The Visual System: Color Vision
advertisement

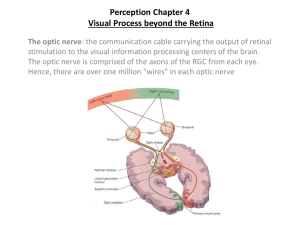
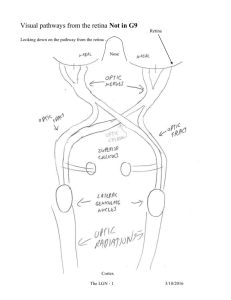
The Visual System: Color Vision Lesson 18 The Trichromatic Theory Young-Helmholtz (1802) 3 types of color receptors Cones Differential sensitivity to light wavelengths red (long) green (medium) blue (short) ~ The Trichromatic Theory Perceived color overall pattern of stimulation Like mixing paint Negative After-image? The Trichromatic Theory? What colors do you see? How can you see colors that weren’t there? Negative After-image Does it fit Trichromatic Theory? ~ Hering Opponent Process Theory Competing theory Center-Surround organization BP, RGC, & LGN Antagonistic for color Red-Green Blue-Yellow Black-White Hering Opponent Process Theory Center- surround antagonistic Each color can be excitatory (+) or inhibitory (-) 12 combinations total ~ Which Theory? Both are correct in retina Photoreceptors: trichromatic Higher levels: Opponent Process BP, RGC, & LGN More complex at cortical level Retinex Theory ~ Retinex Theory Perception of visual stimulus subjective includes context & past experiences color & brightness constancy Color constancy e.g., grass in sun vs. grass in shade perceived as same color green e.g., Rubic’s cube ~ Lateral Geniculate Nucleus 6 layers dorsal ventral 6 1 RFs center-surround Input from each eye monocular 2, 3, 5 from the ipsilateral eye parallel processing ~ LGN: Parallel Processing Parvocellular system layers 3-6 small RFs info from cones color & form Magnocellular system Large RFs layers 1 & 2 info from rods form only, no color ~ Color Processing: Primary Visual Cortex V1 Organization 6 layers Most input Layer 4 1st binocular receptive fields cells get input from both eyes ocular dominance Modular organization Blob cells: color processing Wavelength specific ~ Modular V1 Organization L 2&3 4 LGN 5&6 B L O B R L Blob cells & Color Perception Same color perceived differently Double Opponent Process Cells Different from RGC & LGN center-surround Center: red excitation green inhibition Surround: red inhibition green excitation ~ Double-Opponent Process Blob Cells R-G+ R-G+ R+G- R+G- Higher Level Color Processing V1 V2 V4 V4 in medial occipital cortex V4 damage disrupts color constancy achromatopsia unilateral – 1 visual field bilateral – no color perception ~