MANAGING
INFORMATION
TECHNOLOGY
FIFTH EDITION
CHAPTER 11
METHODOLOGIES
FOR PURCHASED
SOFTWARE PACKAGES
E. Wainright Martin Carol V. Brown Daniel W. DeHayes
Jeffrey A. Hoffer William C. Perkins
THE MAKE-OR-BUY DECISION
Decision should be made jointly by business
managers and IS professionals
Advantages of purchasing:
Cost savings
Faster speed of implementation
Disadvantages of purchasing:
Seldom exactly fits a company’s needs
Often forces trade-offs
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 2
Page 406
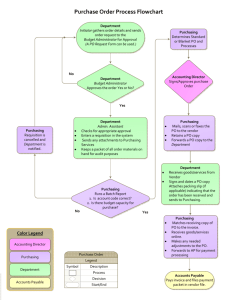
PURCHASING METHODOLOGY
The Purchasing Steps
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 3
Figure 11.1 The Purchasing Process
Page 407
PURCHASING METHODOLOGY
Initiating the Purchasing Process
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 4
Figure 11.2 Comparison of Costs and
Building vs. Purchasing a System
Page 407
PURCHASING METHODOLOGY
Establish Criteria for Selection
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 5
Figure 11.3 Key Criteria for
Software Package Selection
Page 408
PURCHASING METHODOLOGY
Develop and Distribute the RFP
Request for proposal (RFP) – a formal document sent to
potential vendors inviting them to submit a proposal
describing their software package and how it would meet
the company’s needs
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 6
Page 409
Develop and Distribute the RFP
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 7
Figure 11.4 Sample RFP Table of Contents
Page 409
PURCHASING METHODOLOGY
Evaluate Vendor Responses to RFP and Choose Package
Evaluation steps:
Review vendors’ responses from RFPs
Request demonstrations of leading packages
Request references from users of software
packages in other companies
Assess how well package capabilities satisfy
company’s needs
Understand extent of any additional development
efforts or costs to tailor software
Make decision
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 8
Page 410-411
PURCHASING METHODOLOGY
Evaluate Vendor Responses to RFP and Choose Package
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 9
Figure 11.6 Matching Company Needs
with Capabilities of the Package
Page 411
PURCHASING METHODOLOGY
Construction Phase
If no software package modifications required:
Skip system design and building steps
Move directly to system testing
Develop any necessary process changes
If software package is modified:
Consider contracting with vendor or a third party for
changes versus modifying in-house
Determine if changes are required to other existing
company systems
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 10
Page 413
PURCHASING METHODOLOGY
Project Team for Purchasing Packages
Business managers and users
IS professionals
Project manager – usually a business manager
Software vendor personnel
Sometimes includes a third-party implementation
partner
Purchasing specialists
Attorneys
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 11
Page 414-415
PURCHASING METHODOLOGY
Purchasing Advantages and Disadvantages
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 12
Figure 11.7 Advantages and Disadvantages
of Purchasing Packaged Software
Page 416
SPECIAL CASE: ENTERPRISE
SYSTEM PACKAGES
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
system packages:
Companies purchase to achieve business
benefits and IT platform benefits
Enables access to integrated data for
better decision making
Often require heavy reliance on third-party
consultants
Implementation efforts usually complex,
and sometimes not successful
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 13
Page 417
SPECIAL CASE: ENTERPRISE
SYSTEM PACKAGES
Factors that need to be managed well for ERP
implementation to be successful:
Top management is engaged in the project, not just
involved
Project leaders are veterans, and team members are
decision makers
Third parties fill gaps in expertise and transfer their
knowledge
Change management goes hand-in-hand with project
planning
A satisfying mindset prevails
Brown and Vessey, 2003
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 14
Page 417
NEW PURCHASING OPTION:
APPLICATION SERVICE
PROVIDERS (ASPs)
New trend beginning 2000s
Purchasing option: purchaser elects to use a
“hosted” application rather than to purchase the
software application and host it on its own
equipment
ASP is an ongoing service provider
Company pays third party (ASP) for delivering the
software functionality over the Internet to company
employees and sometimes business partners
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 15
Page 418
NEW PURCHASING OPTION:
APPLICATION SERVICE
PROVIDERS (ASPs)
Some advantages:
Cost savings and faster speed of implementation
Usually involves monthly fees rather than large
infrastructure investment
Disadvantages:
Dependence on an external vendor for both software and
ongoing operations
Good assessment of required service levels even more
critical
© 2005 Pearson Prentice-Hall
Chapter 11 - 16
Page 418-419