Ch4NicolePM - MrSafarianHaig
advertisement

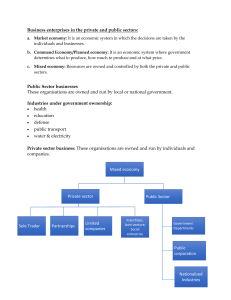
Chapter 4: Business and the Community pages 60 - 77 Economic Systems Economic System: the way the government and businesses work together to provide goods and services - economic systems need to be efficient because the amount of resources used to produce goods and services are limited. Governments and businesses must ask three major economic questions: - what goods and services should be produced - how they should be produced - for whom should they be produced Pure Command Economy (communist system) - the government owns almost all resources, farms, factories, machinery, offices and businesses - the government answers the three major economic questions Pure Market Economy (free market or capitalist) - the buyers and sellers of goods and services direct the economic system - the market place answers the three major questions (consumers decide what will be produced, competition decides how to produce it most efficiently, consumers decide what they want) - free enterprise: consumers free to purchase what they want, businesses are encouraged to establish an operation - private property: individuals are free to own, use and dispose of their things of value - freedom of choice: individuals are free to do as they wish as long as they don’t break laws Modern Mixed Economy - a mix of both economies in varying proportions - both consumers, buyers and the government make decisions and answer the three economic questions - all economies are mixed Public and Private Sectors In every mixed economy, businesses are divided into two sectors, the private sector and the public sector. - Private Sector: Businesses are individually owned and operated. Their purpose is primarily to make a profit. - Public Sector: Different levels of government provide services to Canadians. Schools, public utilities, and hospitals are three examples of services provided by public sector businesses. These businesses do not serve the purpose of generating income for themselves. - Crown Corporation: A business owned and operated by the provincial or the federal government. This could happen to protect Canadian culture from Americans or so the government can have a presence in the industry. - Public-private partnerships: (a.k.a. P3’s) Businesses from the public and private sectors that have pooled resources and gone into business together. These partnerships form because a proposed business venture or project is simply too huge for one sector to assume. Another advantage of private-public partnerships are that they share the risk and responsibilities of both private AND public sectors. - Privatization: This occurs when a publicly owned business or industry is sold to the private sector. A government may decide to privatize a service because it feels that the private sector could do a better job, or because the government is losing money providing that service. - Outsourcing: When a public operation subcontracts a private business to complete a job. This could happen for efficiency reasons. Impact of Businesses on the Community - Standard of Living: the way a person lives as measured by the kinds of goods/services they can afford as provided by businesses (income, the goods/services) - businesses also affect the quality of life of society: higher pay equals a higher standard of living, services (health, childcare, dental, recreational) the business provides - businesses can also have a negative affect on the community, for example increase pollution, construction, changing demographics - businesses also generate wealth, income, and jobs Generation of Wealth The Money Trail - as businesses need services to run, they circulate money through the community - following the circulation is called following the money trail. we follow the money in levels - Level One Money: the money received for work. Example: construction worker receives pay for building a new building - Level Two Money: level one money being spent. Example: the construction worker uses his pay to buy groceries and pay rent Generation of Jobs the amount of jobs a business creates is based on the job market, which is influenced by consumer demand, technology, competition, and the business cycle Consumer Demand - consumers want new things and businesses comply - as businesses create new products for the consumers, new jobs are created as new skills are needed - consumers stop wanting these new products as something more desirable comes along and jobs are lost Competition and Technology - competition may cause a business to fail or go bankrupt in which jobs are lost in order for this not to happen, businesses must be efficient to make money efficiency may mean firing some people to save money technology may make businesses more efficient and this technology may replace some jobs meaning people may get fired - technology may need experts in order to operate properly, therefore creating jobs The Business Cycle - how the economy fluctuates in cycles - one cycle is about 8 - 10 years - four phases: - trough: lowest level of the cycle, high unemployment, businesses have difficulty making profit - recovery: demands for goods and services increase, employment rate begins to rise - peak: highest level of the cycle, low unemployment, demand for goods and services high - recession: businesses overproduced due to high demands and are overstocked, businesses start loosing money and jobs are lost Recovery Generation of Income - businesses sell goods, services, or make investments to generate income income is taxed (as well as property, and sales) and these taxes are used to help the community Chapter 4: Business and the Community Practice Test 1. What is a modern mixed economy? Why are all economies modern mixed? 2. Draw a diagram of the range of economic systems with “command economy” on one end and “market economy” on the other. Place Canada, USA and North Korea on your diagram. 3. Give an example of a public sector and a private sector. 4. If the TTC was sold to a private company, what would it be an example of? Why might this happen? Would a public-private partnership be more beneficial? 5. What is the “standard of living” and how do businesses affect it? 6. A new business is opening a store. They hire an architect to design the store. He is paid $100,000. He uses this money to pay groceries. a) What is the level one money? b) What is the level two money? 7. What are the four phases of the business cycle? Draw a diagram and give a brief explanation of each. 8. How are businesses affected by: a) consumer demand b) technological improvements