simple cell
advertisement

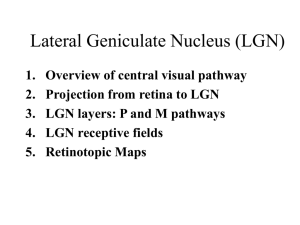
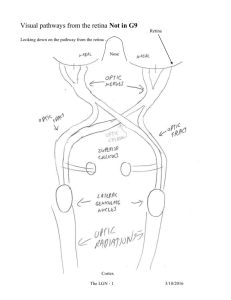
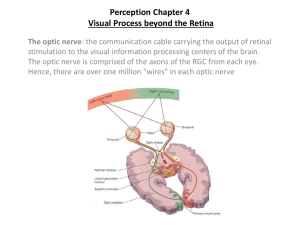
Primary Visual Cortex (V1, area 17, striate cortex) 1. Organization of early visual pathway 2. Circuitry of primary visual cortex a. layering, inputs, outputs b. cell types 3. RF properties of V1 neurons a. orientation selectivity b. simple cell and complex cell 4. Circuitry basis of the RFs 5. Columnar Organization a. orientation columns b. ocular dominance columns c. hypercolumn 6. Horizontal connections Visual pathway from retina to V1 LGN eye V1 A top-down view diagram fixation point left visual field nasal half right visual field left right nasal half temporal half temporal half optic chiasm lateral geniculate nucleus LGN (LGN) V1 V1 axons from nasal retina cross contralateral LGN axons from temporal retina stay ipsilateral LGN left visual field right LGN right V1 right visual field left LGN left V1 Circuitry -- inputs, outputs and layering 1 2/3 4A 4B 4 4C 4C 5 6 M P (LGN) Input LGN layer 4, layer 6 Layer 4 layer 2/3 layer 5 layer 6 Output Layer 2/3, Layer 4B other visual cortical areas Layer 5 superior colliculus Layer 6 LGN two basic morphological types of cells Pyramidal cell Axons Stellate cell Pyramidal cells • large, pyramid shaped cell bodies • project to other areas, also connect to other local neurons • excitatory (glutamate) Non-pyramidal cells • small and stellate shape (spiny stellate or smooth stellate) • local interneurons (smooth) • either excitatory (spiny, with many dendritic spines, glutamate) or inhibitory (smooth, few spines, GABA) Hetergeneity in the interneuron types Morphology Physiology (spiking properties) Biochemistry (neuropeptide contents), Connectivity (dendrite-domain specific innervation of pyramidal cells). David Hubel (left) and Torsten Wiesel V1 cells have orientation selectivity orientation response Response (spikes/sec) Orientation tuning curve 120 80 40 0 0 30 60 90 120 150 Orientation (o) Two cell types based on response property simple cell -- separated ON and OFF regions ON ---- increase its response to light on (bright stimulus) OFF ---- increase its response to light off (dark stimulus) complex cell -- overlapping ON and OFF regions simple cell complex cell position sensitivity position insensitive length summation length summation width summation no width summation orientation sensitive orientation sensitive Simple cell and complex cell simple cell position sensitive (yes) increase response decrease response length summation strong response (no) increase response (yes) little response strong response (no) (yes) Little or no response orientation selectivity (yes) little response width summation complex cell little or no response (yes) (yes) strong response strong response weak response weak response Little or no response Little or no response Circuitry basis of V1 RFs (simple cell) circuitry + + + cortical simple cell LGN cells receptive field Hubel & Wiesel, 1962 LGN cells cortical simple cell 1. Simple cell is built up from many LGN cells 2. These LGN cells have the same center/surround structure 3. The centers of these LGN cells are distributed along a line * you can also add a set of OFF-centered LGN cells, with their centers along the OFF subregion Circuitry basis of V1 RFs (complex cell) circuitry receptive field + + + complex cell complex cell simple cells simple cells 1. Complex cell is built up from many simple cells 2. These simple cells have the same preferred orientation 3. These simple cells have overlapping RFs 4. These simple cells have different arrangement of subregions Columnar Organization--Cells in the same column have similar properties (RF position, orientation preference, ocular dominance) (1) Orientation columns Oblique penetration in V1 --preferred orientation gradually shifts Vertical penetration in V1 --same preferred orientation Afferent pathways from the two eyes right eye nasal temporal left V1 left eye LGN 6 5 C 4 3 2 1 I C I I C Layer 4 R L 2. Ocular dominance (OD) columns in V1 left eye layer 4 . right eye left eye R L R L Rl Lr Rl Lr R L R L Rl Lr Rl Lr right eye ~ 0.5mm Oblique penetration: cells responding to left and right eyes alternately Vertical penetration: cells responding to one eye exclusively or more strongly Definition of Ocular Dominance Groups Eyes Cortical cells 1 contra- 2 3 4 equal 5 6 7 ipsi- groups OD distribution in normal adult V1 (monkey) Number of cells Normal V1 Equal contralateral ipsilateral OD groups Normal adult V1 – Binocular cells are common above & below layer 4), with each eye represented to different degrees Hypercolumn—An ensemble of orientation and ocular dominance (OD) columns in V1, including one set of L and R eye OD columns and a set of orientation columns for lines of all orientations. All cells within the hypercolumn have RFs that cover a similar area in the visual field. Optical imaging of intrinsic light scattering signals reveals pinwheel pattern of orientiation columns Blobs in Layer 2/3 --- Columns (blobs) revealed by cytochrome oxidase staining that are color sensitive --- Cells between the blobs (interblobs) are color insensitive, orientation sensitive Horizontal Connections Cells with similar response properties in different columns (orientation, color) are linked by long-range horizontal connections made by axons of Layer 2/3 C. Gilbert