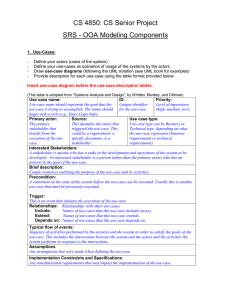
Steps in use case
advertisement
Requirements Functional requirements Use-cases Actors and use cases Use-case diagram Brief notation Prioritization Fully dressed notation What is a use case? A use-case describes a working procedure for a specific actor/user of an IT system. A use-case is used to show the interaction between actor and IT system Functional requirements as use-cases outline, in what way the IT system are going to support the user 2 Good or Bad Use-cases? • Criteria: – Completed; goal fulfilled; coffee break – Small create, read, update and delete tasks are gathered in one description (CRUD) Good or bad? Administration of books Register the title of a book Loan of book Update reservation Delete reservation Check: Are all tasks included? – Are all actor tasks described? – Are critical tasks included? – Can all data be created, read, updated and deleted (CRUD)? 3 What is an actor? An actor is something with behaviour that interacts with the IT system: Person identified as a user role, e.g. cashier, salesman, stock employee Another computer system A device e.g. a temperature sensor Primary actor: Has user goals fulfilled through use-case 4 Use case diagram Use cases from the event table is displayed in a UML use case diagram Use case diagram is a graphic model of the system's functionality and communication with the stakeholders includes: Use cases Actors Associations between use cases and the actor(s) who interact with the use case delimitation 5 Use case diagram for customer - order Small use cases can be assembled in CreateReadUpdateDelete (CRUD) use-cases 6 Description formats for use cases Overall textual descriptions in a short summarized form (customer-facing) Brief: textual description of a happy days scenario Casual: variations of happy days scenario Detailed descriptions of the "expanded" form - fully dressed The steps in the use case and variations thereof are described in detail A graphical representation of the interaction of the use case in a system sequence diagram - SSD (in a later session) All use cases described in brief and / or causal. Only the critical described fully dressed with associated solid state and contracts 7 Use case description, Brief Template for brief description: Use case: Name of the use case Description: An overall but complete description of who initiates the use case, the expected system actions and responses of this that adds value to an actor Input to the system actions retrieved from the event table: Steps in use case 8 Use-case description Casual In addition to the brief form there can be added alternative scenarios in the Causal format Examples of alternative scenarios for the use-case: Register Order: If the goods are sold the system indicates when new products are expected home, so the customer can be informed If the customer wishes to pay immediately ...... ....... 9 Prioritazation af use-cases According UP designing, implementation and testing is done in small chunks through a number of iterations (steps) The highest priority and most complex use-case is analysed, designed and coded in the first iterations (so one must assume that the rest also can be made) The steps in development of use-cases are: 1. 2. 3. Use cases identified and they appear in a UML use-case diagram Then, they are described in brief or casual form. On this basis, use cases are prioritized (based on architecturerelated importance, risks and business value), and then the most important are analysed for the design of prototypes and "fully dressed" descriptions. 10 Use-case description: ”Fully dressed” Detail storyline in use-case in a number of steps (flow of events) consisting of: Actor action<-> System response Add actor, pre- and post-conditions Use essential and black box style Brief- and/or casual descriptions and mock ups are used as the basis for the fully dressed descriptions. 11 Example: Use case: Register Order Flow of events in fully dressed description 1. 2. Use-case starts with a customer inquiry over the telephone to order goods Shop assistant begins a new order the system creates a new order 3. Shop assistant Specifies the ID of the desired products 4. The system returns the item description, price, sub total and running total 5. Shop assistant adds the desired number of items 1. The system adds the items 6. Steps 4-7 are repeated until all items are added 7. Shop assistant specify delivery information 8. The system validates the data and record customer 9. Shop assistant completes order 10. The System saves the order 11. Shop assistant request for an order form and invoice 12. The system prints a confirmation 12